Ⅰ. Overview
Fusidic acid is a steroidal antibiotic, derived from the fungus Fusidium coccineum. It was developed by Leo Pharma in Ballerup, Denmark, and then commercialized in the 1960s.
Fusidic acid has good in vitro activity against staphylococci, including strains sensitive and resistant to methicillin. It is used to treat bacterial infections, such as skin infections, including cellulitis and impetigo, and eye infections, including conjunctivitis.
It comes as a cream, ointment, or eye drops (Fusidic acid eye drops are called by the brand name Fucithalmic. Fusidic acid cream or ointment is called by the brand name Fucidin) .
Note :
It is also given by injection, as a liquid to swallow, or as tablets, but these are usually only used in hospital.
Ⅱ. Fusidic acid uses
Fusidic acid is prescribed mainly for skin infections caused by staphylococci (also for infections with streptococci and Corynebacterium minutissimum). These infections include impetigo, infected cuts and abrasions, infected dermatitis, dermatophytic skin infection, eczematous rash, eczematous rash.
it is also indicated as a local antibacterial treatment of conjunctivitis, keratitis, corneal ulcers, blepharitis and stye due to germs sensitive to fusidic acid.
If the area of the skin is inflamed and infected, your doctor may prescribe a cream that combines fusidic acid with an anti-inflammatory agent, such as hydrocortisone (Fucidin® H) or betamethasone (Fucibet® and Xemacort ®).
Fusidic acid
According to the latest recommendations, HAS 2021 ,
topical fusidic acid is now restricted as a second-line treatment in cases of intolerance or resistance to mupirocin.
Fusidic acid monotherapy, particularly topical preparations, has been strongly associated with the emergence of resistance to fusidic acid in both methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and S. aureus susceptible to methicillin.
A variety of antibiotics have been used in conjunction with fusidic acid therapy, including rifampin, novobiocin, and beta-lactams, although rifampin plus fusidic acid regimens are the most common.
Ⅲ. Structure of fusidic acid
Fusidic acid is a monocarboxylic acid. It is a colorless, crystalline compound sparingly soluble in water. The sodium fusidate used in therapy is water-soluble and liposoluble, which gives it good tissue distribution.
Sodium fusidate is a salt of fusidic acid and it works the same way.
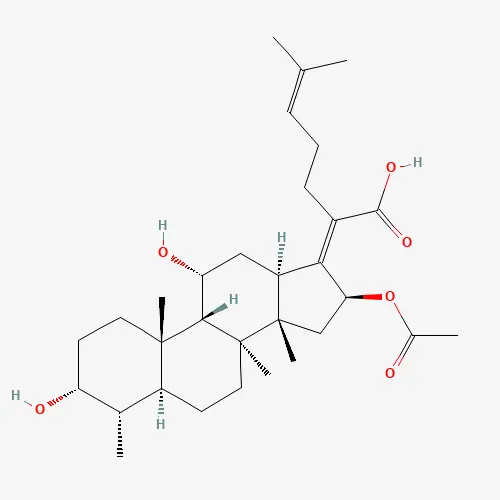
Structure of fusidic acid
Ⅳ. Fusidic acid mechanism of action
Fusidic acid acts by inhibiting the protein synthesis of the bacteria by blocking the ribosome by binding to "factor G", responsible for the translocation of the peptide chain during protein synthesis.
V. Activity spectrum
Fusidic acid is active in vitro against Staphylococcus aureus, most coagulase positive staphylococci, beta-hemolytic streptococci, Corynebacterium species and most Clostridium species.
It is active in vitro and clinically against Mycobacterium leprae but has only marginal activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Species usually sensitive to fusidic acid :
Fusidic acid has good in vitro activity against staphylococci , including strains sensitive and resistant to methicillin.
It also has useful activity against Neisseria spp, Bordetella pertussis, Corynebacterium spp
and Gram-positive anaerobes such as Clostridium difficile and C. perfringens, Peptostreptococcus spp and Propionibacterium acnes
Moderately sensitive to fusidic acid :
MICs for streptococci , enterococci , and Gram-negative anaerobes are generally higher, but at <8 mg / L may provide some clinical activity
Fusidic acid resistant species:
Acinetobacter sp, Pseudomonas sp, enterobactéries.

