Contenu :
◉ Overview
Gardnerella vaginalis is a bacteria that coexists, in a delicate balance, with other bacteria in the vagina to keep it free from infection. But, for various reasons, if there is an imbalance and too much gardnerella develops, you can get a vaginal infection called bacterial vaginosis (the most common cause of abnormal vaginal discharge in women of childbearing age).
Gardnerella is not considered a sexually transmitted bacterium, although it can be transmitted from woman to woman during sexual intercourse or to a man as colonization in the male urethra (very often without symptom).
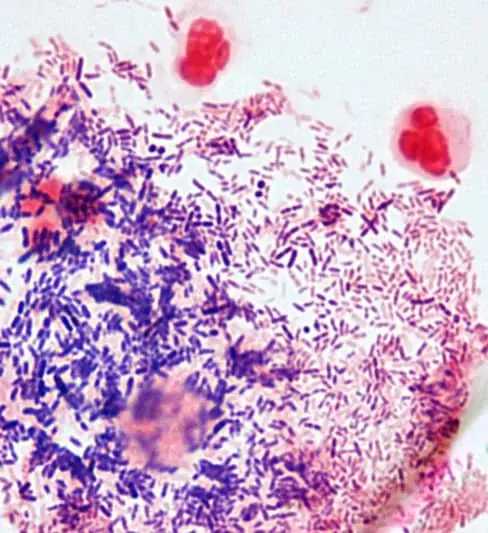
Gram stain of Gardnerella vaginalis
◉ Common symptoms that indicate you have an unhealthy amount of Gardnerella vaginalis ?
Gardnerella vaginalis is one of the bacteria implicated in the development of bacterial vaginosis , many women (>50%) with this vaginal infection have no signs or symptoms, when these are present they are most often :
- Vaginal discharge, gray, white or green, with a strong unpleasant odor
- Strong vaginal odor and fishy smell after sex
- Vaginal itching
- Burning during urination
- Vaginal bleeding after sex
Gardnerella vaginalis can also be responsible for serious infections (sepsis, wound infections) in locations other than those associated with the genital tract or obstetrics, these cases are very rare but have been reported, including in men.
◉ How do I know if I have Gardnerella vaginalis ?
The reference examination for the diagnosis of BV is the direct examination, Gram staining of the vaginal flora, of the vaginal secretions. It is used to determine the Nugent score and the presence of Clue Cells.
◉ Bacteriological characteristics of Gardnerella vaginalis
Gardnerella vaginalis is Gram-variable bacilli or coccobacilli; catalase and oxidase negative, hydrolysis of sodium hippurate positive; acid production from glucose, maltose and sucrose (variable). .
The culture is preferably carried out on vaginal agar (V agar) or HBT agar (Human Blood Tween) for 48 hours in anaerobic conditions.
◉ Treatment
Asymptomatic colonization with Gardnerella does not need to be treated. However, if a patient is bothered by BV symptoms or is pregnant, she should be treated with clindamycin, Secnidazole, or metronidazole orally or vaginally.
◉ Frequently asked questions
Q : Does Gardnerella vaginalis itch?
A : When gardnerella begins to multiply, it will disrupt the vaginal microbiome and create an imbalance that causes the various symptoms such as itching.
Q : how do i get gardnerella
A : Gardnerella is already present in your body in small amounts, You can get BV if too much Gardnerella grows (excessive hygiene, douching, changing sexual partners or even tobacco.).
Q : Is Gardnerella dangerous ?
A :
There is an increased risk of contracting other STIs, including HIV. In pregnant women, it can cause premature rupture of membranes, premature labor and delivery.