- Mucoid isolates of P. aeruginosa from patients with cystic fibrosis may undergo several phenotypic changes, including slow growth, loss of motility, and loss of pigment production.
- Small colony variants may require prolonged incubation, lack motility, be hyperpiled, adhere to agar surfaces, and exhibit self-aggregating properties in liquid media.
Pseudomonas | Bacteriological characters | Culture | Identification
✑ Dr.Midireh.l
☰ Summary :
- Ⅰ. Overview | Taxonomy
- Ⅱ. Bacteriological characters
- Ⅲ. Pseudomonas identification and differentiation between species
- Ⅳ. Antibiotic Sensitivity and Treatment
- Ⅴ. Antibiotics to be tested in the susceptibility testing
Ⅰ. Overview | Taxonomy
The genus Pseudomonas is a large and complex heterogeneous group of organisms belonging to the family Pseudomonadaceae. They are subject to continuous taxonomic revision due to improved species identification methodologies (Organisms previously classified in the genus Pseudomonas are now split between the genera Pseudomonas, Burkholderia, Ralstonia, Comamonas, Acidovorax, Delftia, Hyrodenophaga, Brevundimonas, Stenotrophomonas and Xanthomonas).
Twelve species of Pseudomonas were found in clinical specimens: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas alcaligenes, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Pseudomonas luteola, Pseudomonas mendocina, Pseudomonas monteilii, Pseudomonas mosselii, Pseudomonas oryzihabitans, Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes, Pseudomonas putida, Pseudomonas putida.
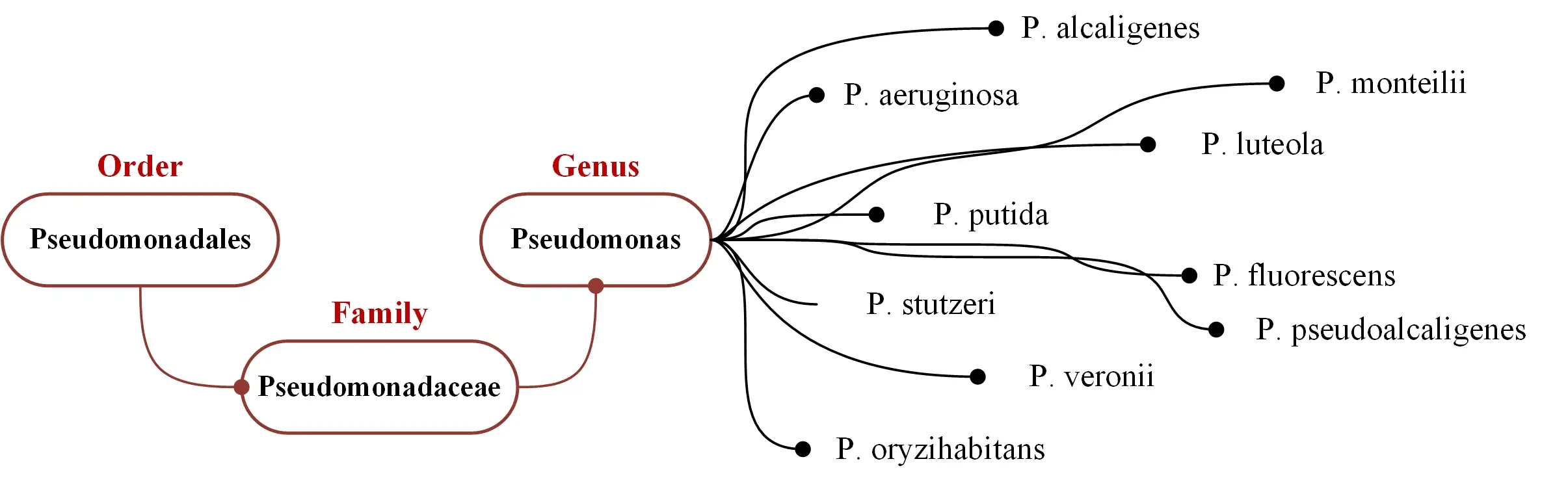
Pseudomonas sp. are widely distributed in the environment and are often found in moist areas, where they can grow as biofilms attaching to surfaces. They are part of the normal microbiota of the intestinal tract. Mucoid strains cause chronic infections in a high percentage of CF patients (Cystic fibrosis).
Ⅱ. Bacteriological characters
Microscopic examination
Pseudomonas sp. are aerobic, non-spore-forming, motile (one or more polar flagella (swimming motility)), Gram-negative rods, measuring 0.5 to 1 µm by 2 to 7 µm. Bacilli are longer and thinner than Enterobacterales but similar in appearance to other non-fermenters (In ancient cultures may appear slightly pleomorphic, P. putida may appear elongated).
Mucoid strains of pseudomonads (mutations in the mucA gene), frequently found in patients with cystic fibrosis tend, microscopically, to clump together or produce filaments of short Gram-negative rods surrounded by darker pink material (exopolysaccharide alginate).
This alginate material makes the organism resistant to phagocytosis and killing by antimicrobials.
It is important to note this on direct examination, as these strains can grow very slowly.
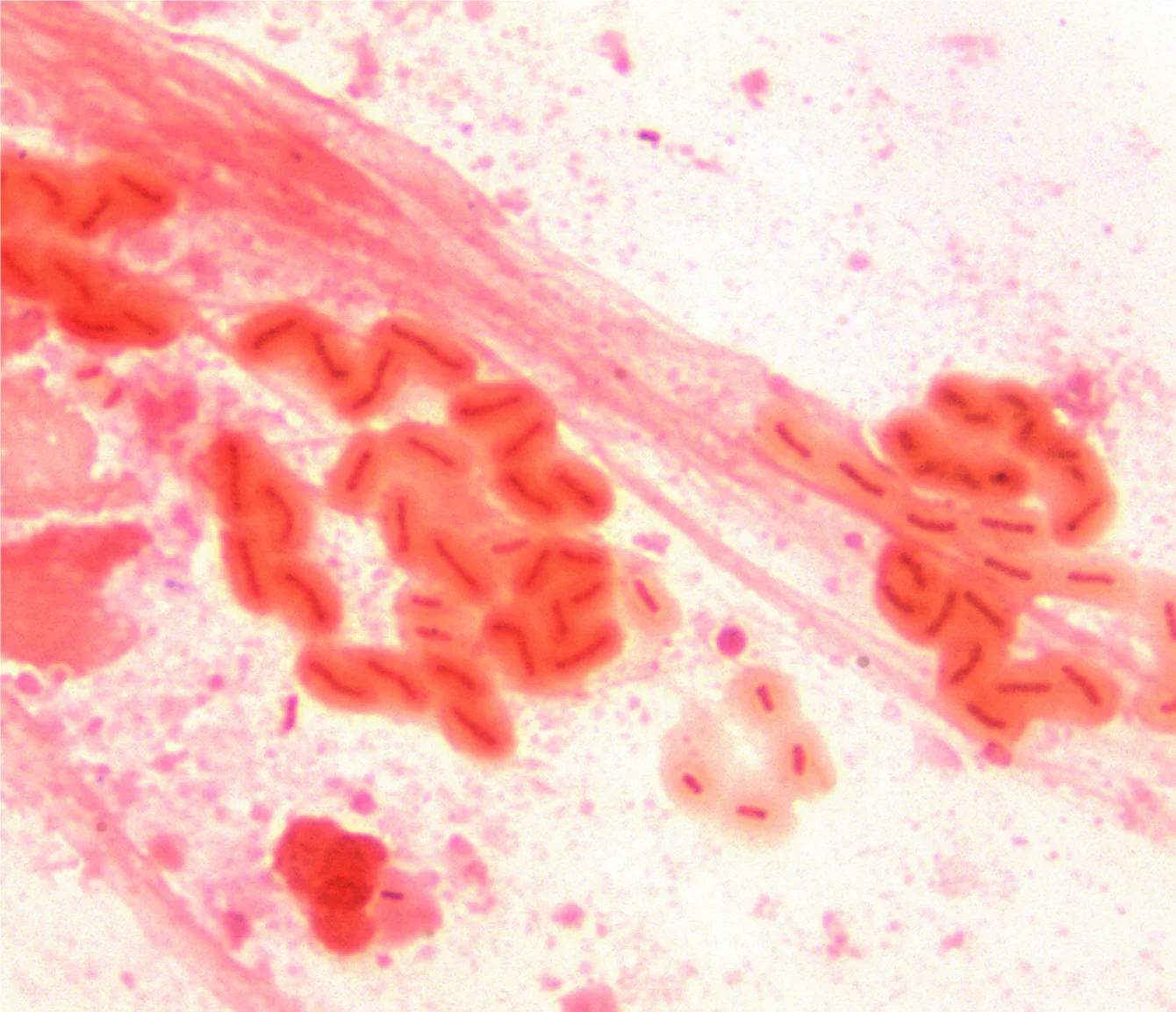
Gram stain of a mucoid strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Culture Pseudomonas
The culture of pseudomonas is easy (have very simple nutritional needs), between 10°C and 42°C, on ordinary media (nutrient agar ), selective (Drigalski, Hektoen Enteric Agar, MacConkey Agar or containing cetrimide) or chromogenic media.
Good growth is generally obtained after 24 to 48 hours of incubation. For cultures of patients with cystic fibrosis, it is recommended to maintain the dishes of solid medium at 35 to 37°C for 5 days because certain strains of chronic infections grow very slowly.
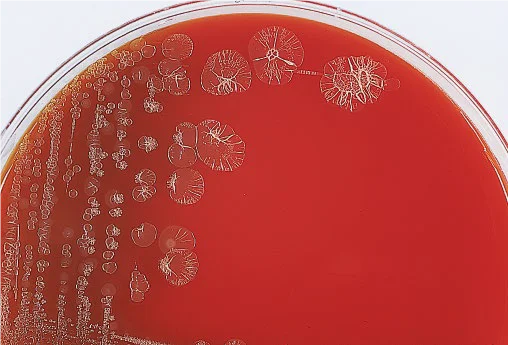
Most Pseudomonas aeruginosa organisms are easily recognized on the basis of characteristic flat, spreading colony morphology and have a jagged edge and metallic sheen that is often associated with colony autolysis, but depending on the composition of the media and the type of infection (acute or chronic), the colonies can present different morphologies (mucoids, variants of small "SVG" or "fried egg" colonies).
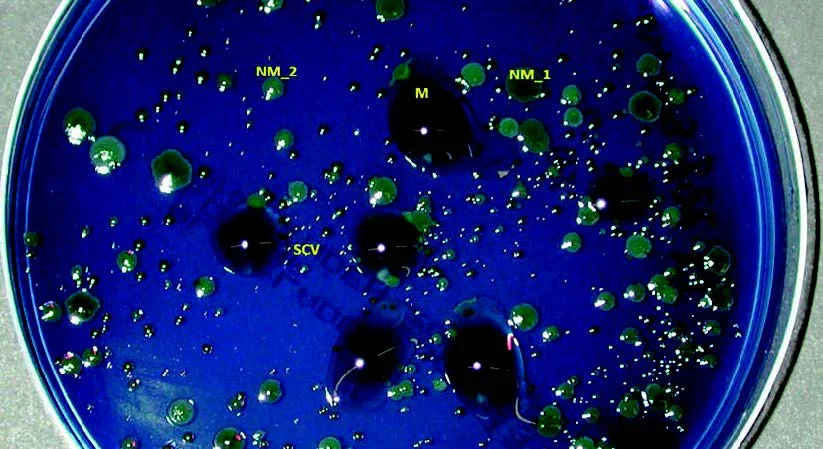
Different colony morphologies of P. aeruginosa from CF sputum cultured on modified Conradi-Drigalski agar. M, mucoid; NM_1, colony no mucoid 1 (dark green); NM_2, non-mucoid colony 2 (light green); SCV, small colony variant. (Source: 10.1128/9781555817381.ch42.f1)
Pseudomonas pigments
Six species, P. aeruginosa, P. fluorescens, P. monteilii, P. mosselii, P. putida, and P. veronii, produce a water-soluble, yellow-green or yellow-brown pigment known as pyoverdine. Because of this pigment, these six species are classified as members of the fluorescent pseudomonad group.
Additionally, Pseudomonas aeruginosa also produces a blue-green pigment, pyocyanin, which combines with pyoverdin, resulting in a bright green color. Occasional strains of P. aeruginosa produce only pyoverdin, making it difficult to differentiate these strains from the other five fluorescent pseudomonads.
P. aeruginosa can also produce other diffusible pigments, for example pyomelanin (black brown) and pyorubin (red)..
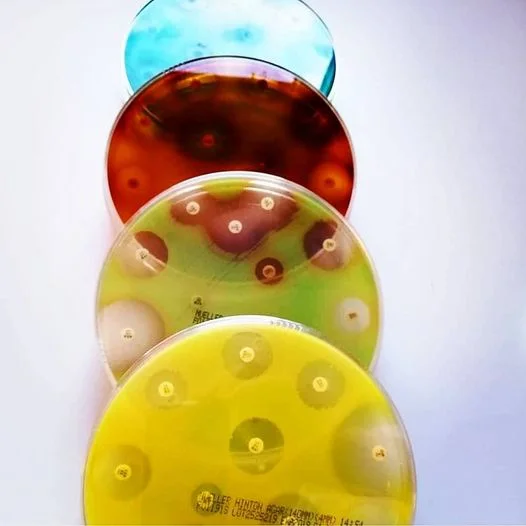

Source: @superteclab | ✔Piocyanin; blue pigment | ✔Pioverdine (fluorescein); greenish yellow color | ✔Pyorubin; red coloring. | ✔Pyomelanin; Its color is brown. |
The identification of P. aeruginosa strains is facilitated by the very frequent production of an aromatic molecule (o-aminoacetophenone) with a characteristic acacia odor.
Ⅲ. Pseudomonas identification and differentiation between species
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Most P. aeruginosa are easily recognized based on characteristic colony morphology, pigment and odor production, and its ability to grow at 42°C.
P. aeruginosa are oxidase positive, catalase positive, have a nitrate reductase and a nitrite reductase production allowing the reduction of nitrates (NO3) in nitric oxide (NO) then in nitrogen (N2), arginine deiminase (ADH positive) with no modification in the test of the triple sugar iron.
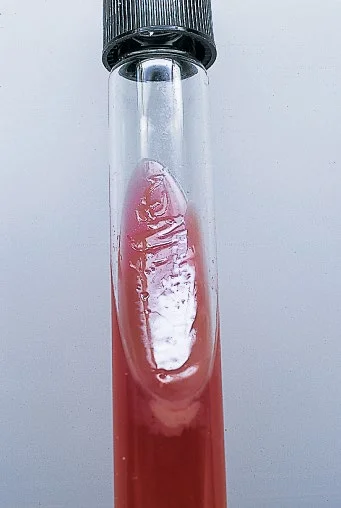
Pseudomonas aeruginosa on TSI agar (source: ASM journals).
Pseudomonas fluorescens
P. fluorescens and P. putida do not possess distinctive colony morphology or odor. Their inability to reduce nitrate to nitrogen gas and their ability to produce acid from xylose distinguishes these two species from other pseudomonads.
P. fluorescens can be differentiated from P. putida by its ability to grow at 4°C and to hydrolyze gelatin. The isolates of P. fluorescens can require 4 to 7 days of incubation for accurate detection of hydrolysis of the gelatin( According to the API 20NE notice (version 7.0; bioMérieux, Inc., Durham, CN), only 39% of P. fluorescens isolates hydrolyze gelatin within 24-48 h.)

Pseudomonas fluorescens incubated with gelatin strips (source: ASM jounals).
❏ Pseudomonas stutzeri
P. stutzeri can grow in the presence of 6.5% NaCl. This biochemical characteristic, along with the ability to reduce nitrate to nitrogen gas, the ability to oxidize glucose but not lactose, and its distinctive dry, wrinkled colony morphology (1–6 mm in diameter), distinguishes group P stutzeri from other Pseudomonas spp.
Pseudomonas fluorescens incubated with gelatin strips (source :ASM jounals).
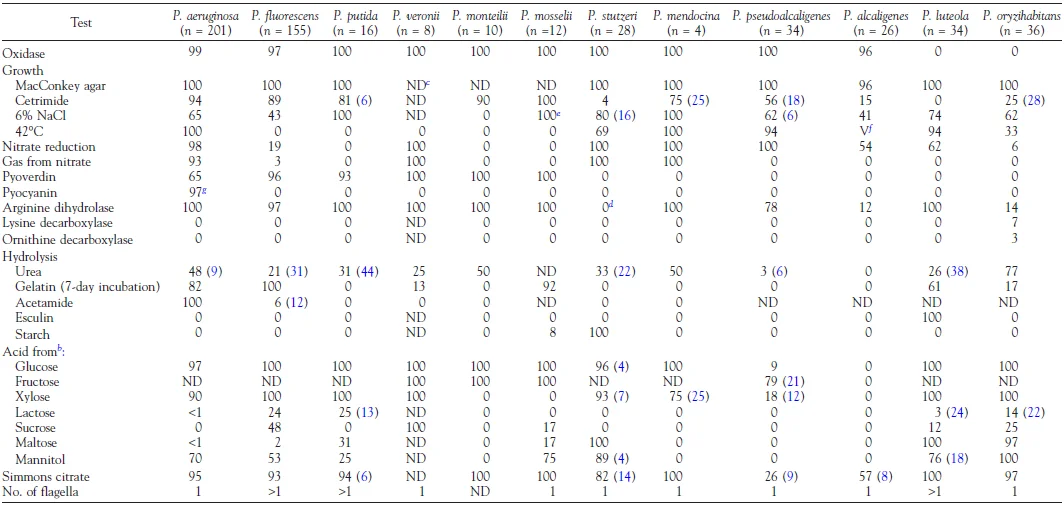
Biochemical characteristics of Pseudomonas species found in clinical samples (source: manual of clinical microbiology).
Ⅳ. Antibiotic sensitivity and treatment of pseudomonas
❏ What antibiotics is Pseudomonas susceptible to? :
ß-lactams: piperacillin and ticarcillin, with or without inhibitor, ceftazidime, cefepime, aztreonam, imipenem, meropenem, doripenem, Aminosides (except kanamycin), Fluoroquinolones: ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin, colistin and fosfomycin
❏ What antibiotics is Pseudomonas has natural resistance to? :
Penicillins G, A, M, 1st and 2nd generation cephalosporins, oxymino cephalosporins (cefotaxime, ceftriaxone), oral broad-spectrum cephalosporins, Ertapenem, Cyclins including tigecycline, Macrolides, Kanamycin, Old quinolones, Rifampicin, Chloramphenicol, Trimethoprim, Cotrimoxazole , Glycopeptides , Fusidic acid.
Ⅴ. Antibiotics to test "Pseudomonas"
❏ Pseudomonas susceptibility testing is performed on Mueller-Hinton agar, Inoculum: 0.5 McFarland
antibiotics testing of Pseudomonas according to CASFM
standard list : Ticarcillin, Ticarcillin-clavulanic acid, Piperacillin, Piperacillin-tazobactam, Ceftazidime, Cefepime, Ceftolozane-tazobactam, Imipenem, Meropenem, Tobramycin, Amikacin, Ciprofloxacin, Aztreonam, Gentamicin.
Complementary list : Netilmicin, Levofloxacin, Colistin, Fosfomycin, Ceftazidime-avibactam.