Summary :
Leukocytes in Urine, or leukocyturia, are usually a sign of a urinary tract infection. This article provides an overview of leukocyturia, including its causes, symptoms, and diagnostic tests.
◉ Definition
Leukocytes are white blood cells that help your body fight germs. When you have more than usual in your urine (called leukocyturia), it's often a sign of a urinary tract infection (UTI) or other underlying inflammatory issues.
Leukocytes in urine can be detected by a simple urine test. This test consists of analyzing a sample of your urine under a microscope or with chemical reactive strips (urine test strip or dipstick).
The presence of leukocytes in the urine is associated with various conditions, it is important to consult your doctor to help you determine the underlying cause and provide appropriate treatment.
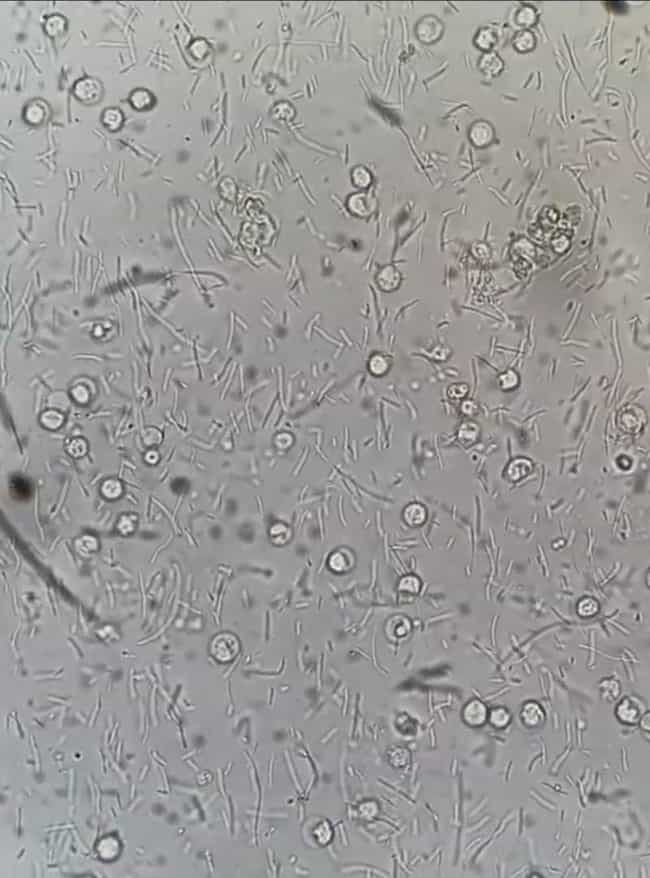
Many white blood cells in a urine sample
◉ Why are there leucocytes in urine?
The presence of a certain low number of leukocytes or a slight increase in their number should not alarm us. In most cases, this is a minor health issue.
Although a high number of white blood cells in the urine is generally associated with the presence of a urinary tract infection, it is important to note that there are other potential causes for this condition. .
1. Leukocyturia due to urinary tract infections
This is the first thing you think of if there are a lot of leukocytes in the urine (more than 10,000 per ml of urine). Whenever you have a urinary tract infection (Cystitis, Kidney infection, etc.), your immune system ramps up the production of these cells to fight bacteria.
It is also possible to have leukocytes in the urine and to suffer from symptoms of bacterial infection without such an infection being demonstrated. This phenomenon is called aseptic leukocyturia (ex: STI, decapitated urinary tract infection, viral UI, fungal UI, tuberculosis, etc.).
2. Lithiasis or urinary stones
Are accumulations of minerals and salts in your kidneys, can cause leukocytes to appear in your urine
3. Glomerulonephritis
This is when the filters of the kidneys (glomeruli) become inflamed and scarred. High levels of white blood cells in the urine are typical in glomerulonephritis.
4. Leukocyturia due to interstitial cystitis
Interstitial cystitis, known as painful bladder syndrome, is chronic pain, pressure, or discomfort in the area of the bladder.
5. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
SLE is an autoimmune disease that can cause inflammation in various parts of the body, including the kidneys and urinary tract.
6. Certain tumors
Like prostate, bladder or kidney cancer
7. Leukocyturia due to certain blood disorders
Sickle cell disease can cause increased white blood cells in the urine due to kidney damage or infection, which are common complications of the disease.
8. Use of certain medications
Certain antibiotics, such as penicillin and cephalosporins, aspirin, corticosteroids, diuretics and certain chemotherapy drugs can cause inflammation of the urinary tract, which can lead to the presence of leukocytes in the urine.
9. Other causes of leukocyturia
Cystinuria, urinary retention, urinary catheter, certain autoimmune diseases, leukocytes can also arise from sites of inflammation other than the urinary tract, particularly the female genital tract.
◉ What are the symptoms of leukocyturia?
The white blood cells in the urine by themselves may not cause any symptoms. However, leukocyturia is often associated with an underlying condition, which can cause symptoms:
- urinary tract infection can cause symptoms such as painful urination, frequent urination, strong urge to urinate, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and pelvic pain.
- Kidney stones can cause symptoms such as severe pain in the back or side (renal colic), nausea and vomiting, and blood in the urine.
- Retention of urine can weaken the bladder and accumulation of urine increases the risk of bacterial infection.
◉ How to detect leukocytes in urine?
White blood cells in urine can be detected by a simple urine test in which a sample of your urine is analyzed for the presence of white blood cells or other abnormalities.
You will be asked to provide a clean urine sample, which will be analyzed in the laboratory using a microscope, dipstick or automated analyzer.
1. To collect a clean urine sample:
- Wash your hands thoroughly and then your genital area with soap and water.
- Start urinating into the toilet, then stop and place the sterile collection container under your urine stream.
- Collect at least 30 milliliters of urine in the container, then finish urinating in the toilet.
- Close the container tightly and bring it promptly to your lab.
2. Leukocyturia detection by dipstick :
A test strip usually contains a series of reagent pads that can detect various substances in urine, including leukocyte esterase.
A leukocyte esterase is a protease-like enzyme present in leukocytes, detection of this enzyme indicates the presence of leukocytes.

Note : Although dipstick tests can be a useful screening tool, they are not always accurate and can produce false positive or false negative results.
3. Detection of leukocyturia under the microscope:
The sample is usually prepared by centrifuging the urine to concentrate any cells present before placing a small amount between slide and coverslip.
The slide is examined under the microscope directly or after staining, using bright field or phase contrast microscopy.
4. Automatic Urine Analyzer:
The automated urine analyzer can detect and quantify the number of leukocytes in urine, as well as other substances (proteins, glucose and ketones). Some analyzers can also identify the types of leukocytes present, such as neutrophils or eosinophils.
◉ Treatment
If leukocytes are detected in your urine, your health care provider may recommend additional tests to determine the underlying cause (urine analysis, CT scans, ultrasounds, etc.)
Treatment for leukocyturia depends on the cause of the condition. If a bacterial infection causes leukocyturia, treatment usually involves a course of antibiotics.
If the cause is non-infectious such as kidney stones or interstitial cystitis, treatment may include pain management and lifestyle changes, increasing fluid intake, avoiding certain foods or beverages that irritate the bladder.
If cancer is the culprit, additional treatments may be needed: Surgery, chemotherapy or radiotherapy.