Content
A urinary tract infection is a microbial infection of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra. In this article we are going to discuss the predisposing factors of UTI, its etiology, types, symptoms, diagnosis and possible treatment.
◉ Definition
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is defined by the invasion of microorganisms, most commonly bacteria, into any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra
UTIs most often affect the lower urinary tract, causing symptoms such as frequent urination, painful urination, or strong-smelling urine. In more severe cases, UTIs can affect the upper urinary tract, leading to more serious indications like fever, chills, back pain, and nausea.
The causes of urinary tract infections are primarily bacterial, with the most common cause being Escherichia coli (E. coli), a bacteria normally present in the gastrointestinal tract.
An accurate diagnosis of UTIs is necessary for proper treatment to avoid recurrent infections and prevent complications

◉ Types of urinary tract infections
There are several types of urinary tract infections, which can affect different parts of the urinary system and in different situations. These include:
- Uncomplicated cystitis: This is the most common type of urinary tract infections and refers to an infection of the bladder.
- Recurrent cystitis: Is usually defined as 3 episodes of urinary tract infection in the previous 12 months, or 2 episodes in the previous 6 months
- Pyelonephritis: This type of UTI occurs when the infection reaches the kidneys. It is usually more severe than cystitis.
- Urethritis: Urethritis is an infection of the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
- Asymptomatic Bacteriuria (ASB): ASB is the presence of bacteria in the urine without any signs or symptoms of infection.
- Catheter-associated Urinary Tract Infections (CAUTI): CAUTI occurring in an individual whose urinary bladder is catheterized or has been catheterized within the past 48 hours.
- Catheter-associated Asymptomatic Bacteriuria (CA-ASB): CA-ASB is the presence of bacteria in a urine sample due to bacterial colonization of the urinary tract and/or indwelling urinary catheter.
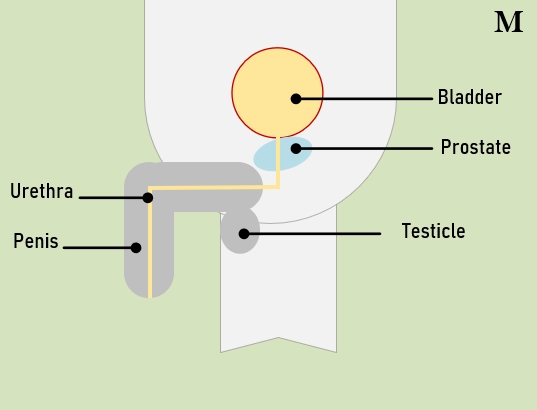
◉ Risk factors for urinary tract infection
The predisposing factors for urinary tract infections can vary. Some common factors that can increase the risk of developing a UTI include:
- Female anatomy: Women have a shorter urethra compared to men, making it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder.
- Sexual activity: Sexual intercourse can introduce bacteria into the urethra, increasing the risk of a urinary tract infection.
- Certain types of birth control: The use of diaphragms or spermicide-coated condoms can increase the risk of UTIs.
- Menopause: Changes in hormonal levels during menopause can lead to changes in the urinary tract, making it more susceptible to infection.
- Urinary tract abnormalities: Structural abnormalities in the urinary tract, such as urinary stones, can create a favorable environment for bacteria to grow and cause infection.
- Catheterization: Insertion of a urinary catheter may introduce bacteria directly into the bladder.
- Kidney stones or an enlarged prostate can slow down urine flow, causing urine to get stuck in the bladder, increasing the chances of getting a UTI.
- A very weak immune system unable to fight infections.
- A recent urinary procedure, such as a cystoscopy or urinary surgery, has the potential to introduce bacteria into the urinary system.
◉ Causes
The causes of urinary tract infections are mainly bacterial. The most commonly encountered bacteria is Escherichia coli (E. coli), a bacteria normally present in the gastrointestinal tract.
Other bacteria, such as Enterococcus faecalis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Staphylococcus saprophyticus, can also cause UTIs, but they are less common.
In some cases, UTIs can also be caused by viruses, parasites or fungi, although this is rare.
Urinary tract infections can take place through several routes:
- UTIs typically occur when bacteria from the rectal area enter the urethra and travel up into the urinary tract.
- Hematogenous spread is less frequent and usually occurs in patients with ureteral obstructions or those who have compromised immune systems or are in a weakened state.
- Exceptionally, urine can become infected after a breach of the urinary tree: trauma, fistula…
◉ Symptoms of urinary tract infections
The symptoms of urinary tract infections can vary from person to person, but some common signs and symptoms include:
- Frequent urge to urinate: You may feel the need to urinate more frequently than usual, often in small amounts.
- Burning sensation during urination
- Painful urination (dysuria).
- Cloudy, dark, or bloody urine: Your urine may appear cloudy, have an unusual odor, or contain blood.
- Lower abdominal pain or discomfort: You may have mild to severe pain or cramping in the lower abdomen or pelvic area.
- Pelvic pressure or discomfort: You may feel pressure or discomfort in your lower abdomen.
- Fatigue or general malaise: UTIs can cause feelings of tiredness, weakness, or overall discomfort.
- Fever or chills: In more severe cases, a UTI may cause a low-grade fever or chills.
- Back or flank pain: Infections that have spread to the kidneys may result in pain in the back, sides, or lower abdomen.
Note
- It's important to note that these symptoms may not appear simultaneously, and certain individuals might experience atypical or milder symptoms.
- If you experience one or more of these symptoms, it is important to consult your doctor.
◉ Diagnosis
To diagnose a urinary tract infection, a doctor may consider the following steps:
- Medical history and physical examination: The doctor will ask about symptoms and any relevant medical history.
- Urinalysis : A urine sample will be collected to check for the presence of white blood cells (leukocyturia), red blood cells, nitrites (nitrites in urine) and bacteria in the urine.
- Urine culture: In some cases, a urine culture may be performed to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection and determine the most effective antibiotic treatment.
- Imaging tests: If recurrent infections or complicated UTIs are suspected, the doctor may order imaging tests like ultrasound or CT scan to look for any abnormalities in the urinary tract.
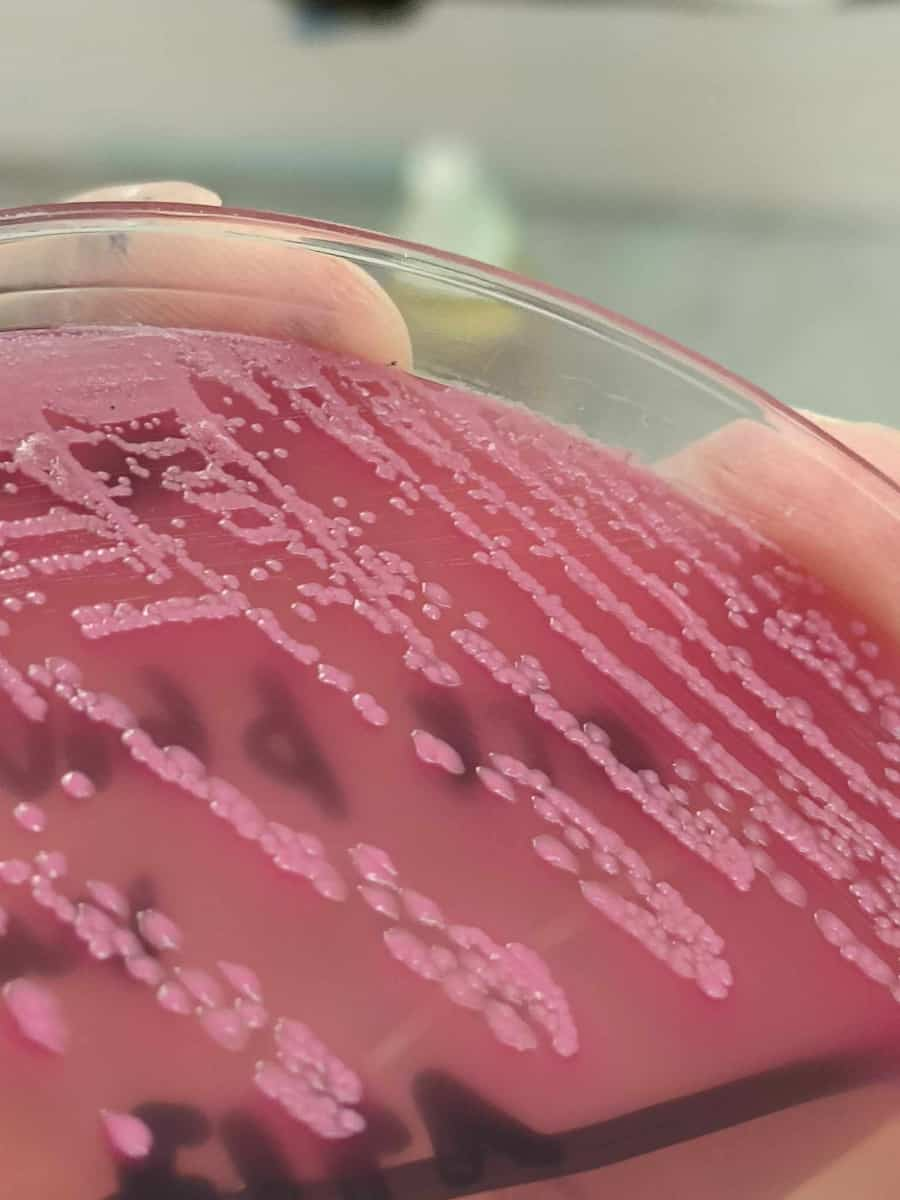
Positive Urine Culture on macconkey agar
◉ Treatment
The treatment of urinary tract infections (UTIs) typically involves a course of antibiotics to kill the bacteria causing the infection. The specific antibiotic prescribed will depend on the type of bacteria causing the UTI and its susceptibility (Antibiotic susceptibility testing) to certain medications.
- Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim)
- Nitrofurantoin (Macrobid)
- Ciprofloxacin (Cipro)
- Levofloxacin (Levaquin)
- Fosfomycin (Monurol)
It's essential to complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if your symptoms improve, to ensure that the infection is fully eradicated. It's also important to stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water, as well as urinate frequently to help flush out the bacteria.
In addition to antibiotics, you can take over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, to alleviate any pain or discomfort. Applying a heating pad to the lower abdomen can also help soothe pain.
◉ What are the complications of a urinary tract infection?
An improperly or untreated urinary tract infection allows bacteria to multiply and spread, leading to a variety of health issues:
- Spread of Infection to more serious parts of the urinary system.
- Recurrent or Chronic UTI.
- Possible premature delivery when a urinary tract infection occurs during pregnancy.
- Permanent bladder or kidney damage.
- Urosepsis is a type of sepsis that begins in the urinary tract.
- Bacterial resistance
◉ Conlusion
A UTI is therefore a symptom that must be traced back to its underlying cause. In this way, the responsible germ can be treated with antibiotics, and sometimes any potential surgical cause must be treated, because it would be serious to neglect it.