Content :
◉ Overview
As early as 1889, the indole test was used as a means of distinguishing between Escherichia coli and Enterobacter aerogenes , the test looks for the ability of an organism to degrade tryptophan and produce indole, Indole production is demonstrated by the addition of Kovac's reagent which acts with the indole giving a red color.
◉ Principe of indole test
● The indole test determines the ability of an organism to produce indole from the breakdown of the amino acid tryptophan. Tryptophan is hydrolyzed by tryptophanase to produce three possible products: indole, pyruvate and ammonium ion :
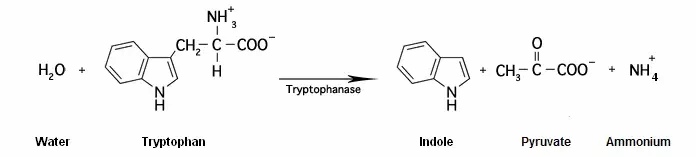
Indole test reaction
● Detection of indole is based on the chemical reaction between indole and Kovac's reagent (isoamyl alcohol, para-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde, concentrated hydrochloric acid) under acidic conditions:
- Para-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde reacts with the indole present in the medium to form a rosindole red dye.
- Isoamyl alcohol forms a complex with the "rosindole" dye, causing it to precipitate.
- The remaining alcohol and the precipitate then rise to the surface of the medium.
◉ Procedure and results
◍ Two methods are described:
- Tube method : the conventional method which identifies weak indole producing organisms after overnight incubation.
- Spot indole test : detects organisms that produce indole quickly.
1- Conventional tube method
The main requirement for a suitable indole test medium is that it contains a sufficient amount of tryptophan (Tryptone broth, indole-free peptone water medium, Urea-indole medium, Tryptophan peptone broth, Sulfide-indole motility medium ( SIM) ...).
- Inoculate the tryptophan (or peptone) broth with the organism to be tested and incubate at 37 ° C for 24 to 48 hours.
- Add 0.5 ml (5 drops) of Kovác's reagent and shake gently.
- Examine the top layer of liquid after about 1 min.
◉ Results : A positive result is indicated by the presence of a red or red-violet color in the alcohol layer on the surface of the broth. A negative result appears in yellow. A variable result may also occur, displaying an orange color as a result. This is due to the presence of skatole, also known as methyl indole or methylated indole, another possible breakdown product of tryptophan.
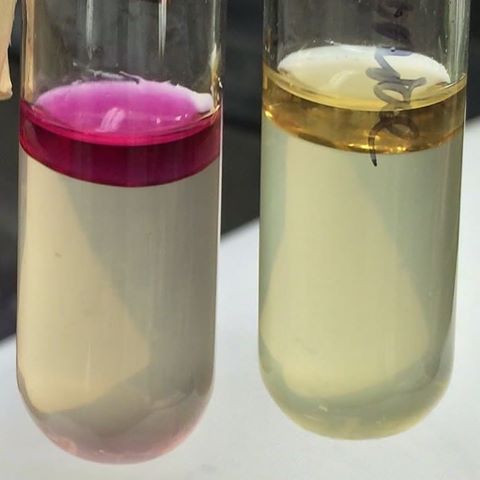

Indole positive and negative test
2- Spot test
- Place several drops (1 -1.5 ml) of Indole Spot reagent (1% or 5% p-methylaminobenzaldehyde or 1% p-dimethylaminocinnamaledhyde) on a piece of filter paper.
- Spread an isolated pure colony (from an 18-24 hour culture) on the saturated surface of the filter paper using a sterile loop.
- Examine immediately
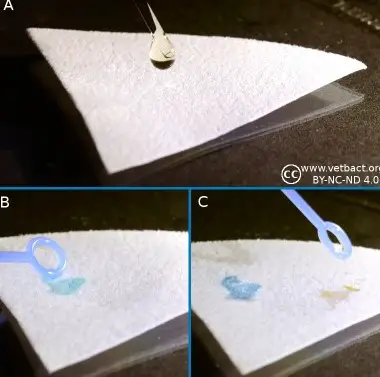
Indole Spot test
◉ Result : Depending on the reagent used for the indole spot test, the resulting colors differ. If you are using p-methylaminobenzaledhyde the presence of indole is indicated by a red color and if you are using p-dimethylaminocinnamaledhyde a blue-green color is observed.
◉ Indole test positive and negative
◍ Indole positive and negative bacteria (9, 10, 11) |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | Indole positive | Variable indole | Indole negative | ||||||
| Escherichia spp. | Escherichia coli , Escherichia fergusonii | / | Escherichia albertii | ||||||
| Shigella spp. | / | Shigella boydii , Shigella dysenteriae , Shigella flexneri | Shigella sonnei | ||||||
| Salmonella spp. | / | / | Salmonella spp. | ||||||
| Klebsiella spp. | K. oxytoca | / | klebsiella pneumoniae | ||||||
| Raoultella spp. | R. ornithinolytica | R. planticola | R. terrigena | ||||||
| Serratia spp. | / | S. odorifera biogroup 1, S. odorifera biogroup 2 | S. entomophila, S. ficaria, S. fonticola, S. liquefaciens group, S. marcescens, S. plymuthica, S. rubidaea | ||||||
| Citrobacter spp. | C. amalonaticus, C. farmeri, C. koseri, C. murliniae, | C. braakii ,C. freundii , C. sedlakii, C. youngae | C. gillenii , C. werkmanii | ||||||
| Edwardsiella tarda | Edwardsiella tarda | / | / | ||||||
| Proteus | P. hauseri , P. vulgaris | / | Proteus mirabilis , P. penneri | ||||||
| Providencia | P. stuartii , P. rettgeri , P. rustigianii , P. alcalifaciens | / | P. heimbachae | ||||||
| Morganella | M. morganii | / | / | ||||||
| Yersinia spp. | / | Y. enterocolitica | Y. pestis , Y. pseudotuberculosis | ||||||
| Bacilles à Gram négatif non fermentaire | Elizabethkingia ,Chryseobacterium , Balneatrix, Bergeyella, Empedobacter, Wautersiella, Weeksella | / | Acinetobacter , Moraxella, Paracoccus, Sphingobacterium, Shewanella, Rhizobium, Ochrobactrum, Psychrobacter, Sphingomonas, Pseudochrobactrum | ||||||
| Actinobacillus spp | / | / | A. lignieresii, A. equuli , A. suis, A. ureae, A. hominis | ||||||
| Actinobacillus spp | / | / | A. lignieresii, A. equuli , A. suis, A. ureae, A. hominis | ||||||
| Aggregatibacter spp | / | / | A. actinomycetemcomitans , A. aphrophilus, A. segnis | ||||||
| Capnocytophaga spp | / | / | C. ochracea , C. sputigena, C. gingivalis, C. granulosa, C. haemolytica, C. canimorsus, C. cynodegmi | ||||||
| Cardiobacterium spp | C. hominis (faible) | C. valvarum | / | ||||||
| Chromobacterium spp | / | C. violaceum | C. haemolyticum | ||||||
| Dysgonomonas spp | D. hofstadii , D. mossii | D. capnocytophagoides , D. gadei | / | ||||||
| Eikenella spp | / | / | E. corrodens | ||||||
| Kingella spp | / | / | K. kingae , K. denitrificans, K. negevensis, K. oralis , K. potus | ||||||
| Pasteurella spp | P. multocida , P. canis , P. dagmatis , P. oralis , P. stomatis | / | / | ||||||
| Streptobacillus spp | / | / | S. moniliformis | ||||||
| Suttonella spp | S. indologenes | / | / | ||||||
| Haemophilus influenzae | Biotype I II V VII | / | Biotype III IV VI VIII | ||||||
| Actinomyces spp. | / | / | Actinomyces spp. | ||||||
| Bacteroides spp. | B. ovatus , B. thetaiotaomicron | / | B. fragilis , B. vulgatus | ||||||
| Fusobacterium spp. | F. necrophorum , F. nucleatum | F. varium | F. mortiferum | ||||||
| Clostridium spp. | C. sordellii , | C. tetani | C. tertium , C. septicum, C. ramosum, C. perfringens, C. innocuum, Clostridium botulinum | ||||||
◉ Limits and technical advice
- The tube test is more sensitive than the Spot test.
- Ehrlich's reagent is an alternative to Kovács's reagent, Ehrlich is more sensitive while Kovács is more stable
- Media containing glucose should not be used for indole testing due to the formation of acidic end products which reduce indole production. Mueller Hinton Agar should also not be used for this test because tryptophan is destroyed during the acid hydrolysis of casein.
- If peptone broth is used instead of tryptophan broth, the batch should be checked with a positive control. This is because there are varieties of peptone broths, and some are not suitable for indole production because they contain too little tryptophan.
- The organisms to be tested by the indole spot method must be collected in a medium containing tryptophan (for example blood agar) and never in MacConkey agar because they have pH indicators and pigmentation of lactose-positive colonies which will make the interpretation of the color reaction difficult.
- Indole is a diffusible product. To attenuate indole scattering, select a well-isolated colony for the indole spot test.