Summary :
What type of antibiotic is fosfomycin ?
Fosfomycin is a broad-spectrum bactericidal antibiotic that interferes with cell wall synthesis in Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. It was first isolated in 1969 under the name “phosphonomycin” from colonies of Streptomyces fradiae.
The oral form of fosfomycin is often indicated for the treatment of acute uncomplicated infections of the lower urinary tract (acute cystitis ) in women. The intravenous form is available in some countries and is used for more serious infections in combination with other antibiotics.
This antibiotic still remains the only representative of its own family.
Presentation
Fosfomycin currently exists in two galenic forms :
- The injectable route in the form of disodium salt (Fosfocine®): vial of 1 and 4 g, to be diluted in an ampoule of solvent before administration by slow venous infusion.
- The oral route in the form of trometamol salt (Monuril®, Monurol®): 3 g sachets of fosfomycin reserved for the single-dose treatment of uncomplicated urinary tract infections.
Mechanism of action of fosfomycin
Fosfomycin is effective against bacteria by inhibiting the early stages of cell wall assembly:
- It enters the bacterium by active transport via sugar transporters located in the cytoplasmic membrane.
- It acts by inhibiting the enzyme MurA (UDP-N-acetylglucosamine enolpyruvyl transferase) by structural analogy with its substrate PEP (phospho-enolpyruvate). This inhibition is irreversible and dose-dependent.
- MurA is an enzyme responsible for catalyzing the formation of N-acetylmuramic acid, a precursor of peptidoglycan, by the binding of N-acetylglucosamine and phosphoenolpyruvate, causing bacterial lysis
Pharmacokinetics
Intravenous fosfomycin disodium
Has great tissue diffusibility thanks to its small size, solubility, low degree of ionization and protein binding. Half-life = 2h with urinary elimination in active form.
Fosfomycin trometamol
Significant oral absorption=70%. Half-life = 3-5h with urinary elimination in active form.
Indications and Dosages
Intravenous fosfomycin: (Fosfocine®)
Always in combination, intravenous fosfomycin indicated in the treatment of nosocomial staphylococcal infections: meningeal, ventricular or osteo-articular with CTX in post-neurosurgical meningitis with fluoroquinolones in osteo-articular infections. With a cephalosporin, a penem or an aminoglycoside, in severe Enterobacteriaceae (serratia) or P.aeruginosa infections .
Used in 2nd line in the treatment of acute meningitis caused by S.pneumoniae with decreased sensitivity to penicillin and enterococcal infections vanco-R.
According to CA-SFM :
- 4 g intravenously every 8 to 6 hours in infusions over 30 minutes to 4 hours
Oral fosfomycin dose
Cet antibiotique est utilisé dans le traitement des cystites sans signe de gravité chez la femme et l'adolescent.
According to CA-SFM :
- Simple cystitis: 3 g per os in a single dose.
- Cystitis with risk of complication: 3 g per os on D1, D3 and D5.
Fosfomycin side effects
In addition to its necessary effects, this medicine may cause side effects:
- Itchy vagina or genital area
- Pain during sex
- Thick, white vaginal discharge without odor or with a slight odor
- Headache, back pain, dizziness,
- Diarrhea, nausea, upset stomach
- Stuffy nose, sore throat,
Contraindication
Monuril® is contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to this drug or to any ingredient in the formulation, including any non-medicinal ingredient (such as flavorings that contain sulfites), or component of the container.
Activity spectrum
Due to its mechanism of action, fosfomycina has a broad spectrum of action both on gram-positive bacteria and also on gram-negative bacilli.
Among gram-negative bacteria, fosfomycin is active against the vast majority of enterobacteriaceae (except Morganella morganii), Nesseiria meningitidis, N. gonorrhoeae, Pasteurella spp and pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Other non-fermentative BGNs (including Acinetobacter spp. and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia), as well as anaerobic bacteria are naturally resistant.
Among gram-positive bacteria, fosfomycin is active against Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis (irrespective of their resistance to methicillin), pneumococcus and enterococci (Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium), regardless of their resistance to methicillin phenotype. vancomycin. Its activity is inconstant against streptococci.
◉ Natural resistance to fosfomycin
- Certain gram-positive bacteria including: Listeria monocytogenes, Corynebacterium urealyticum and jeikeium, Staphylococcus capitis and Staphylococcus saprophyticus
- Some gram-negative bacteria: Leclercia adecarboxylata, Acinetobacter baumannii-calcoaceticus complex, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, Ochrobactrum Anthrop and Burkholderia cepacia.
- Strict anaerobes (except Fusobacterium spp.)
Mechanisms of resistance
The mechanisms of resistance of fosfomycin include:
- Reduced intracellular transport of the antibiotic (mutations of the transporter glpT or uhpT and cAMP regulatory genes).
- Change in target due to mutations or alterations in murA expression.
- Direct inactivation of the antibiotic by metalloenzymes (fosA, fosB and fosX), transmissible and frequently found in enterobacteriaceae ESBL and carriers of carbapenemases, in particular Escherichia coli.
- Inactivation of the antibiotic by kinases (formA and formB).
Testing the sensitivity of fosfomycin in the laboratory
The reference method for determining the MIC of fosfomycin is the method of dilution in agar medium (the MICs must be determined in the presence of glucose-6-phosphate, at a rate of 25 mg/L in the medium).
It involves the use of a 200 μg fosfomycin disk containing 50 μg of glucose-6-phosphate.
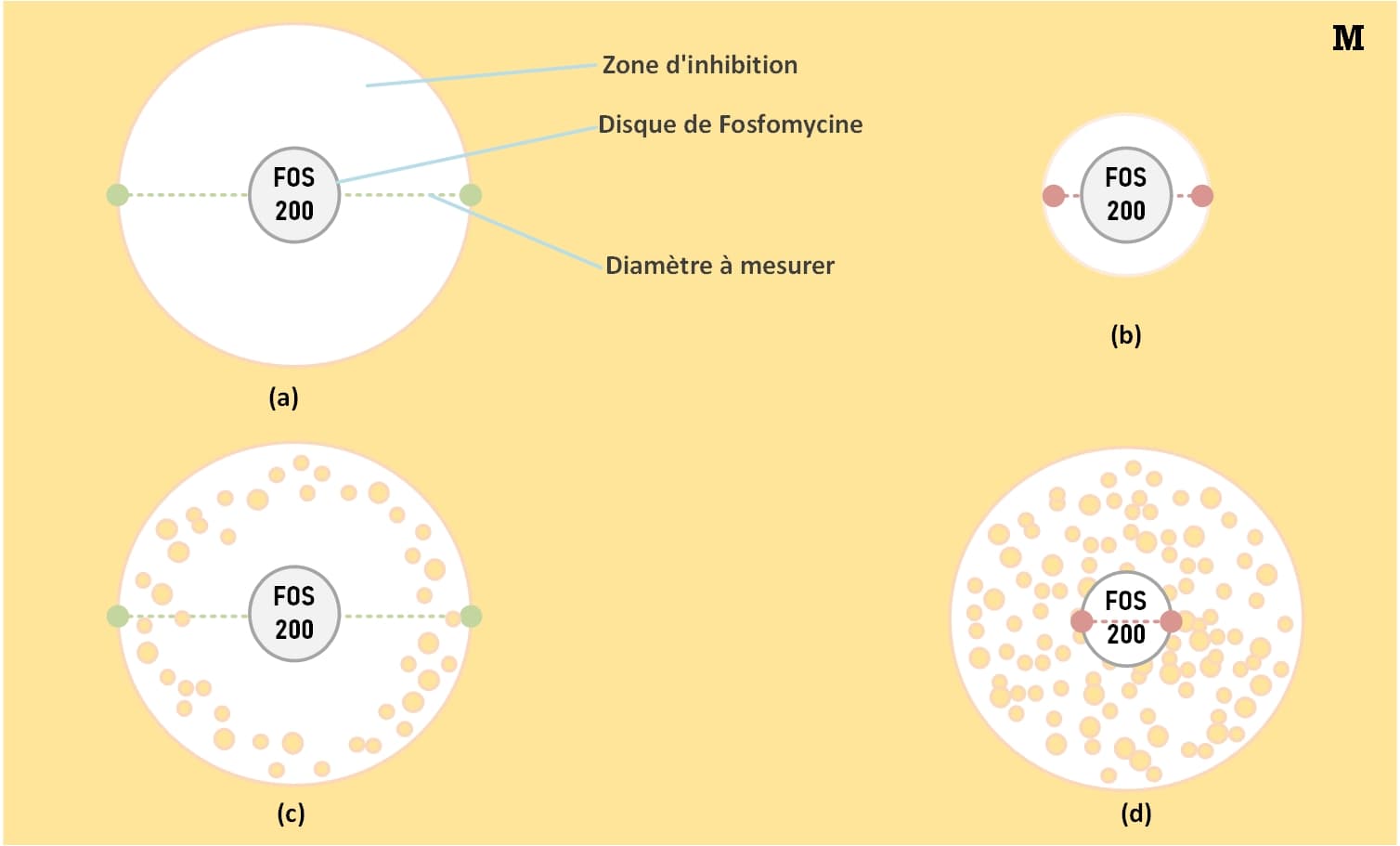
- (a): Susceptible strain (∅ measured ≥ D(CCinf)).
- (b): Resistant strain (∅ measured < d(CCsup)).
- (c): Susceptible strain. According to EUCAST: Acquired resistance to fosfomycin is homogeneous, ignore the presence of colonies in the zone of inhibition and read the diameter at the outer rim.
- (d): No zone of inhibition.