Content :
Bacterial vaginosis
◉ What is bacterial vaginosis ?
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a clinical syndrome manifested mainly by vaginal discharge (gray, white or green), a “fishy” odor, more rarely, itching and burning sensation or being completely asymptomatic. Diagnosis is based on clinical criteria of Amsel and direct Gram stain, Score de nugent, vaginal secretions
Bacterial vaginosis is universally recognized as the most common cause of vaginal problems in women of childbearing age, present in approximately 10-20% of white women and 30-50% of black women.
Bacteriologically, bacterial vaginosis is dysbiosis, a low genital infection due to deep imbalance of the vaginal ecosystem, a significant depletion of lactobacilli following a strong proliferation of strict or facultative anaerobes previously in the minority in the vagina, such as Gardnerella vaginalis, Atopobium vaginae, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Mycoplasma hominis, Prevotella, Peptoniphilus, Megasphaera, Mobiluncus, and other tedious

◉ Normal vaginal flora
The normal vaginal flora, Döderlein flora, is a constantly evolving environment, present from the first days of a little girl's life, it remains poor until puberty, then estrogen will induce the secretion of glycogen, the favorite substrate of Lactobacilli. spp. (Protective bacteria), the acidifying power of the latter is at the origin of a vaginal pH between 3.8 and 4.5 and thus makes it possible to rule out any multiplication of most pathogens.
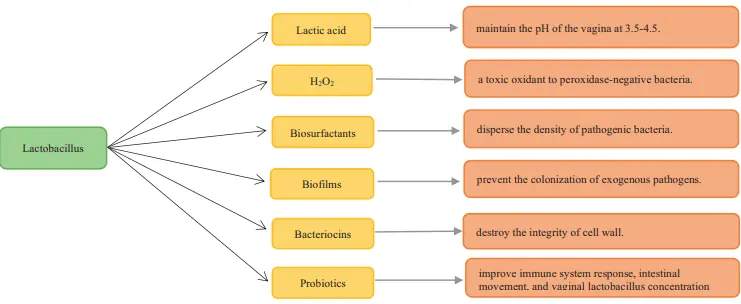
Fig 1 : Function of lactobacilli in inhibiting pathogenic microorganisms(C. Ding, et al)
◉ Risk factors
Bacterial vaginosis is associated with having multiple male sex partners, female partners, sex with more than one person, a new sex partner, lack of condom use, douching, and being HIV positive. -2.
Male circumcision reduces the risk of Bacterial vaginosis in women. In addition, the prevalence of BV increases during menstruation. Women who have never been sexually active are rarely affected.
The imbalance increases in women with IUDs containing copper. Hormonal contraception does not increase the risk and may protect against the development of BV.
Douching is a risk factor for bacterial vaginosis
Women with BV are at increased risk of contracting STIs, such as HIV, N. gonorrhoeae, C. trachomatis, T. vaginalis, M. genitalium, HPV, and HSV-2; complications after gynecological surgery; complications of pregnancy; and recurrence of BV
Note : Bacterial vaginosis is not a sexually transmitted infection (STI), but it can increase your risk of getting an STI such as chlamydia.
◉ Symptoms
◈ Anaerobes produce large amounts of carboxylase-like proteolytic enzymes, which break down vaginal peptides into a variety of volatile, smelly amines associated with increased vaginal transudation and exfoliation of squamous epithelial cells, resulting in the typical clinical features seen. in patients with BV
◈ Many women (around 50%) with bacterial vaginosis do not have any signs or symptoms.
◈ Signs and symptoms of bacterial vaginosis may include :
- Thin, gray, white, or green vaginal discharge
- Foul "fishy" vaginal odor: more noticeable after sex and during menstruation
- Vaginal itching (not specific)
- Burning during urination (not specific)
- Vaginal bleeding after sex (not specific)
Note : The presence of itching, burning, dyspareunia, suggests mixed vaginitis (VB-candida coinfection in 20% to 30% and VB-T. vaginalis in 60% to 80%)
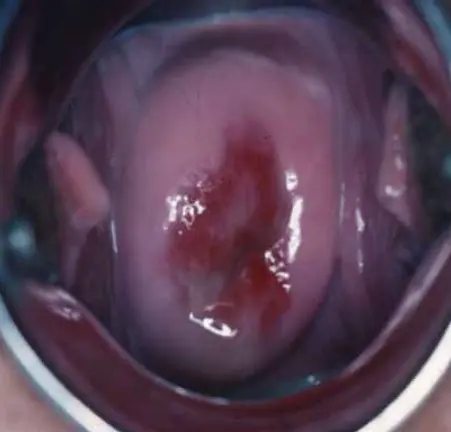
White discharge adhering to the vaginal walls
◉ Diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis
For a long time, Amsel's diagnostic criteria were the most commonly used clinical criteria. However, these criteria failed to diagnose asymptomatic BV. Subsequently, the Nugent score , developed in 1991, is currently considered the gold standard for the diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis.
❶ Amsel's diagnostic criteria, it requires at least three of the following four symptoms or signs
- Fine flow, white, yellow, homogeneous
- Clue cells on microscopic examination
- Vaginal fluid with a PH greater than 4.5
- Odor of "rotten fish", either spontaneous or after adding a drop of 10% potash to vaginal secretions (sniff test)
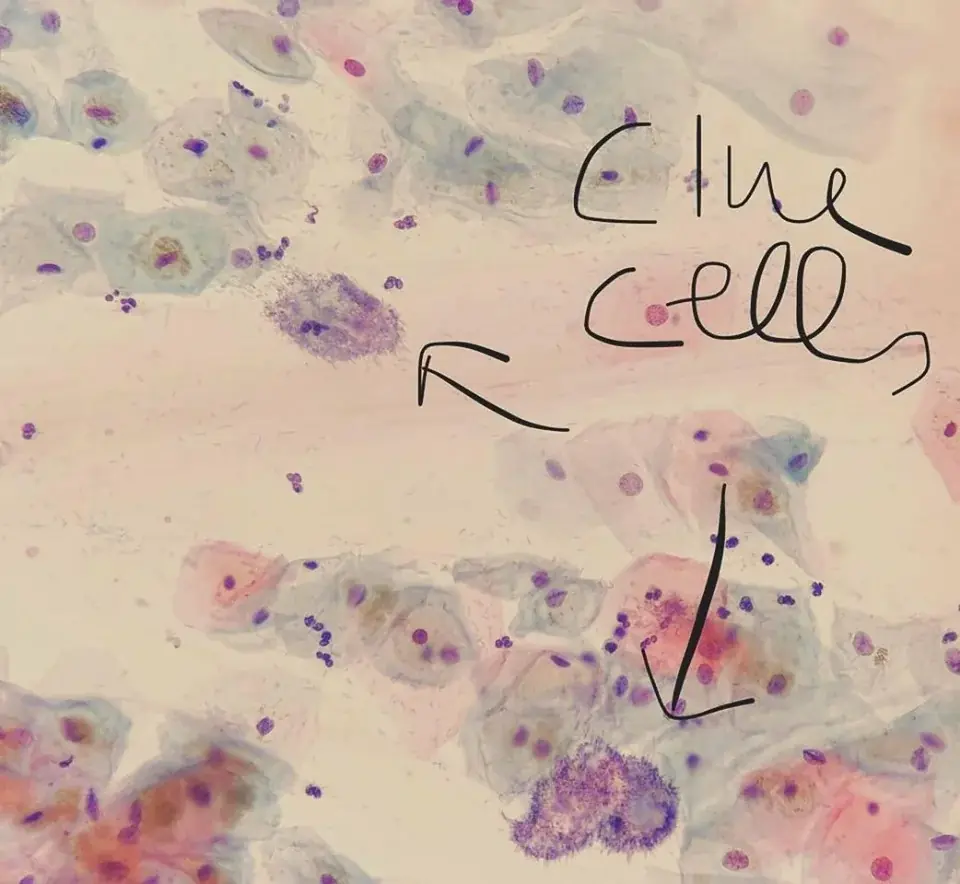
Clue cells
❷ Gram stain of vaginal flora, considered the gold standard laboratory method for the diagnosis of BV, is used to determine the Nugent score. A score of 0 to 3 is consistent with a vaginal microbiota predominantly of Lactobacillus, 4 to 6 with an intermediate microbiota (emergence of G. vaginalis) and 7 to 10 with bacterial vaginosis
The sensitivity and specificity of the Amsel criteria are respectively 37% to 70% and 94% to 99% compared to the Nugent score
◉ Bacterial vaginosis during pregnancy
WHO : There is some evidence that bacterial vaginosis is associated with an increased incidence of adverse pregnancy outcomes (eg, premature rupture of membranes, premature delivery, and low birth weight). Symptomatic pregnant women should be treated and those with a history of preterm labor should be screened for asymptomatic infections.
Pregnant women with recurrence of symptoms should be retreated. Screening of asymptomatic pregnant women without a history of preterm delivery is not recommended.
◉ Treatment (the American College of Obstetricians)
Treatment is indicated for the relief of symptoms in women with symptomatic infection and for the prevention of postoperative infection in those with asymptomatic infection prior to abortion or hysterectomy. Note that BV resolves spontaneously in up to a third of non-pregnant women and half of pregnant women.
- Metronidazole 500 mg orally twice / day for 7 days or
- Metronidazole 0.75% gel one full applicator (5 g) intravaginally, once daily for 5 days or
- Clindamycin 2% cream one full applicator (5 g) intravaginally at bedtime for 7 days
Recommended alternative treatments
- Secnidazole (oral) 2 g as a single dose; or
- Tinidazole (oral) 2 g once daily for 2 days, or 1 g once daily for 5 days; or
- Clindamycin (oral) 300 mg twice daily for 7 days or 100 mg ova intravaginally once at bedtime for 3 days.
◈ Women should be advised to abstain from all sexual activity or to use condoms consistently and correctly during the treatment regimen. Douching may increase your risk of relapse.
Sources:
- The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG). Updated guidance 2020 [Internet]. Available from: https://www.acog.org/
- Colonna C. Amsel Criteria [Internet]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542319/
- Linda et al. Exploring the global vaginal microbiome and its impact on human health [Internet]. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34500016/
- Bertholom C. Comment interpréter un prélèvement vaginal chez la femme enceinte ? [Internet]. Available from: https://www.em-consulte.com/article/1442331/figures/comment-interpreter-un-prelevement-vaginal-chez-la
- Ravel J. Bacterial Vaginosis and Its Association with Infertility, Endometritis, and Pelvic Inflammatory Disease.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Sexually Transmitted Infections Treatment Guidelines, 2021.
- Bondarenko O. Pratique du prélèvement vaginal par les médecins généralistes dans la prise en charge des vaginoses bactériennes.
- World Health Organization (OMS). Guidelines for the Management of Sexually Transmitted Infections.
- Ding C. Bacterial Vaginosis: Effects on reproduction and its therapeutics [Internet]. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34087449/
- Powell K. Bacterial vaginosis: diagnosis and treatment.
- Sobel JD. Bacterial vaginosis: Clinical manifestations and diagnosis.
- Sobel JD. Mixed vaginitis-more than coinfection and with therapeutic implications.