Content
The oxidase test is a laboratory test used in microbiology to differentiate between different groups of bacteria based on the detection of the enzyme cytochrome c oxidase. In this article, we explore the principle, the procedure, the uses and the possibles resultes of oxidase test .
◉ Principle of oxidase test
☰ The oxidase test is a test to detect the enzyme cytochrome oxidase in Gram-negative bacteria which produce this enzyme, such as Neisseria or Pseudomonas.
☰ Oxidase Discs (OX) are absorbent paper discs impregnated with N, N, N ’, N’-Tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride. In the presence of cytochrome oxidase, N, N, N ’, N’-Tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride (colorless) forms a compound.
◉ Oxidase test protocol
- Using tweezers, place an oxidase disk on a slide.
- Choose a colony that is well isolated and representative of the fresh culture to be tested.
- Collect the chosen colony using a stick or an ose.
- DO NOT USE a metal loop (except platinum) it may cause false positive reactions.
- Gently rub the colony on the disc and observe the appearance of a purple / blue color within 30 seconds.
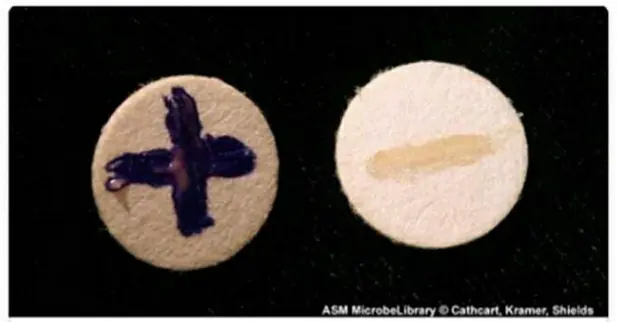
Oxidase test positive and negative (source : ASM MicrobiologyLibrary)
◉ Oxidase test results
☰ Positive reaction : dark blue to purple coloration appearing within 30 seconds.
☰ Negative reaction : absence of coloration or coloration beyond 30 seconds.
◉ Bacteria with Oxidase Positive / Negative
| Oxidase Positive Bacteria | Neisseria (toutes espèces) / Actinobacillus lignieresii / Aeromonas spp. / Actinobacillus equuli / Pasteurella spp. / Bordetella pertussis / Vibrio spp. / Bac. anthracis / Cordiobacterium hominis / Bac. subtillis / Pseudomonas spp. / Brucella spp. / Flavobacterium spp. / Chromobacterium spp. / Alcaligenes spp. / Eikenella corrodens / Moraxella spp. / Plesiomonas spp. / Campylobacter spp. / Branhamella catarrhalis / Micrococcus spp. |
| Negative Oxidase Bacteria | Staphylococcus spp. / Pseudomonas mallei / Streptococcus spp. / Pseudomonas maltophilia / Gemella haemolysans / Bordetella parapertussis Peptococcus spp. / Actinobacillus / Peptostreptococcus spp. / actinomycetem-comitans / Leuconostoc spp. / Anaerobier (tous) / Corynebacterium spp. / Listeria spp. / Pasteurella haemolytica / Lactobacillus spp. / Bacillus spp. / Streptobacillus / Enterobacteriaceae / Mycoplasma spp. / Acholeplasma spp. |
☰ Variable oxidase : (positive or negative depending on the strain): Actinobacillus, Brucella, Haemophilus, Pasteurella.
Usage limits:
- Candida albicans will occasionally give positive result with oxidase test when grown on chocolate agar but give negative reactions when grown on Sabouraud dextrose agar.
- Kovac’s oxidase reagent, 1% aqueous solution of N, N, N′, N′ -tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride is less toxic and more sensitive than the 6% solution of N, N, N′, N′-tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine in dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO) but more expensive and relatively unstable.
- It is necessary to carry out additional biochemical and / or serological tests for a precise identification of the species.
- Insufficient inoculum may cause weak or late staining.
- Colonies taken from media containing nitrates may produce an inconsistent result.
- Media containing a high proportion of blood may generate a false positive result.
- It is essential to proceed from pure and fresh cultures so that the results can be interpreted.
◉ Frequently asked questions
What does the oxidase test determine?
The oxidase test is a biochemical reaction that determines the presence or absence of cytochrome oxidase, it is one of the main bacterial identification tests.
What color is a positive oxidase test?
Dark purple
Does E coli test positive for oxidase?
Non, E coli test negative for oxidase, the entire family of Enterobacteriaceae are oxidase negative
Why is it important to read oxidase results within 30 seconds?
In this test, the timing is important. The reagents of oxidase test is unstable, If it is exposed to air for too long , the oxygen will change the reagent color as time passes (spontaneously become oxidized