Content :
Baird-Parker Agar : Principle, Composition, Uses and Interpretation
Baird-Parker Agar is one of the essential agar media utilized in microbiology laboratories. Its wide application and reliability have made Baird-Parker Agar a valuable tool in microbiological analysis and quality control. In this article, we explore its principle, its preparation, its interpretation and its different uses.
◉ Overview
Baird-Parker Agar, introduced by Baird-Parker (1962), serves as a medium for counting Staphylococcus aureus in various food sources. This moderately selective and differential medium is used to isolate and quantify Staphylococcus aureus from food, environmental and clinical samples.
Colonies of Staphylococcus aureus are black and shiny, with a thin white border, surrounded by a light area.
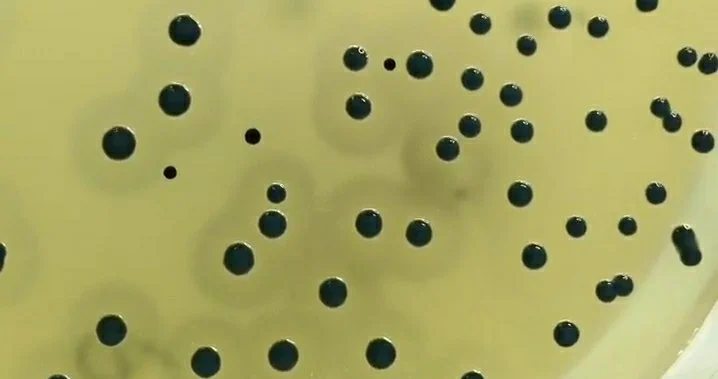
Staphylococcus aureus on Baird Parker
◉ Composition of Baird-Parker Agar
Baird Parker agar composition |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ingredients | gram / liter | ||
| Pancreatic digestion of casein | 10.0g | ||
| Meat extract | 5.0g | ||
| Yeast extract | 1.0g | ||
| Sodium pyruvate | 10.0g | ||
| L-glycine | 12.0g | ||
| Lithium chloride | 5.0g | ||
| Agar | 20.0g | ||
| pH | 7.2 ± 0.2 | ||

Dehydrated Baird Parker Agar
◉ Principle of Baird-Parker Agar
Baird Parker Agar contains casein peptone, beef extract and yeast extract as sources of nitrogen, carbon, sulfur, vitamins and trace elements.
- Sodium pyruvate : Stimulates the growth of S. aureus without destroying the selectivity of the medium
- The egg yolk : Not only enrichment, Staphylococci which contain lecithinase break down egg yolk (lipolysis) and create clear areas around colonies
- The tellurite additive : Almost 100% of coagulase positive Staphylococci are able to reduce tellurite, toxic to strains clarifying egg yolk, which produces black colonies
- Glycine and lithium chloride : Have an inhibitory action against organisms other than S. aureus.
- The optional addition of sulfamethazine after autoclaving ensures the inhibition of almost all Proteus.
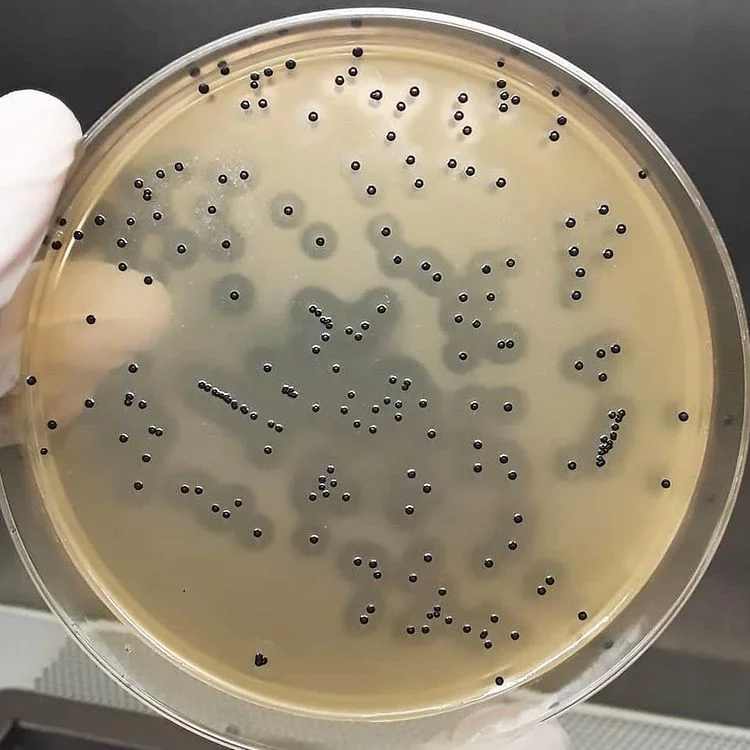
Baird Parker Agar
This culture media can also be used to detect coagulase activity by adding fibrinogen plasma
◉ Interpretation
Staphylococcus aureus is characterized by the formation of black, shiny, convex colonies surrounded by a lightening halo of the egg yolk. Coagulase negative staphylococci are almost completely inhibited and if, however, a culture does appear, areas of thinning would be absent.
- In principle, other microorganisms are inhibited. However, it is possible to observe brown or greenish colonies of micrococci, white colonies of yeast, brown colonies of Bacillus or Proteus.

Sources
- Baird Parker Agar Base -HEMIDIA
- AN IMPROVED DIAGNOSTIC AND SELECTIVE MEDIUM FOR ISOLATING COAGULASE POSITIVE STAPHYLOCOCCI
- Baird Parker Agar Base - NLS
- Baird Parker Agar Base - REMEL
- Baird Parker Agar - Handbook of Culture Media for Food Microbiology 2003
- BD Baird-Parker Agar
- Oxoid - Baird-Parker Agar