Content :
The Widal test, also referred to as the Widal agglutination test, is a serological test used for a presumptive diagnosis of typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever, which are caused by certain bacteria named Salmonella. In this article, we will explore its principle, procedures, and how to interpret the test results.
◉ Definition
A Widal test is a blood test that detects the presence of antibodies against the bacteria that cause typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever. These bacteria are Salmonella Typhi and Salmonella Paratyphi A and B.
Typhoid fever, also known as enteric fever, is typically spread through contaminated food and drinks. It causes symptoms like high fever, tiredness, headache, stomach pain, and diarrhea, and it can be a very serious illness.
The test is based on the principle of agglutination, which means the clumping of bacteria and antibodies together by detecting specific antibodies produced by the immune system in response to antigens present in Salmonella bacteria.
The Widal test is simple and inexpensive; however, it suffers from a lack of standardization, poor specificity, and inappropriate interpretation of results, especially in endemic areas. Therefore, test results should be interpreted carefully and in conjunction with other clinical and laboratory findings
◉ Who should get the Widal test?
The Widal test is indicated for patients who have a:
- History of fever for more than five days.
- Gastrointestinal symptoms.
- Have no response to empirical antibiotic treatment.
- Have clinical signs and symptoms suggestive of typhoid fever (fever, diarrhea, red spots on the body, etc.).
- Have no other obvious focus of infection.
◉ Principle
The patient's immune system reacts to a Salmonella bacterial infection by generating antibodies against the bacteria. These antibodies aim to neutralize the infection, typically becoming detectable in the blood approximately 6 days after the infection starts.
- Antibodies against flagellar antigen of Salmonella typhi (H).
- Antibodies against flagellar antigen of S.paratyphi A (AH).
- Antibodies against flagellar antigen of S.paratyphi B (BH).
- Antibodies against somatic antigen of S.typhi (O).
The Widal test works by checking these specific Salmonella antibodies in the patient's serum using prepared Salmonella antigens (commercially available reagents).
- Positive result is indicated by the presence of agglutination.
- Absence of agglutination indicates a negative result.
Note:
- A negative result does not rule out a diagnosis of salmonellosis
- The paratyphoid O antigens are not employed as they cross react with the typhoid O antigen.
◉ Reagents
Test kit contains the following reagents
- Reagent 1: S.typhi (H), contains the H antigen from Salmonella typh.
- Reagent 2: S.typhi (O), contains the O antigen from Salmonella typh.
- Reagent 3: S.paratyphi A (AH), contains the H antigen from Salmonella paratyphi A.
- Reagent 4: S.paratyphi B (BH), contains the H antigen from Salmonella paratyphi B.
- Negative control (NC): This control sample does not contain antibodies to Salmonella typhi and is used as a reference to validate the test results. It should not produce a positive reaction.
- Positive control (PC): It is used to ensure that the test is functioning correctly and should produce a positive reaction.
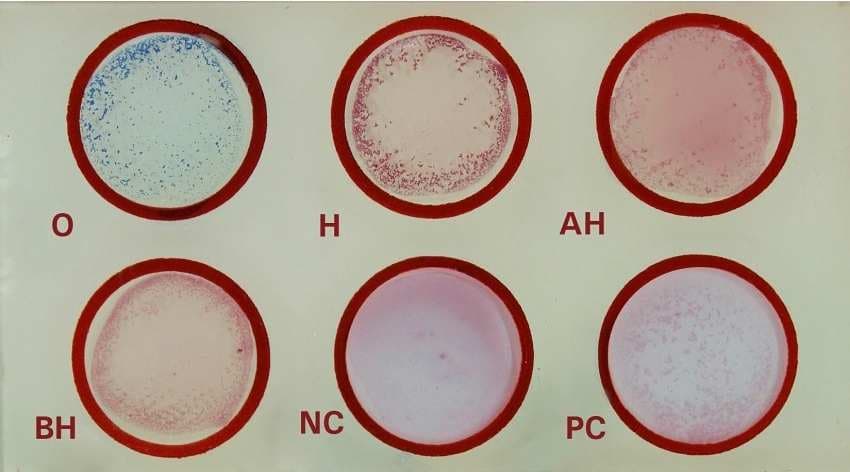
◉ What are the preparations for performing a Widal test?
There is no specific preparation required for the Widal blood test. However, your healthcare provider may advise you to avoid certain medications, certain foods or strenuous activity in the hours leading up to the test.
◉ Types and methods of WIDAL test
The Widal test can be conducted either on a slide or in a tube and can be either qualitative or quantitative, depending on the specific testing protocol and the medical requirements
- Widal Slide Method: A drop of the patient's serum is mixed with the antigens on the slide, and the reaction is observed for agglutination (clumping).
- Widal Tube Method: The tube agglutination test is conducted in small test tubes and offers more accuracy compared to the slide agglutination technique.
- Qualitative test: It is conducted on a slide for screening purposes, determining whether antibodies against specific Salmonella antigens are present or absent in the patient's serum and does not provide specific antibody concentration levels.
- Quantitative Testing: This is performed for samples that showed positive agglutination in the qualitative test. The antibody titers (concentration) in the patient's serum are determined.
◉ Procedures of the Widal test
◉ 1. Widal Slide Method
- Collect a blood sample from the patient and let it clot.
- After the clot has formed, centrifuge the sample to separate the serum from the cells.
- Place a drop of the serum on a clean glass slide and label it with the patient's name and the date.
- Add a drop of antigen solution (containing killed Salmonella typhi and Salmonella paratyphi) to the serum drop.
- Mix the two drops using a clean toothpick or glass rod, making sure they are thoroughly combined.
- Rotate the slide slowly for 4 minutes to allow agglutination to occur.
- Examine the slide under a microscope at 40x magnification to look for agglutination. The clumping of the bacteria indicates a positive result.
◉ 2. Widal Tube Method
- Collect a blood sample from the patient and let it clot.
- After the clot has formed, centrifuge the sample to separate the serum from the cells.
- Label 4 test tubes with the patient's name and the date.
- Add a different dilution of the antigen solution to each of the test tubes.
- Add a fixed amount of the patient's serum to each test tube.
- Combine the contents of each test tube thoroughly.
- Incubate the test tubes at 37°C for 24 hours.
- Examine the test tubes for agglutination. The clumping of the bacteria indicates a positive result.
◉ Normal result of Widal test
The result of the test is reported as a ratio of the highest dilution of the patient's blood that gives a positive reaction. For example, a result of 1:160 for O antigen means that the patient's blood had to be diluted 160 times before no clumping was observed.
The normal result for the Widal test varies slightly from lab to lab, but generally, the titres of O and H antigens should be less than 1:160 to be considered negative. Titres above 1:160 to 1:320 or beyond are considered positive and indicate the presence of typhoid or paratyphoid.
◉ Interpretations of the results
The interpretation of the Widal test can vary based on the type of test (qualitative or quantitative), antibody levels, disease progression, the patient's symptoms, and the results of other tests.
◉ 1. Antibody titre
S. Typhi interpretation:
- Negative result: S. Typhi titer is smaller than or equal to 1:80.
- Positive result: S. Typhi titer is more than or equal to 1:160
S. Paratyphi interpretation
- Negative result: S. Paratyphi titer is smaller than or equal to 1:80.
- Positive result: S. Paratyphi titer is more than or equal to 1:160.
◉ 2. Disease progression
- The O antibodies appear earlier and disappear faster than the H antibodies. The H antibodies appear later and persist longer than the O antibodies.
- If anti-O antibodies are detected at a high level without the presence of anti-H antibodies, this indicates a recent infection.
- An isolated increase in anti-H antibodies suggests a long-standing Salmonella infection.
- The presence of anti-H antibodies directed against S. Typhi, Paratyphi A and B indicates previous vaccination.
- For an accurate diagnosis, two blood samples should be taken 15 days apart.
◉ 3. Test limitations
There are some limitations and challenges in interpreting the Widal test results, such as:
- Previous typhoid vaccination may lead to an incorrect positive outcome.
- Cross-reactivity with other anfections (Typhus, immunological disorders or chronic liver disease).
- Variation in antibody levels among different populations.
- Tests done within 7 days of illness and after 4 weeks are usually negative.
- Operator-dependent test.
The Widal test results need to be interpreted carefully and in conjunction with other clinical and laboratory findings.
◉ Related tests
In addition to the Widal test, several other diagnostic tests are commonly used to diagnose typhoid and paratyphoid fever and differentiate them from other febrile illnesses. Some of the commonly used diagnostic tests include:
- Blood culture: Blood culture consists of taking venous blood, which is then cultured to look for microorganisms. It is considered the gold standard for diagnosing typhoid and paratyphoid fever
- Stool culture: Stool culture is performed to isolate Salmonella typhi and Salmonella Paratyphi from fecal samples. Although it have lower sensitivity compared to blood cultures, they can be useful for detecting carriers of the bacteria.
- Bone marrow culture: Bone marrow culture is a highly sensitive test for diagnosing typhoid and paratyphoid fever, especially in cases where blood and stool cultures are negative or inconclusive.
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR): such as Typhoid/paratyphoid (TPT) assay, PCR is a molecular diagnostic technique that can detect the genetic material (DNA) directly from clinical specimens.
- Serological tests: such as (ELISA-Ty test), are available for detecting specific antibodies against Salmonella typhi and Salmonella Paratyphi in the patient's serum. These tests measure the presence of IgM and IgG antibodies and can be helpful in detecting recent infections.
◉ Conclusion
In summary, the Widal test is a serological test used to detect antibodies against Salmonella typhi and Salmonella paratyphi in the blood. It aids in the diagnosis and monitoring of typhoid and paratyphoid fever cases, complementing other clinical findings.
While the test has its limitations, it plays a significant role in the management and surveillance of these infectious diseases