Ⅰ. Overview
Salmonella-Shigella agar or SS agar is a selective and differential medium for the isolation
of pathogenic enteric bacilli, particularly Salmonella and Shigella, from stool, food and clinical material.
🏾 The principle of agar is based :
- On the use of bile salt, sodium citrate and brilliant green for the inhibition of gram-positive bacteria.
- On lactose fermentation and hydrogen sulphide (H2S) production for the differentiation of organisms
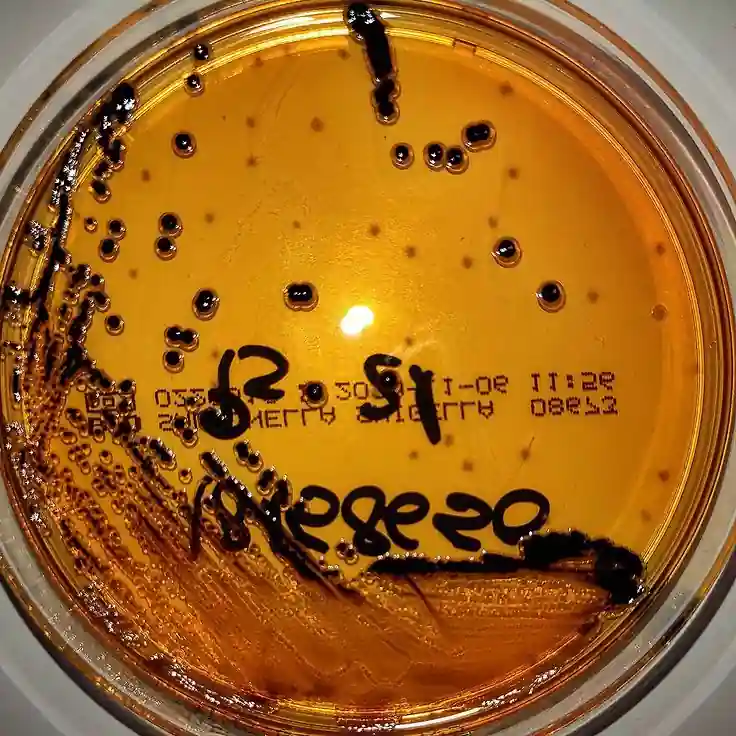
Salmonella Shigella Agar (source : @diplococologia )
◈ La Salmonella Shigella Agar is a modification of deoxycholate-citrate agar described by
Einar Leifson in 1935.
Ⅱ. Preparation / composition
Suspend the components, dehydrated powder, in water (63 grams in 1000 ml of purified/distilled water). Boil, stirring frequently to completely dissolve the medium.
Do not autoclave or overheat: Overheating can destroy the selectivity of the medium.
Cool to 50°C and pour into Petri dishes.
SS agar composition |
| Ingredients |
gram/liter |
Ingredients |
gram/liter |
| Pancreatic casein digestion |
2.5g |
Peptic digestion of animal tissues |
2.5g |
| Beef extract |
5g |
Lactose |
10,0g |
| Sodium thiosulphate |
8.5g |
Sodium citrate |
8.5g |
| Bile salts |
8.5g |
Ferric Ammonium Citrate |
1.0 g |
| Brilliant Green |
0.00033g |
Neutral red |
0,025g |
| Agar |
15,0g |
pH final |
7,0 ± 0,2 |
Ⅲ. Principle of Salmonella-Shigella (SS) agar
◈ Selectivity :
The selectivity of this medium is based on the presence of brilliant green, sodium citrate and bile salts which completely inhibit the growth of Gram-positive bacteria and partially inhibit the growth of Enterobacteriaceae and Proteus.
◈ Differentiation : Differentiation of enteric organisms in SS medium is achieved by :
- The incorporation of lactose into the medium. Organisms that ferment lactose produce acid which, in the presence of the neutral red indicator, results in the formation of red colonies. Lactose non-fermenters form colorless colonies
- Further differentiation based on the production of hydrogen sulphide (H2S) is possible thanks to the presence of sodium thiosulphate and iron citrate. It results in black or black-centered colonies.
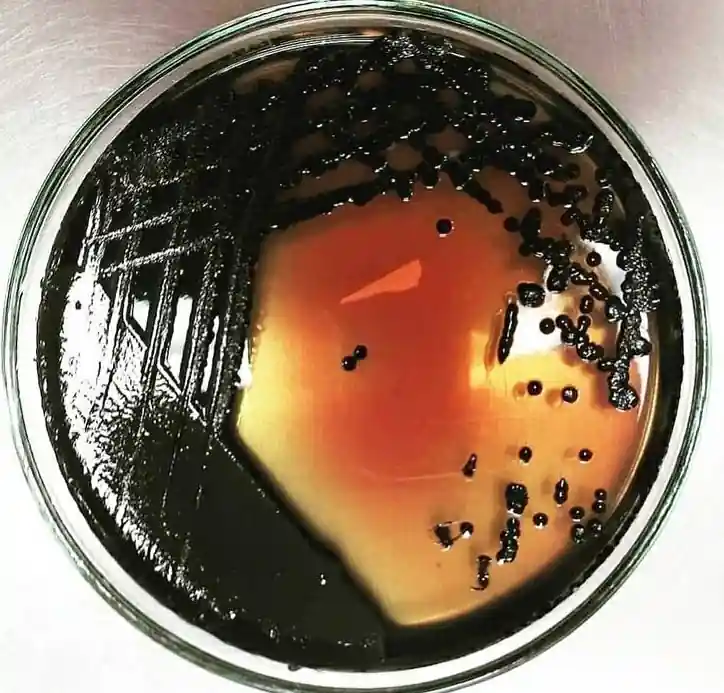

Salmonella on SS agar (source : @microbzoo )
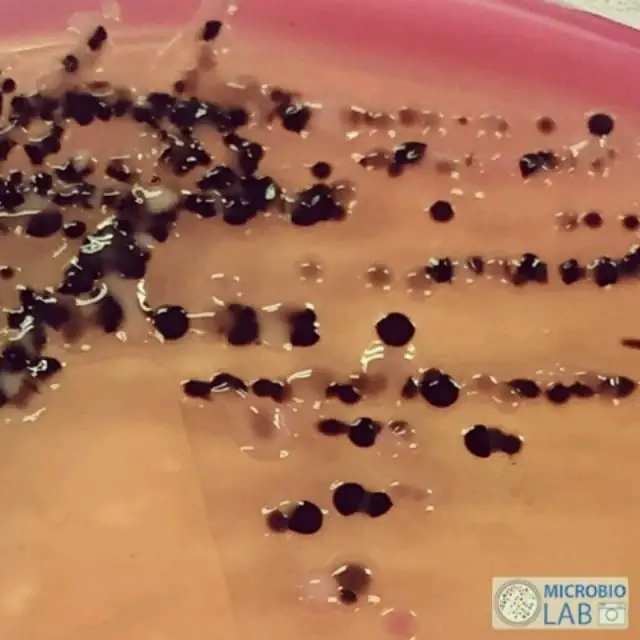

Salmonella and Shigella on SS agar (source :@micro-lab )
Note :
- SS agar can inhibit some species of Shigella such as S. sonnei and S. dysenteriae
- Lactose late fermenters may require 48 hours of incubation to develop and produce a color reaction on SS agar
Ⅳ. Reading / Interpretation
◈ After 24 hours at 37°C aerobically, in general :
Lactose-negative colonies are colorless. Lactose-positive colonies are pink to red. Colonies producing H2S have a black center..
| Bacteria |
Growth |
| Shigella spp. and Salmonella spp non-H2S producers. |
colorless colony |
| Salmonella spp producing H2S. |
Colonies with large black centers with a clear perimeter |
| Klebsiella |
Pink to red colony with or without an area of precipitated bile. |
| Proteus |
Translucent colonies, smaller than Salmonella, with a black centre.
|
| Gram-positive |
Partially or totally inhibited. |


