Sabouraud Dextrose Agar (SDA)
☰ Summary :
Ⅰ. Overview
Sabouraud Dextrose Agar (SDA) is a selective medium for fungal cultivation and primarily used for the isolation of dermatophytes, yeasts and various other pathogenic and non-pathogenic fungi.
Sabouraud medium, developed by French dermatologist Raymond J. A. Sabouraud in 1892, is recommended by the European Pharmacopoeia for the isolation and identification of Candida albicans from non-sterile specimens and for the preparation and maintenance of test strains fungal.
The traditional formula relies on a low pH (5.6) to inhibit bacterial growth. However, the addition of antibiotics to the acid medium to inhibit bacteria is common in currently used versions. In addition, the high glucose concentration provides an advantage for the growth of (osmotically stable) fungi while most bacteria do not tolerate the high sugar concentration.
Sabouraud Dextrose Agar
Note :The maltose in the original formula is less used today than glucose (dextrose) so the medium is commonly referred to as "Sabouraud's dextrose agar".
Ⅱ. Composition of Sabouraud Dextrose Agar
Suspend 65.0 grams in 1000 ml of purified/distilled water. Bring to a boil to completely dissolve the medium. Sterilize by autoclaving at 15 pounds (121°C) pressure for 15 minutes. Cool to 45-50°C. Mix well and pour into sterile Petri dishe.
Composition of Sabouraud Dextrose Agar |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ingredients | gram/litre | Ingredients | gram/litre |
| Peptic digestion of animal tissues | 5.0g | Pancreatic casein digestion | 5.0g |
| Dextrose | 40.0 g/L | Agar | 15.0g |
Ⅲ. Different types of Sabouraud agar
🏾 Sabouraud agar with antibiotics
Commonly used antibiotics are gentamicin, which inhibits gram-negative bacteria, and/or chloramphenicol, which inhibits a wide range of gram-positive and gram-negative fungi, and cycloheximide, which primarily inhibits saprophytic fungi but not dermatophytes or yeasts.
- Chloramphenicol can have an inhibitory effect on several pathogenic fungi.
- Penicillin, gentamicin, and streptomycin, or a combination of these, have been shown to be effective in inhibiting bacteria without affecting fungal growth
Antibiotics should only be added after the medium has been autoclaved and then cooled to approximately 45-50°C.
🏾 Sabouraud agar with methyl blue
Sabouraud Methyl Blue Agar contains 0.01% methyl blue in addition to Sabouraud Agar. This medium has been reported to distinguish between C. albicans and C. dubliniensis based on the yellow fluorescence of C. albicans under a Woods lamp
🏾 Emmon’s Modification of Sabouraud’s Agar
In 1977, Emmons formulated an alternative version of Sabouraud's agar, he modified the formula by adjusting the pH and reducing the dextrose concentration. This neutral pH promotes the recovery of certain pathogenic fungi.
🏾 Sabouraud Broth
The same composition of SDA but without agar.
Ⅳ. Results
The yeasts develop creamy to white colonies. The molds will grow as filamentous colonies of different colors. Count the number of colonies and take into account the dilution factor (if the sample to be tested has been diluted) to determine the number of yeasts and/or molds per gram or milliliter of material.
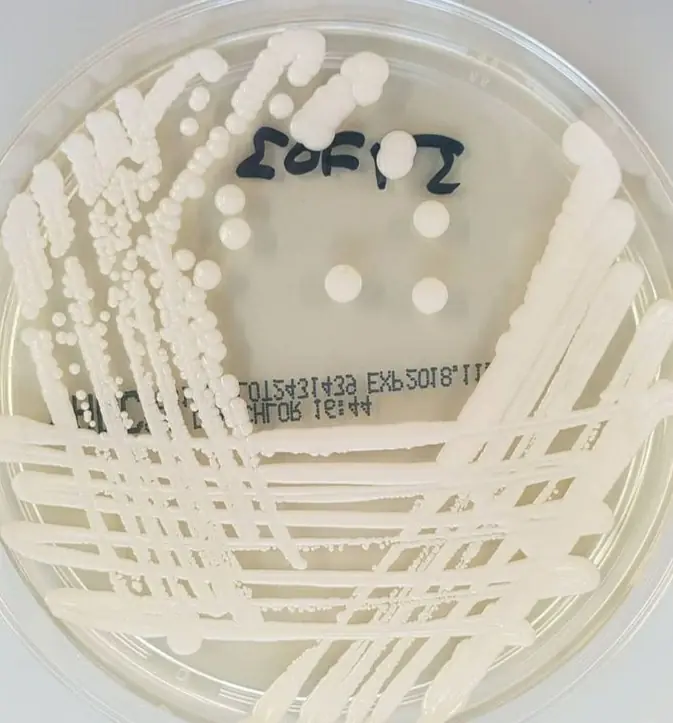
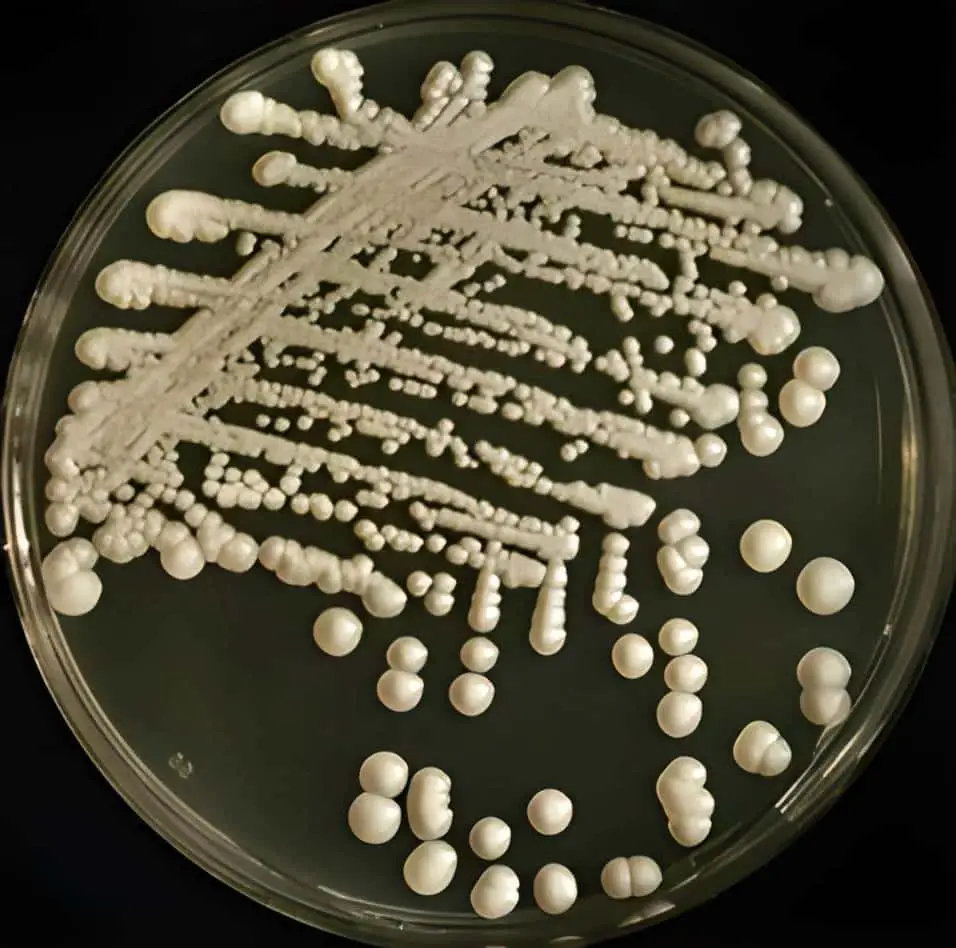
Candida auris on Sabouraud agar (source :@in_petri)
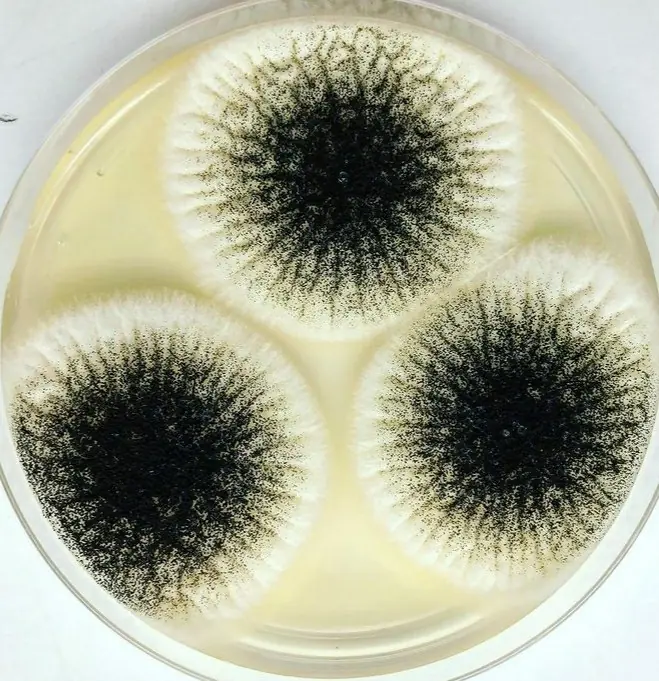
Aspergillus niger on Sabouraud agar (source :@smallbutcool)
Reference
- F. C. ODDS - Sabouraud('s) agar
- neogen - Sabouraud Dextrose Agar
- Liofilchem - Sabouraud Dextrose Agar
- HUMEAU - Sabouraud Dextrose Agar
- HIMEDIA - Sabouraud Dextrose Agar
- thermofisher - Simmons Citrate Agar (Dehydrated)
- BD - Sabouraud Glucose Agarl
- ASM - Sabouraud Agar for Fungal Growth Protocols
- Handbook of MICROBIOLOGICAL MEDIA Fourth Edition
- Manual of Commercial Methods in Clinical Microbiology 2ed