Content :
I use nutrient agar every day in my laboratory; it is one of the most important culture media in medical bacteriology. In this article, I will discuss its composition, uses, limitations, and how to prepare it.
◉ What is Nutrient Agar?
Nutrient agar is a general purpose medium suitable for the cultivation of a wide variety of nonfastidious microorganisms.
This nutrient medium, with a relatively simplified composition, is used to subculture organisms for maintenance purposes or to check the purity of subcultures and for the enumeration of organisms in water, wastewater, urine, feces and other material.
Nutrient agar lacks indicators, selective agents, differential ingredients, and enriching substances. Therefore, it is employed for better pigmentation expression, biochemical testing, and even serotyping.
The formula for nutrient agar was initially published by the American Public Health Association in 1917.

Nutrient Agar Plate
◉ Composition of nutrient agar
◈ The composition of nutrient agar can be adjusted to obtain optimal performance:
- 0.5% peptone: Provides organic nitrogen.
- 0.3% beef extract/yeast extract: Contributes water-soluble elements supplying vitamins, carbohydrates, nitrogen, and salts.
- 1.5% bacteriological Agar: Imparts solidity to the mixture.
- 0.5% sodium chloride: Adjusts the mixture's proportions to resemble those found in the cytoplasm of most organisms.
- Distilled water: Serves as a transport medium for the various substances in agar.
- pH adjusted to neutral (6.8) at 25 °C (77 °F).

Dehydrated Nutrient Agar
◉ Preparation of nutrient agar
◉ 1- Dehydrated medium
- Suspend 28.0 grams in 1 litre of purified/distilled or deionized water.
- Heat to a boil to completely dissolve the medium.
- Sterilize by autoclaving at a pressure of 15 lb (121°C) for 15 minutes.
- After autoclaving, cool to 45-50°C.
- Pour nutritious agar into Petri dishes (until the agar is solidified).
- Keep boxes in the refrigerator at 2-8°C.
◉ 2- Prepared medium
Liquefy the agar (e.g., using a bain-marie), cool it to 45-50°C, and pour it into Petri dishes. Allow it to stand for at least 30 minutes.

Prepared nutrient agar
Note : Nutrient agar with 0.8% NaCl and pH 6.0 is used for the culture of bacteria requiring slightly acidic conditions. Nutrient media can be used as enriched media by the addition of 10% blood or other biological fluids such as ascetic fluid, serum, etc.
◉ What is nutrient agar used for?
Nutrient agar provides essential nutrients required for the growth of bacteria, yeast, and molds. Here are some of the primary uses of nutrient agar:
- Culturing Microorganisms: Provides a solid surface for the cultivation of bacteria, yeast, and molds.
- Urine culture: Is commonly used in clinical microbiology to culture and identify microorganisms present in urine samples.
- Enumeration of Microorganisms: Can be employed to estimate the number of viable microorganisms in a given sample.
- Educational settings: Is commonly used in educational institutions for teaching microbiology concepts.
- Used in quality control procedures.
- Short-term storage and transportation of microorganisms.
- Isolation anf purification of culture: Streaking or spreading a sample on the agar surface allows for the separation and identification of individual colonies.
◉ What bacteria grow on nutrient agar?
Nutrient agar contains a balanced mixture of nutrients and lacks selective components, allowing the growth of a wide variety of bacteria, yeast, and molds. Here are some examples of bacteria that commonly grow on nutrient agar:
- Gram-Positive Bacteria: Staphylococcus species (e.g., Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus saprophyticus), Enterococcus species (enterococcus faecalis, enterococcus faecuim)
- Gram-Negative Bacteria: Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella, Proteus mirabilis etc.
- Yeast: Candida species.
Fastidious bacteria, including species like Haemophilus and certain Streptococcus strains, have specific nutritional requirements that may not be met by the general-purpose nutrient agar alone. They typically require enriched media that provide additional nutrients and growth factors to support their growth.
◉ What is the difference between Nutrient Agar and Nutrient Broth?
Nutrient agar and nutrient broth share almost the same media composition. The main difference between them lies in the fact that:
- Nutrient agar (solid medium) contains a solidifying agent, agar powder, causing the medium to solidify at room temperature. In contrast, nutrient broth (liquid medium) does not include agar, remaining in a liquid state.
- Bacterial growth in nutrient agar results in the formation of colonies, while in nutrient broth, the broth becomes more turbid.
◉ Pictures
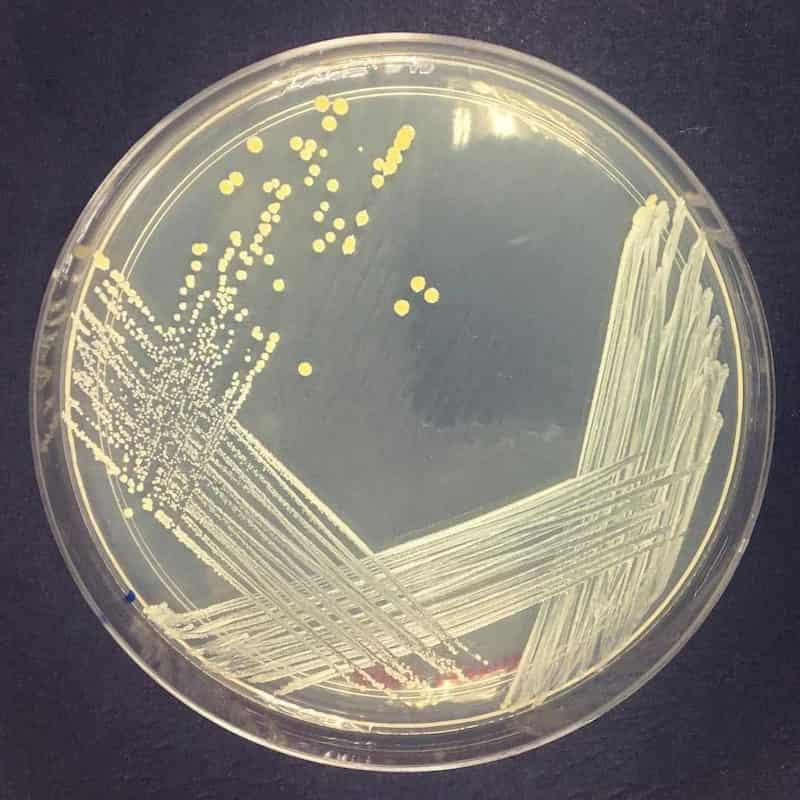
Staphylococcus aureus on nutrient agar
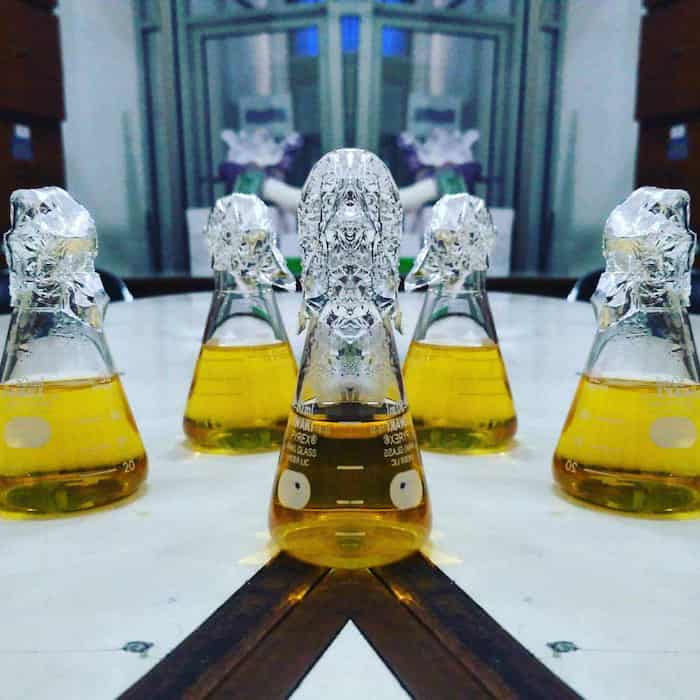

Melted nutrient agar before pouring it into a petri dish
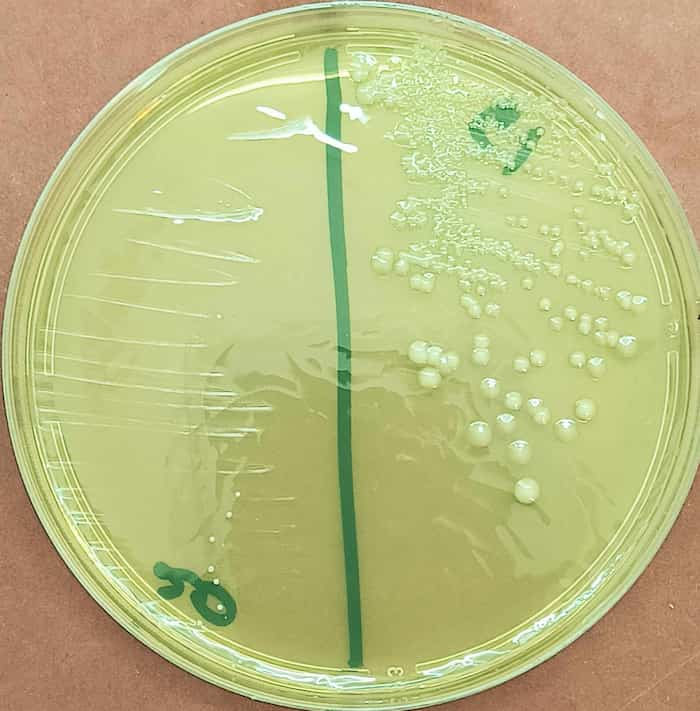
Urine culture on nutrient agar
◈ Some colonies may exhibit characteristic pigmentation:
- Not diffusible: Serratia appears red, Staphylococcus aureus can appears golden yellow on nutrient agar.
- Diffuse: Pseudomonas aeruginosa displays a middle green coloration.

Pseudomonas on nutrient agar

Serratia on nutrient agar
◉ Conclusion
In conclusion, nutrient agar stands out as a versatile and widely used medium in microbiology, facilitating the growth of a diverse range of bacteria, making it highly suitable for routine laboratory work. However, it's essential to note that while nutrient agar is effective for many bacteria, it may not support the growth of extremely fastidious organisms with specific nutritional requirements.