Summary :
The urinary urobilinogen test is commonly requested by doctors to assess liver function, in this article we will discover the importance of this test, how it is performed and what the results can indicate.
◉ Definition
In healthy individuals, there may be several compounds present in small amounts in urine, including urobilinogen.
urobilinogen is a chemical compound that forms in the intestines when bacteria break down bilirubin, a substance that is produced when old red blood cells are broken down. It is then released into the bloodstream and filtered by the kidneys, which can excrete it in the urine.
Abnormal levels of urobilinogen in the urine, whether elevated or reduced, can signal a range of possible medical conditions, such as liver disease, hemolytic anemia and certain infections
Urobilinogen in urine can be detected using a simple, routine urinalysis test. It is important to note that interpretation of results should always be done in consultation with your doctor, as other factors can affect the test results and overall diagnosis.

Measurement of urobilinogen by dipstick
◉ What is urobilinogen?
urobilinogen comes from the transformation of bilirubin, a product of the breakdown of hemoglobin, which is formed when old red blood cells break down, during a normal process, in the body.
It is then transported to the liver where it is conjugated (combined with other molecules) and secreted into the bile. Bile is a liquid produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder.
When food enters the small intestine, bile is released from the gallbladder into the intestine to help break down fats and facilitate their absorption. Bile also plays a role in removing waste products from the body, including bilirubin.
Bilirubin that is excreted in bile eventually enters the large intestine (duodenum), where it is metabolized by bacteria to form urobilinogen. Some of the urobilinogen is then absorbed into the bloodstream and excreted in the urine (about 5%), while the rest is eliminated in the stool (about 90%).
◉ Urobilinogen values
It is important to note that the normal and pathological levels of urobilinogen in the urine vary slightly according to the laboratories and the analytical methods used. However, in general
- The normal level of urobilinogen in urine is usually less than 1 mg/dL (0.2 - 1.0 mg/dL).
- Elevated level of urobilinogen in the urine is greater than 2 mg/dL
- A low level of urobilinogen in the urine is less than 1.0 mg/dL (3.2 µmol/L)
◉ Causes and Interpretation
• Causes of increased urobilinogen in urine :
- Liver disease: Certain liver diseases, such as cirrhosis, hepatitis (viral, alcoholic, drug-induced, etc.) and liver cancer, can increase the amount of bilirubin and cause high levels of urobilinogen in the urine.
- Biliary disease: a blockage or inflammation of the bile ducts.
- Increased destruction of red blood cells: Increased lysis of red blood cells (Haemolytic anaemia. Pernicious anaemia. Malaria, etc.) can increase the level of bilirubin in the blood, which leads to an increase corresponding urobilinogen in urine.
- Lead poisoning
• Cause of low urobilinogen level in urine :
A low amount of urobilinogen in the urine can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
Urobilinogen is converted to urobilin in the presence of oxygen and upon exposure to air. For this reason, the test should be performed on a fresh sample.
- Liver failure: When the liver is severely damaged or not functioning properly, it may produce less urobilinogen, leading to less of it in the urine.
- Obstruction of the bile ducts: Obstruction of the bile ducts can prevent bilirubin from reaching the intestines, thus reducing the formation of urobilinogen and its presence in the urine.
- Crigler-Najjar Syndrome: This is a rare genetic disorder characterized by a congenital inability of the liver to properly conjugate bilirubin.
- Gilbert's Syndrome: This is a common genetic condition characterized by a slight decrease in the activity of the enzyme that conjugates bilirubin. Although this does not usually cause serious health problems, it can cause a decrease in urobilinogen in the urine.
- Treatment with antibiotics: Destruction of the intestinal bacterial flora following the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics.
• Comparing urinary bilirubin results with urobilinogen results may provide additional information about the potential source of the increased urine bilirubin.
| Hemolysis of red blood cells | Urinary bilirubin and urobilinogen will both be elevated | When there is an increase in the destruction of red blood cells (hemolysis), bilirubin is produced in large quantities. This can lead to increased bilirubin in the urine as well as increased urobilinogen because some bilirubin is converted to urobilinogen |
| Liver diseases | Increased urinary bilirubin, urobilinogen can be either high or normal to low | Liver disease can affect the liver's ability to metabolize bilirubin properly (leakage of bilirubin into the urine). The variation in urobilinogen is a function of the cause and severity of liver disease. |
| Biliary obstruction | Bilirubin increased, urobilinogen may be low or absent. | When there is an obstruction of the bile ducts, bilirubin cannot be excreted normally in the intestine and accumulates in the blood and does not reach the intestines where it is converted into urobilinogen by bacteria. |
Note: It is important to note that other factors and tests may be needed to arrive at an accurate diagnosis. Urinary bilirubin and urobilinogen results should be considered within the patient's overall clinical context.
◉ How to detect urobilinogen in urine
◉ Procedure
The detection of urobilinogen in urine is a simple and non-invasive procedure that can be performed in a clinical setting or at home using a test strip. Here are the main steps:
Urobilinogen is converted to urobilin at rest in the presence of oxygen and upon exposure to air. For this reason, the test should be performed on a fresh sample.
- Read the manufacturer's specific instructions carefully.
- Wash your hands thoroughly and then your genital area with soap and water.
- Start urinating into the toilet, then stop and place the sterile collection container under your urine stream.
- Collect at least 30 milliliters of urine in the container, then finish urinating in the toilet.
- Remove a strip from its wrapper.
- Soak the strip in the urine sample for the recommended time (usually a few seconds).
- Remove the test strip from the urine and tap it gently to remove excess urine.
- Wait the recommended time (usually 60 seconds) for the test results to develop.
◉ Results
The urine urobilinogen test is read by comparing the color of the test strip to a color chart provided by the manufacturer. The color of the test strip will change depending on the level of urobilinogen in the urine sample.
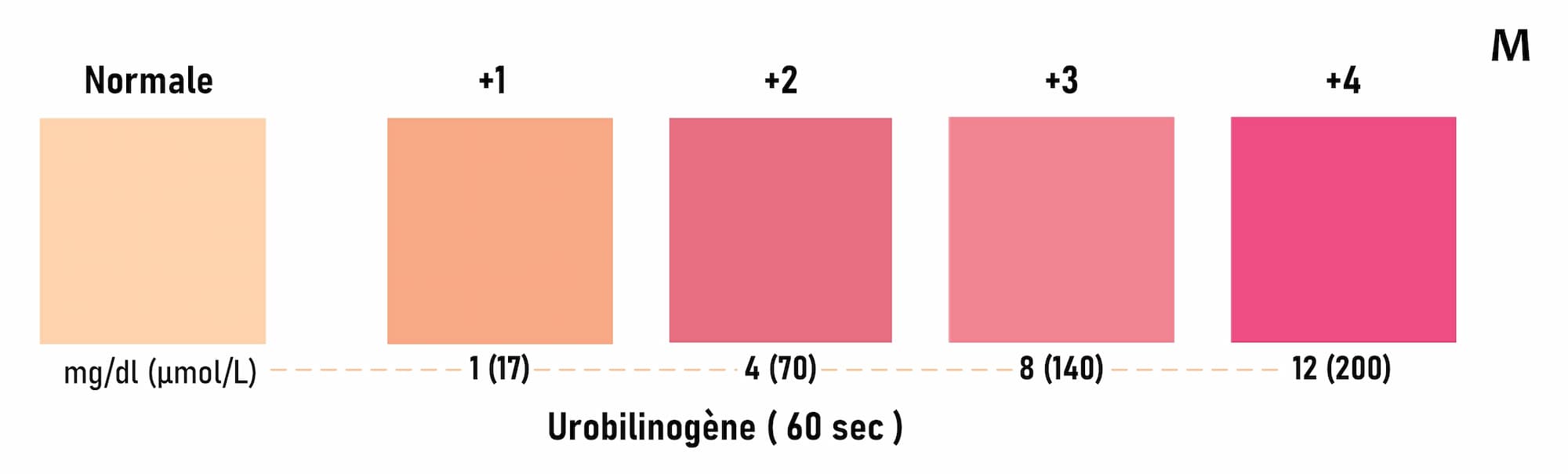
Urinary urobilinogen test
False positive results:
- Highly colored pigments and their metabolites.
- Any other Ehrlich reagent
False negative results:
- Formaldehyde (>200 mg/dL), a urine preservative.
- Improper storage, leading to oxidation of urobilinogen to urobilin.
Note:
- The urine dipstick is not sensitive enough to check for abnormally low levels.
- The specific recommendations of the urine test manufacturer should be followed to ensure accurate and reliable interpretation of results.
◉ Treatment
The treatment of abnormal urobilinogen levels depends on the underlying cause of this abnormality (treatment of anemia, limitation of alcohol consumption, surgery of the bile ducts, etc.). If urobilinogen levels are high or low, it is important to see your doctor to assess the situation and determine the appropriate treatment plan.