Summary :
A urine specific gravity test is one of the urinalysis parameters, commonly used for the evaluation of kidney function and to aid in the diagnosis of various kidney diseases. This article explains the test, the different analysis methods, and what the results may indicate.
◉ Introduction
Urine specific gravity measures the ability of the kidney to concentrate or dilute urine and compares the specific gravity of urine to the specific gravity some water. The more concentrated the urine, the higher the specific gravity of the urine.
The test is often used by clinicians in routine practice to assess hydration status, kidney function, and to diagnose certain medical conditions and monitor treatment effectiveness.
To measure urine specific gravity, a urine sample is taken and analyzed using a refractometer or urine dipstick. Using the same test method consistently for a patient is essential to ensure accurate results and facilitate correct interpretation.

Urine specific gravity measurement by dipstick
◉ Normal value of Urine specific gravity
Normal value ranges may vary slightly from lab to lab. Some labs use different measurements or test different samples. However, in general, the normal specific gravity value for urine is 1.003 to 1.030.
◉ Causes
◉ High urine specific gravity (Hypersthenuria)
Increased urine specific gravity may be due to conditions such as:
- Dehydration (water restriction, vomiting, diarrhea), especially in elderly or pediatric patients
- Reduced renal blood flow (e.g. renal artery stenosis)
- Liver failure
- Diabetes mellitus
- Congestive heart failure.
- High level of sodium in the blood
- Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH)
- The adrenal glands do not produce enough hormones (Addison's disease)
◉ Low urine specific gravity (Hyposthenuria)
Decreased urine specific gravity may be due to:
- Excess fluid intake.
- Diabetes insipidus.
- Glomerulonephritis, Pyelonephritis.
- Kidney failure.
- Some treatment: glucocorticoids, diuretics, anticonvulsants and excessive thyroid hormone supplementation.
◉ Fixed specific gravity
In patients with certain chronic kidney diseases, the kidney cannot produce urine with a higher or lower concentration than protein-free plasma (1.008 to 1.012). This situation is called fixed urinary specific gravity or isosthenuria, the specific gravity does not vary with fluid intake
Note : The specific gravity value should always be interpreted in conjunction with other clinical information and individual patient circumstances.
◉ What is the test used for?
A healthcare professional may order the measurement of specific gravity of urine for several reasons. Here are some common prescribing goals:
- Assessment of hydration status.
- Assessment of kidney function.
- Monitoring of certain diseases: Ex: diabetes, kidney disease.
- Monitoring response to treatment.
- Assessment of urinary tract disorders: Such as urinary tract infections, kidney stones or other conditions affecting urine concentration.
- Monitoring for hyponatremia or hypernatremia.
- Heart failure
◉ How to measure the specific gravity of urine
Different laboratories or health care providers may use different methods or equipment to measure the specific gravity of urine. It is important to use the same method consistently to maintain consistency of results and facilitate correct interpretation.
Before the test, a healthcare professional may advise the person to temporarily discontinue or avoid certain medications and foods that may affect the results.
There are several methods for measuring the urine specific gravity. Here are some commonly used methods :
◉ Measurement of urinary density by refractometry
It is considered the most accurate method. This method uses a refractometer, which measures the bending of light (refraction) as it passes through the urine sample.
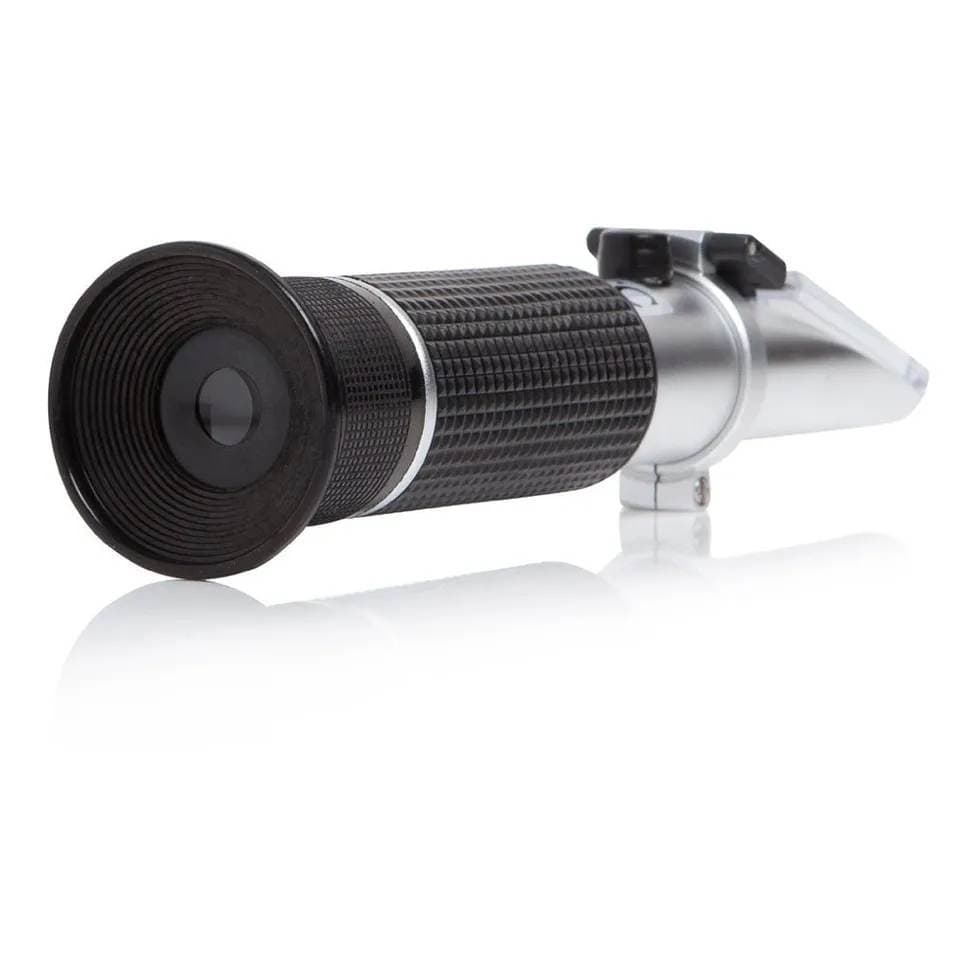

Refractometer
◉ Urinary specific gravity measurement by dipstick
An indicator changes color depending on the concentration of ions in the urine. However, dipstick urine specific gravity measurements can have limitations in terms of accuracy and reliability.
Procedure
- Wash your hands thoroughly and then your genital area with soap and water.
- Start urinating into the toilet, then stop and place the sterile collection container under your urine stream.
- Collect at least 30 milliliters of urine in the container, then finish urinating in the toilet. Remove one strip from its packaging.
- Soak the strip in the urine sample for the recommended time (usually a few seconds).
- Remove the test strip from the urine and tap it gently to remove excess urine.
- Wait the recommended time (60sec) for the test results to develop.
Results
A Urine Specific Gravity test is read by comparing the color of the test strip to a color chart provided by the manufacturer.
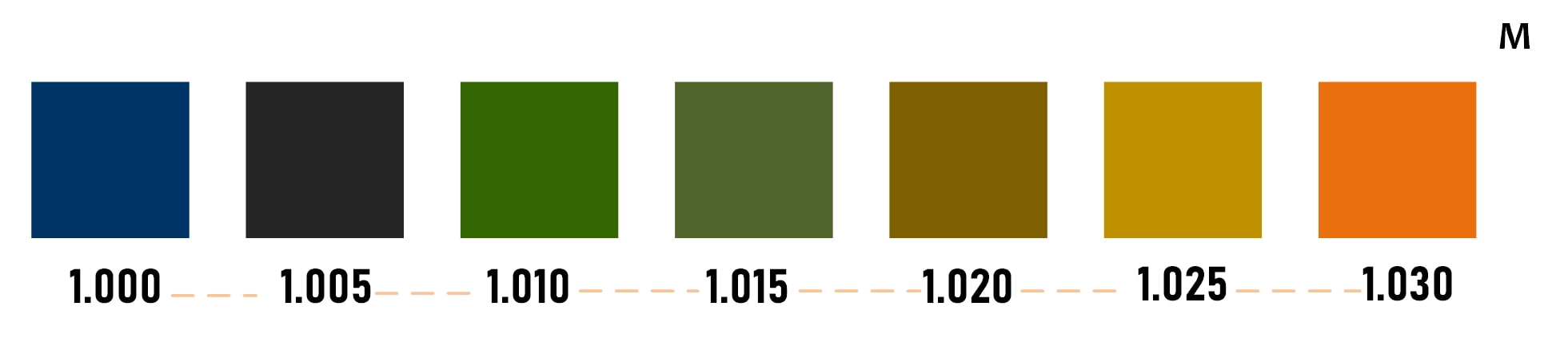
Urine specific gravity color chart
◉ Measurement of urine specific gravity by Urinometry
Urinometers are cylindrical glass or plastic tubes with a weighted float that measures the specific gravity of the urine sample. The higher the specific gravity, the deeper the float will sink into the urine.
◉ Measurement of urinary specific gravity by automated analyzers
Some modern laboratory instruments can automatically measure the urine specific gravity. These analyzers use different principles, such as refractometry or conductivity, to determine specific gravity.
◉ What can affect the result?
Other factors that may cause an inaccurate result include:
- Exposing the sample to light and temperature, which can change the composition of some particles
- Bacterial growth
- pH alkaline
- The presence of glucose, proteins, red blood cells (blood in urine) or white blood cells in urine.
- Contrast agents used in scans and other procedures
- Certain foods: such as beets and rhubarb contain natural pigments that can discolor urine and potentially interfere with test results.
- Certain drugs: I.V. albumin, I.V. dextran, lithium salts, ibuprofen, chloroquine and metronidazole
◉ Additional analysis
Additional testing may be required to identify the underlying cause of the abnormality.
- Osmolality analysis
- Complete renal profile
- Urinary pH
- Chemical analysis of urine: electrolytes, proteins in urine, glucose, Ketones in urine.
- Specific tests according to symptoms.