Contenu :
◉ Qu'est-ce que l'ANCA ?
Les ANCA, anticorps cytoplasmiques anti-neutrophiles, sont un groupe d'auto-anticorps, principalement de type IgG, dirigés contre les antigènes du cytoplasme des neutrophiles (le type le plus courant de globules blancs) et des lysosomes des monocytes.
La positivité des ANCA et l'identification de leur cible sont une aide précieuse au diagnostic des vascularites (inflammations des vaisseaux sanguins, veines et artères), particulièrement, certaines vascularites systémiques, appelées vascularites associées aux ANCA (VAA).
Il existe deux principaux types d'ANCA. Chacun cible une protéine spécifique à l'intérieur des globules blancs :
- p-ANCA (fluorescence périnucléaire) : cible une protéine appelée MPO (myéloperoxydase)
- c-ANCA (fluorescence cytoplasmique) : cible une protéine appelée PR3 (protéinase 3)
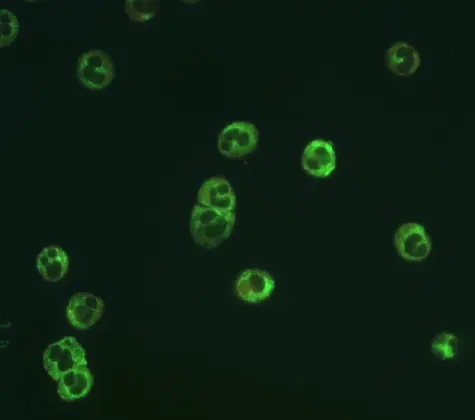
c-ANCA : fluorescence cytoplasmique
◉ Pourquoi le test sanguin ANCA est-il effectué?
La détection des ANCA est un test de diagnostic bien établi pour l'évaluation des patients suspectés d'avoir un VAA et certaines maladies inflammatoires de l'intestin.
Les vascularites auto-immunes provoquent une inflammation et un gonflement des petits vaisseaux sanguins. Ces petits vaisseaux sanguins se trouvent partout dans le corps humain, de sorte que n'importe quelle partie du corps peut être affectée, mais le plus souvent les reins, les poumons, les articulations, les oreilles, le nez et les nerfs.
| Organes | Symptômes |
|---|---|
| Symptômes générales | Fièvre, Fatigue, Perte de poids, Douleurs musculaires et/ou articulaires. |
| Les yeux | Rougeur, Vision floue, Perte de vision. |
| Les oreilles | Bourdonnement dans les oreilles (acouphènes), Perte d'audition. |
| Les sinus | Douleur des sinus, Nez qui coule, Saignements de nez. |
| La peau | Éruptions cutanées, Plaies ou ulcères, un type de plaie profonde qui tarde à guérir et/ou qui revient sans cesse. |
| Les poumons | Toux, Difficulté à respirer, Douleur thoracique. |
| Les reins | Du sang dans les urines, Urine mousseuse, qui est causée par des protéines dans l'urine |
Chaque type d’ANCA affecte différents vaisseaux sanguins et parties du corps. Les types de vascularite auto-immune comprennent :
- Granulomatose avec polyangéite (autrefois appelée granulomatose de Wegener) : Elle affecte le plus souvent les poumons, les reins et les sinus.
- Polyangéite microscopique (MPA) : Ce trouble peut affecter plusieurs organes du corps, notamment les poumons, les reins, le système nerveux et la peau.
- Granulomatose éosinophile avec polyangéite (autrefois appelée syndrome de Churg-Strauss) : Ce trouble affecte généralement la peau et les poumons. Il provoque souvent de l'asthme.
◉ Prise de sang pour test ANCA
Les ANCA sont détectés à l'aide d'un un simple prélèvement sanguin. Il n'y a pas de préparations particulières à faire avant l'analyse et ne nécessite pas de jeûne, sauf si votre échantillon de sang sera utilisé pour des tests supplémentaires.
◉ Dosage ANCA
Les techniques les plus couramment utilisées pour détecter les ANCA sont l'immunofluorescence indirecte (IFI) et le dosage immuno-enzymatique (ELISA).
◉ 1. L'immunofluorescence indirecte (IFI)
Dans l'immunofluorescence indirecte, des neutrophiles sont fixés à l'éthanol sur une lame (pendant 5 minutes à +4 °C avec de l'éthanol à 96-99 %). Le sérum de l'échantillon sanguin est ensuite mélangé avec les neutrophiles sur la lame, ce qui permet à tous les ANCA de l'échantillon de se fixer aux protéines neutrophiles. Ensuite, le traitement de la lame avec un anticorps coloré au fluorochrome réagit avec tous les ANCA présents.
Les deux schémas majeurs d'immunocoloration les plus fréquents sont désignés par les sigles C-ANCA et P-ANCA :
- Le schéma cytoplasmique granulaire avec accentuation centrale, connu sous le nom de C-ANCA.
- Le schéma périnucléaire, qui est défini comme une fluorescence périnucléaire avec extension nucléaire et connu sous le nom de P-ANCA.
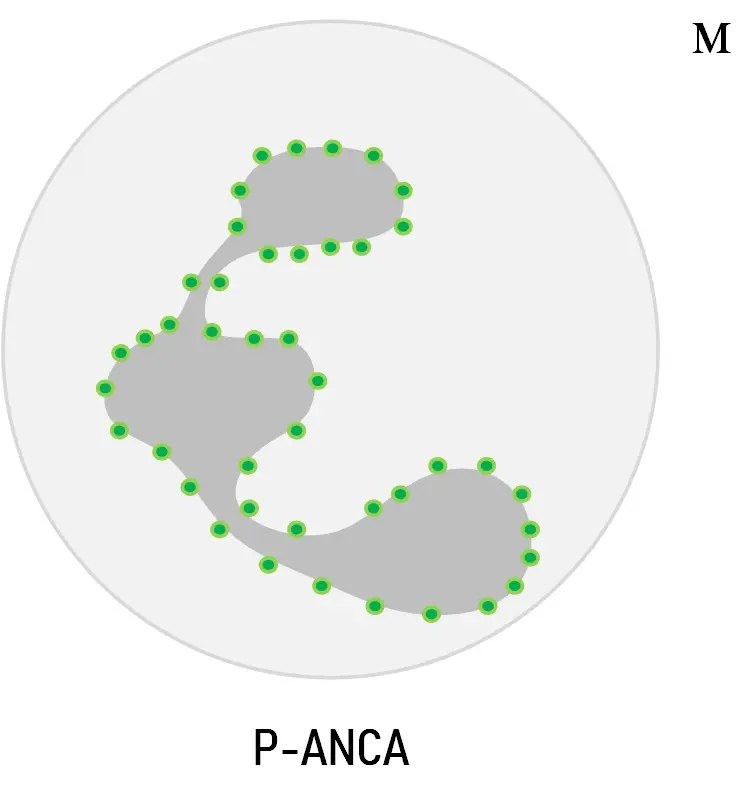
P-ANCA : il apparaît comme un marquage intense de la périphérie des lobes nucléaires avec un centre presque négatif, conférant une image en « chou-fleur ».

C-ANCA : il correspond à une fluorescence cytoplasmique granulaire diffuse avec, le plus souvent, un renforcement entre les lobes du noyau.
Note :
- Un troisième aspect, décrit en dernier et qui fait le plus débat, est appelé atypique (aANCA), et combine des caractéristiques des
deux premiers
- Si un résultat de test ANCA est positif, une étape supplémentaire peut être effectuée pour déterminer la quantité d'anticorps présents. C'est ce qu'on appelle un titre
◉ 2. ELISA
Le typage des deux spécificités principales (myélopéroxydase et protéinase 3) se fera par ELISA. Ce type de test aide à identifier la protéine ciblée dans les neutrophiles.
◉ Interprétation des résultats
◾ Les résultats des tests ANCA doivent être interprétés avec prudence en tenant compte de plusieurs facteurs. Votre médecin examinera vos signes et symptômes en plus des résultats des tests de laboratoire et d'autres types de tests, tels que les études d'imagerie
| État | % de patients présentant un profil cANCA (anticorps PR3) | % de patients présentant un profil pANCA (anticorps MPO) |
|---|---|---|
| Granulomatose avec polyangéite (granulomatose de Wegener) | 90 % en cas de maladie active, 60 à 70 % sans maladie active | Moins de 10 % |
| Polyangéite microscopique | 30 % | 60 % |
| Granulomatose éosinophile avec polyangéite (syndrome de Churg Strauss) | Rare | 50-80% |
| Polyartérite noueuse | Rare | Rare |
Les niveaux d'ANCA peuvent changer au fil du temps et peuvent parfois être utilisés de manière générale pour surveiller l'activité de la maladie et/ou la réponse au traitement.
◾ En cas de suspicion de maladie inflammatoire de l'intestin (MICI):
- Si ANCA est positif et ASCA (anticorps anti- Saccharomyces cerevisiae ) est négatif, il est probable que vous ayez une rectocolite hémorragique
- Si ANCA est négatif et ASCA est positif, il est probable que vous souffriez de la maladie de Crohn
◉ Quels autres tests pourrais-je avoir avec ce test ?
Des tests supplémentaires pouvant être effectués pour faciliter le diagnostic : la vitesse de sédimentation des érythrocytes (VS), CRP, Numération formule sanguine (NFS), La concentration de l'azote uréique sanguin (BUN) et de la créatinine pour évaluer la fonction rénale.
◉ Questions fréquemment posées
Q : Dans quels laboratoires effectues la recherche des ANCA?
R : Les tests ANCA nécessitent un équipement spécialisé et une interprétation minutieuse par des professionnels formés. Les résultats peuvent prendre plusieurs jours à une semaine.
Q : Comment différencié entre des vrais anticorps pANCA d'une éventuelle interférence avec les anticorps antinucléaires (ANA)?
R : Les sérums de patients positifs avec des profils périnucléaires ou nucléaires sont répétés à l'aide d'un substrat fixé au formol, ainsi que le méthanol, afin de les différencier
Q : Les anticorps cytoplasmiques antineutrophiles (ANCA) disparaîtront-ils un jour ?
R : Comme les autres maladies auto-immunes, les niveaux peuvent fluctuer, mais une fois que vous aurez développé un auto- anticorps , vous continuerez à l'avoir.
Q : Quels sont les différents fixateurs utilisés ?
R : Éthanol, Formol, Méthanol