Summary :
◉ What is Klebsiella pneumoniae?
Klebsiella pneumoniae is a bacterium that normally lives inside the intestines and colonizes the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract of humans and blood-blooded animals without causing problems
However, this germ can cause a wide range of infections, mainly nosocomial or in vulnerable subjects (diabetics, alcoholics), including pneumonia, wound infection, blood, urinary tract infections or meningitis.
It is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped, nonmotile, encapsulated bacterium that belongs to the Klebsiella genus of Enterobacteriaceae.
Klebsiella pneumoniae can be treated with antibiotics, but the increase in antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria has reduced the choices available to doctors.
◉ How is Klebsiella pneumoniae transmitted? ?
Klebsiella pneumoniae is hand-borne, which means that this bacterium can be transmitted through person-to-person skin contact (caregiver hands), through contaminated objects or surfaces. The bacteria do not spread through the air.
In hospital settings, patients may also be exposed to K. pneumoniae when they are on ventilators (breathing machines) or have intravenous or ureteral catheters or wounds (injury or surgery).
The infection can develop from germs carried by the patient himself.
◉ Clinical Manifestations
Symptoms and treatment for Klebsiella pneumoniae infection differ depending on where the infection is located (blood, meninges, wound). It is the cause of many ailments, including:
- Lung infections: of community or nosocomial origin (pneumonia or lung abscess).
- Sepsis (blood infection).
- Urinary tract infection
- Meningitis
- Intra-abdominal infection.
- Pyogenic liver abscess.
- Angina
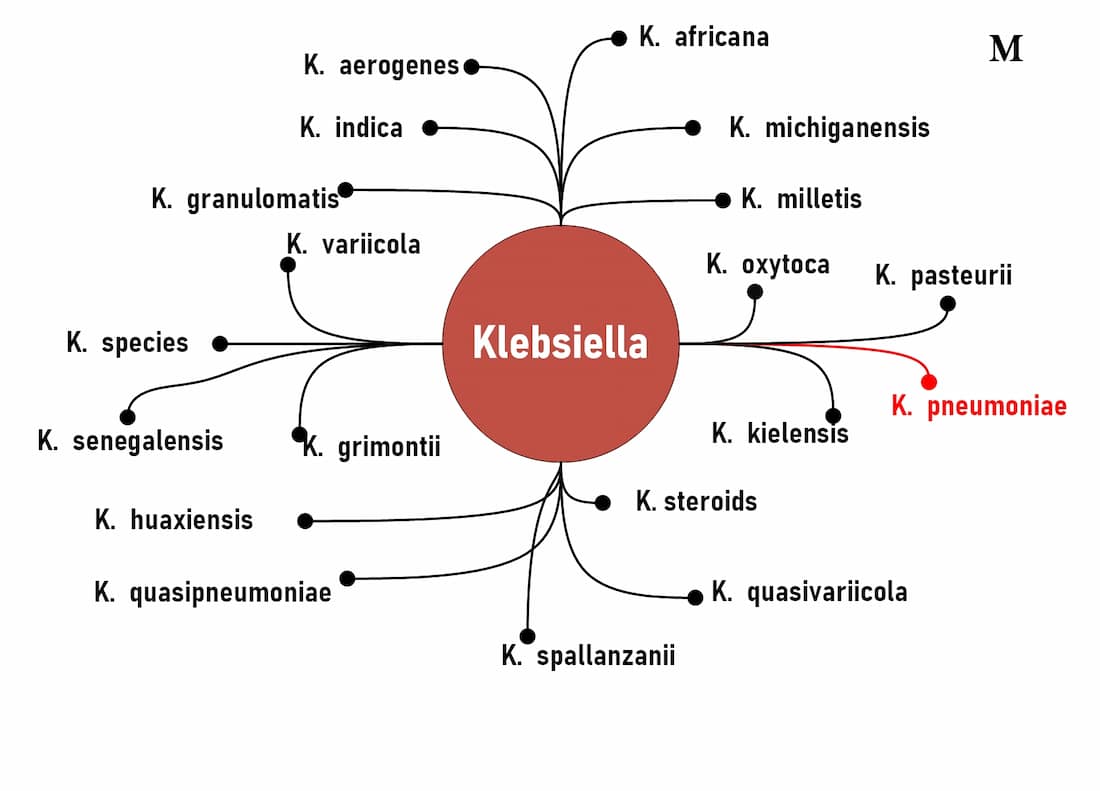
◉ Classification and taxonomy
According NCBI Taxonomy Browser, The species Klebsiella pneumoniae belongs to the order Enterobacterales, the family Enterobacteriaceae and the genus Klebsiella.
It was first described in 1882 by Carl Friedlander and initially named Friedlander's bacillus, it was not until 1886 that the bacterium was given the name Klebsiella in honor of microbiologist Edwin Klebs.
◉ Biochemical test and identification of Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Immobile bacteria
- ONPG test : positive.
- It ferments : Glucose, Glycerol, Inositol, Lactose (late), Maltose, Mannitol, Mannose, Melibiose, Raffinose, Rhamnose, Sorbitol, Sucrose, Trehalose, Xylose.
- Gas production: positive.
- H2S: negative.
- Indole test: negative.
- VP (Voges-Proskauer) test: positive.
- Nitrate reduction: positive.
- Methyl red: negative.
- Citrate test: positive
- Hydrolysis of urea (Urease): positive.
- Hydrolysis of gelatin: negative.
- Catalase test : positive
- Oxydase test: negative
- On TSI agar : yellow base, yellow slope.
- On MacConkey agar : pink colonies (lactose positive).
- On Hecktoen agar : yellow colonies.
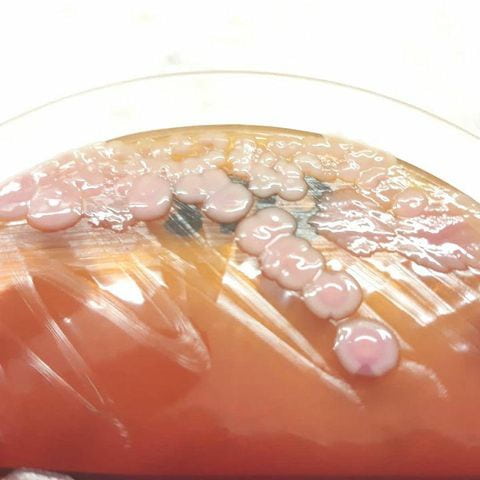
- Klebsiella pneumoniae on blood agar : colonies are large (about 4-6 mm in diameter), gray, opaque and somewhat mucoid.