Summary :
◉ What is a Kidney Infection ?
A kidney infection, also known as pyelonephritis, is an inflammation of the renal pelvis and kidneys.
Although the urinary system is designed to keep bacteria out, kidney infection often occurs as a complication of an ascending urinary tract infection that spreads from the bladder to the kidney parenchyma.
Symptoms may be different in children and older adults than in other people where it typically presents as a triad of:
- Fever
- Pain in the flank
- Nausea or vomiting
Pyelonephritis can be acute or chronic, simple or complicated, affect one or both kidneys. If not treated properly, the infection can cause lasting damage to the kidneys or spread through the bloodstream and cause a dangerous infection.
It is important to distinguish between cystitis (bladder infection), complicated and uncomplicated pyelonephritis, as the management and condition of the patient depend on this.
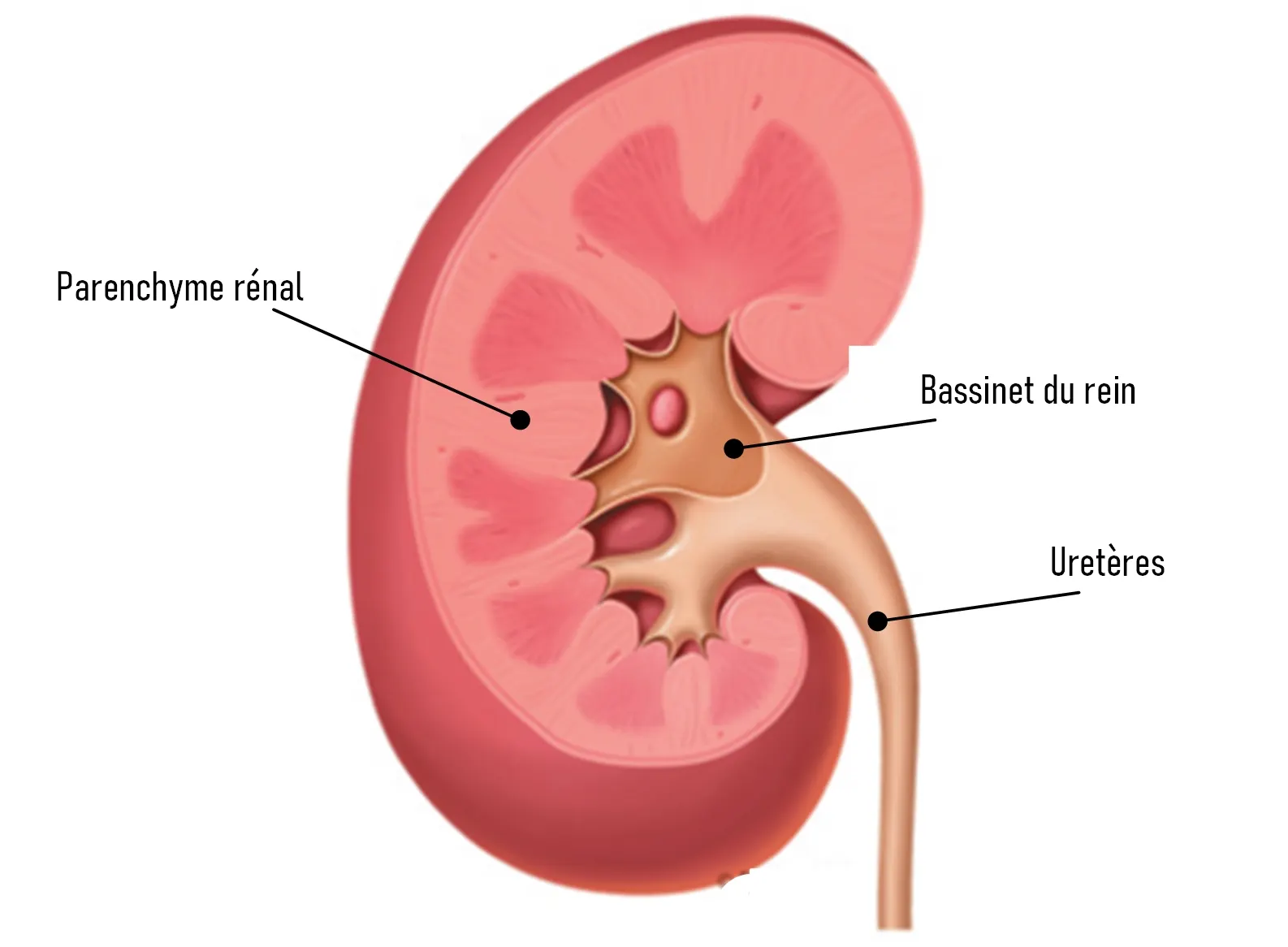
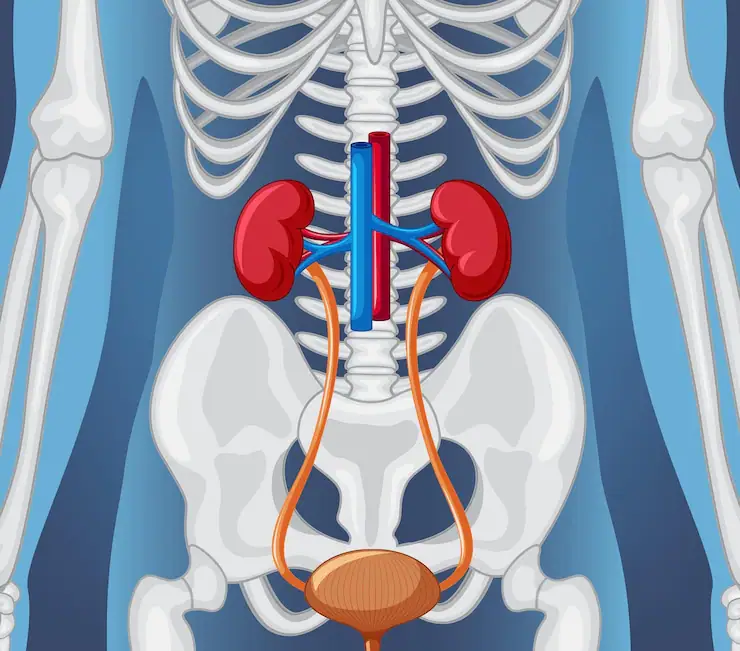
◉ Where are the kidneys located ?
The urinary tract consists of two kidneys, two ureters, a bladder and a urethra.
The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs, each the size of a fist. They are located near the middle of the back, just below the rib cage, one on each side of the spine.
◉ kidney infection symptoms
The spectrum of kidney infection is broad, ranging from mild disease to septic syndrome. Symptoms can vary depending on a person's age and can include the following:
- Fever
- Chills
- Back, side (under the ribs) and groin pain (usually unilateral over the affected kidney).
- Nausea and/or vomiting.
- Blood in the urine (haematuria), occurs in 30-40% of women.
- Pus or blood in the urine, cloudy or bad-smelling urine.
- A burning sensation or pain when urinating
- Abdominal muscle spasm
The classic manifestations of acute pyelonephritis seen in adults are often absent in children, especially newborns and infants:
- Newborns: no fever but poor feeding and vomiting.
- Children under 2 years old may only have a high fever without urinary tract symptoms.
Elderly patients may present with typical manifestations of pyelonephritis, or they may experience the following:
- Change in mental state
- Signs of confusion or confused speech
- Decompensation in another organ system
- Abdominal pain in the area of the bladder.
- General deterioration
- Some patients will appear sick and uncomfortable, while others may appear healthy
Note :
- Pelvic or perineal pain in men may suggest accompanying prostatitis.
- Confusion is common among older people and is often their only symptom.
- Symptoms of cystitis are often but not universally present.
◉ Causes of kidney infection
Although many bacteria and viruses can cause pyelonephritis, the bacterium Escherichia coli is often the cause.
Bacteria that enter the urinary tract through the urethra can multiply and travel to your kidneys. It is the most common cause of kidney infections.
Bacteria can also reach the kidney via the bloodstream (Ex: bacteremia or Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis). Hematogenous spread is less common and usually occurs in patients with chronic diseases and those receiving immunosuppressive therapy.
Metastatic staphylococcal or fungal infections can spread to the kidney from distant foci in bone or skin.
Rarely, kidney infection occurs after kidney surgery.
◉ Risk factors
Factors that increase the risk of developing a kidney infection include:
- Any problem that interrupts the normal flow of urine: urinary tract of unusual size or shape, enlarged prostate, vesicoureteral reflux...
- Being a woman: Women's urethras are much shorter than men's, so it's easier for bacteria to enter their bodies.
- Having a weakened immune system: diabetes, HIV, cancer, certain medications.
- Pregnancy
- Nerve or spinal cord damage.
- Urinary tract surgery
- Using urinary catheter (Foley catheter).
- Cystoscopic examination
⮜ Kidney infection : Symptoms and causes Kidney infection : Diagnosis and Treatment