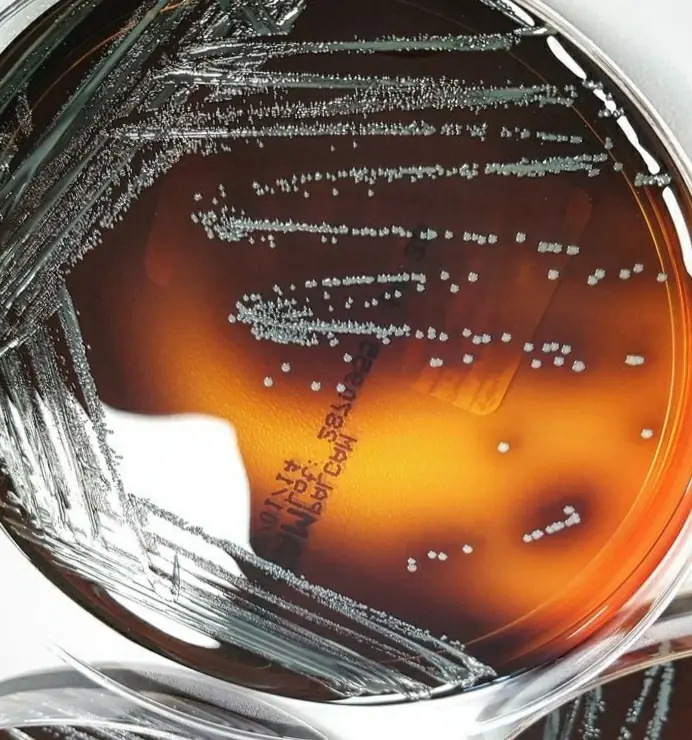
◈ Selectivity : The selectivity of the medium is ensured by the presence of lithium chloride, polymyxin B, acriflavin and ceftazidime sulphate, which inhibit the growth of most species other than Listeria spp. contained in foods and clinical samples. Polymyxin B acts against gram-negative bacteria, CEFTAZIDIME is active against gram-positives and enterobacteria, acriflavin inhibits many gram-positive bacteria.
◈ The differentiation : differentiation is based on the hydrolysis of the esculine and the fermentation of Mannitol.
- Listeria hydrolysis, and this manifests itself by a blackening of the agar. hydrolyse, et cela se manifeste par un noircissement du milieu.
- Listeria does not ferment Mannitol, so easy differentiation of contaminants, such as enterococci and staphylococci, which ferment mannitol.
Ⅳ. Interpretation
◈ After 42 to 48 hours at 37 ° C in aerobic, in general :
| Bacteria | Growth |
|---|---|
| Listeria monocytogenes | Good growth to important; gray-green colonies circled with a dark brown halo in black in the medium |
| Escherichia coli | Partial inhibition to complete |
| Enterococcus faecalis | Complete inhibition |
| Pseudomonas | Partial inhibition to complete |
| / | Red, transparent appearance to very slightly veiled |
References:
- N al-Zoreky - Highly selective medium for isolation of Listeria monocytogenes from food
- Handbook of Culture Media for Food Microbiology, J.E.L. Corry et al : Hektoen Enteric (HE) agar 2003
- ASM : Hektoen Enteric Agar Protocol
- Color Atlas of Medical Bacteriology
- liochem - LISTERIA PALCAM Supplement
- BD PALCAM Listeria Agar
- thermofisher - PALCAM AGAR BASE