Contents:
Chapman Agar | Composition | Reading
◉ General Information
Chapman Agar or Mannitol Salt Agar is a selective medium used for the isolation, enumeration, and differentiation of Staphylococcus from clinical, food, antiseptic, and cosmetic samples.
This medium is both a selective and differential agar. It selects organisms that can survive in high salt (sodium chloride) concentrations, while mannitol fermentation—indicated by a yellow color change due to the pH indicator (phenol red)—helps guide diagnosis.

Chapman Agar (@lablife)
◉ Principle
◈ The selectivity of this medium is based on sodium chloride (7.5%), which inhibits most Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria.
◈ The differentiation is based on the ability to ferment mannitol (the only sugar in the medium). Fermentation causes acidification, leading to a yellow color change (at pH < 6.9) in the presence of phenol red (pH indicator).
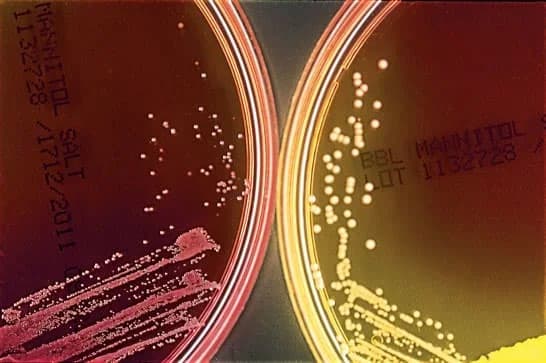
Coagulase-negative Staphylococcus (left) and S. aureus (right) were inoculated on the agar and incubated overnight.(8)
Note:
- In clinical samples, mannitol-positive isolates are suggestive of Staphylococcus aureus and should undergo further testing.
- Non-fermenting bacteria that resist high salt concentrations produce a red-to-pink zone due to peptone degradation.
◉ Preparation / Composition of Chapman Agar
☰ For 1 liter of medium:
Composition of Chapman Agar |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ingredients | grams/liter | ||
| Peptone | 10 g | ||
| Beef extract | 1 g | ||
| Sodium chloride | 75g | ||
| Mannitol | 10g | ||
| Phenol red | 0.025g | ||
| Agar | 15g | ||
| Final pH | 7.4 ± 0.2 | ||

Dehydrated Chapman Agar
Preparation of Dehydrated Medium
Add 111 grams of dehydrated medium to 1 liter of sterile distilled water. Mix until a homogeneous suspension is obtained. Heat slowly while stirring frequently, then bring to a boil until completely dissolved. Sterilize in an autoclave at 121°C for 15 minutes. Dispense into Petri dishes or flasks.
Prepared Medium
Melt the contents of the flask in a water bath at 100°C (with the cap partially loosened) until fully dissolved. Tighten the cap and check the homogeneity of the dissolved medium by inverting the flask. Cool to 45-50°C, mix well (avoiding foam formation), and pour aseptically into Petri dishes.

Prepared Chapman Agar
◉ Interpretation
Staphylococcus aureus forms luxuriant, pigmented colonies surrounded by a yellow halo due to mannitol fermentation. Non-pathogenic staphylococci typically form small red colonies that do not alter the medium's color.
Note: The color change indicates mannitol fermentation, NOT colony color. This is particularly important as many Micrococcus species are pigmented.
Several Staphylococcus species other than S. aureus are mannitol-positive, producing yellow colonies with yellow zones (e.g., S. capitis, S. xylosus, S. cohnii, S. sciuri, S. simulans). Therefore, additional biochemical tests are needed to confirm S. aureus or other species.
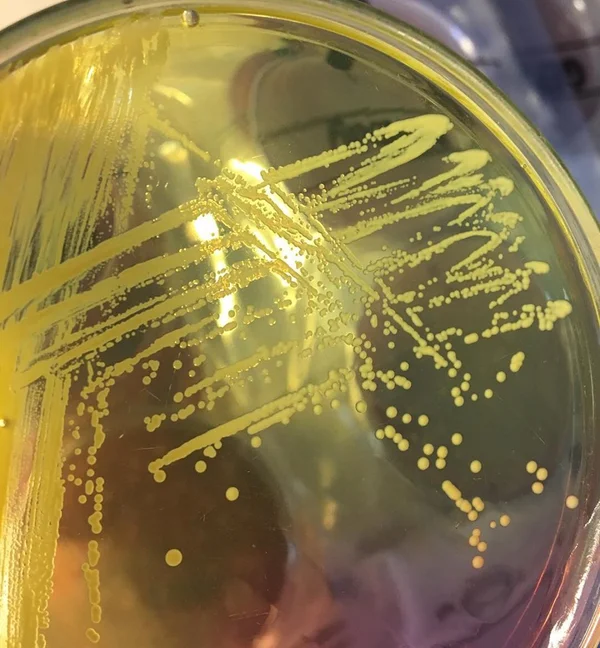
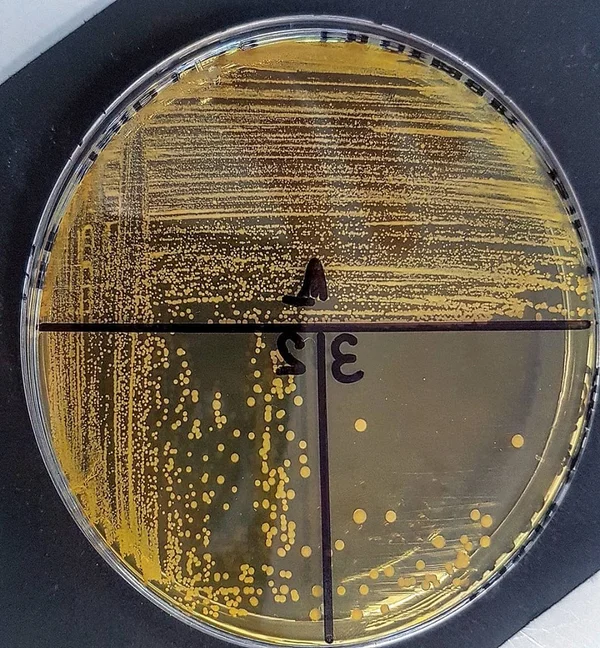
Chapman Agar with oxacillin can be used to screen for MRSA in nasal samples, as the 7.5% salt and 6 µg/mL oxacillin inhibit most other organisms that normally colonize the nostrils.
Adding 5% v/v egg yolk emulsion allows detection of staphylococcal lipase activity alongside mannitol fermentation. The salt clarifies the egg yolk emulsion, and lipase production appears as a yellow opaque zone around colonies.
Note:- Other genera like Micrococcus luteus and Micrococcus roseus produce yellow and pink colonies, respectively.
- Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium are also salt-tolerant and may ferment mannitol, producing yellow colonies.
- Group D streptococci can grow on this medium and show slight mannitol fermentation. However, their colonies are small and can be differentiated from staphylococci by Gram stain or catalase testing.
- Inoculated plates stored in the refrigerator may lose color over time.