☰ Sommaire :
- Ⅰ. Overview
- Ⅱ. Composition and preparation of Simmons Citrate Agar
- Ⅲ. Principle of Simmons Citrate Agar
- Ⅳ. Interpretation
Ⅰ. Overview
Simmons Citrate Agar is a selective and differential medium based on citrate utilization. The medium tests the ability of organisms to utilize citrate as the sole carbon source
Simmons Citrate Agar is a solidified form of Koser's citrate medium which suffered from the disadvantage that a false appearance of growth occurred when large inoculums were employed. Simmons modified Koser's formulation by adding agar and bromothymol blue
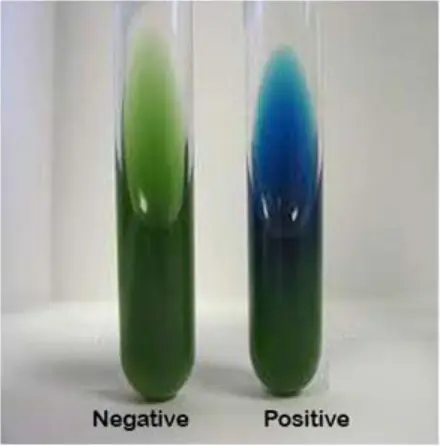
This medium is part of the IMViC tests. A positive reaction is indicated by growth with an intense blue color in the slant : Klebsiella, Enterobacter , Citrobacter, Providencia, Proteus, Serratia, vibrio cholerae, Pseudomonas, Salmonella enteritidis and members of the subgenera Salmonella II, III and IV.

Simmons Citrate Agar
Ⅱ. Composition and preparation of Simmons Citrate agar
Suspend the components, dehydrated powder, in water (23.3 grams in 1000 ml of purified/distilled water). The medium is boiled for a few seconds until the ingredients are completely dissolved. Distribute in tubes or bottles and sterilize by autoclaving at 121°C for 15 minutes. Allow the tubes to cool on a slope.
Composition of Simmons Citrate Agar |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ingredients | gram/litre | Ingredients | gram/litre |
| Sodium citrate | 1g | Sodium chloride | 5.0g |
| Magnesium sulfate | 0.2g | Mono-ammonium phosphate | 1g |
| Dipotassium phosphate | 1g | Bromothymol blue | 0,08g |
| Agar | 15g | pH final | 6,8 ± 0,2 |
Ammonium Dihydrogen Phosphate is the sole source of nitrogen in Simmons Citrate Agar. Dipotassium Phosphate acts as a buffer. Sodium Chloride maintains the osmotic balance of the medium. Sodium Citrate is the sole source of carbon in this medium. Magnesium Sulfate is a cofactor for a variety of metabolic reactions. Bromthymol Blue is the pH indicator.
Ⅲ. Principle of Simmons Citrate agar
Bacteria that can utilize citrate as the sole carbon source and inorganic ammonium salt as the sole source of nitrogen grow on this medium.
In organisms capable of using citrate as a carbon source, the enzyme citrase hydrolyzes citrate into oxaloacetic acid and acetic acid. The oxaloacetic acid is then hydrolyzed into pyruvic acid and CO2. If CO2 is produced, it reacts with the components of the medium to produce an alkaline compound (eg Na2CO3).
The alkaline pH changes the pH indicator (bromthymol blue) from green to blue.
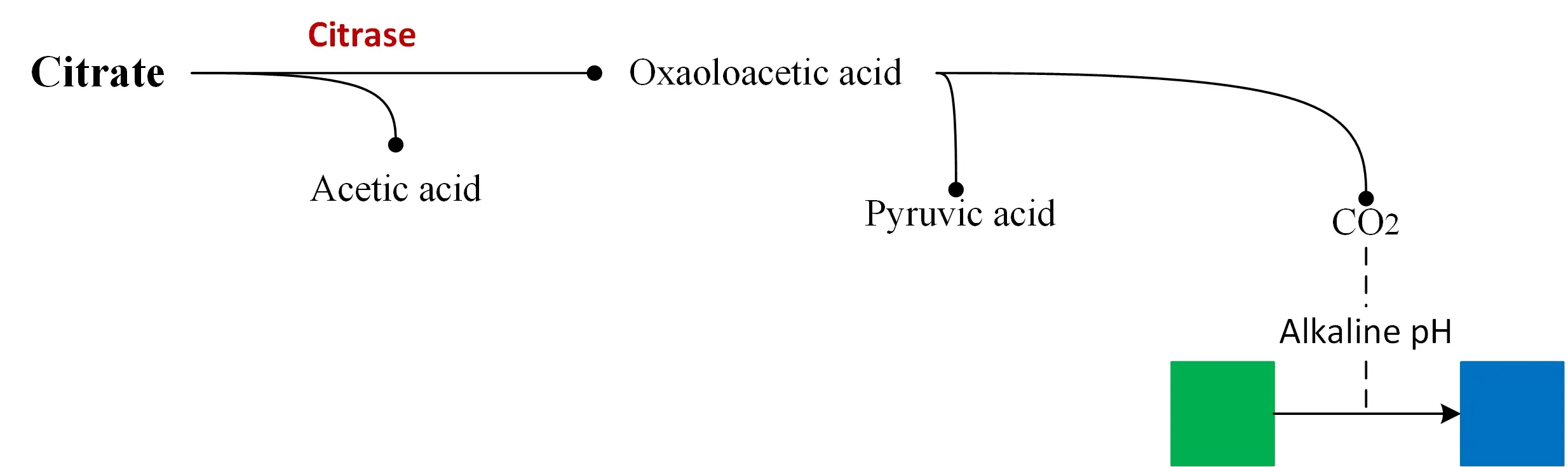
Simmons Citrate Agar principle
Ⅳ. Interpretation of Simmons Citrate agar
Bacteria citrate positive
A positive reaction is indicated by growth with an intense blue color in the slant : Klebsiella, Enterobacter , Citrobacter, Providencia, Proteus, Serratia, vibrio cholerae, Pseudomonas, Salmonella enteritidis and members of the subgenera Salmonella II, III and IV.
Bacteria citrate Negative
A negative reaction is evidenced by the absence of growth to a trace of growth with no color change (the medium remains dark green): Escherichia coli, Shigella, Yersinia, Edwardsiella

Simmons Citrate reaction positive and negative
Ⅴ. Frequently asked questions
Q : What is the Simmons citrate agar test for?
A : Simmons Citrate agar is used to to differentiate between bacteria based on the ability to utilize citrate as a source of energy.
Q : What type of indicator does the citrate test use?
A : pH indicator bromthymol blue
Q : Does ecoli use citrate?
A : E coli cannot use citrate as a carbon source, aerobically, because it lacks a citrate transporter, but can use citrate under anaerobic conditions via expression of the CitT citrate/succinate antiporte
Q : What bacteria are citrate positive?
A : Klebsiella, Enterobacter , Citrobacter, Providencia, Proteus, Serratia, vibrio cholerae, Pseudomonas, Salmonella enteritidis and members of the subgenera Salmonella II, III and IV.
Reference
- wyoming university - SIMMON’S CITRATE AGAR
- FDA - BAM Media M138: Simmons Citrate Agar
- BBL™ Simmons Citrate Agar Slants
- thermofisher - Simmons Citrate Agar (Dehydrated)
- Rapid Evolution of Citrate Utilization by Escherichia coli by Direct Selection Requires citT and dctA
- ASM - Citrate Test Protocol
- Sigma-Aldrich - Simmons Citrate Agar
- Handbook of MICROBIOLOGICAL MEDIA Fourth Edition