🏾 Definition
Rheumatoid factor is an abnormal protein produced by the immune system (immunoglobulin type igM), which has antibody activity that is mistakenly directed against healthy cells and tissues in the body (autoantibodies).
The RF test is a blood test that measures the amount of rheumatoid factors in the blood. It is most often used in conjunction with other tests (Anti CCP, VS, CRP..) when rheumatoid arthritis is suspected.
Despite its name, rheumatoid factor is not unique to rheumatoid arthritis, the test lacks specificity (65-85%) and sensitivity (60-80%), and many other diseases can have high levels of the factor rheumatoid.
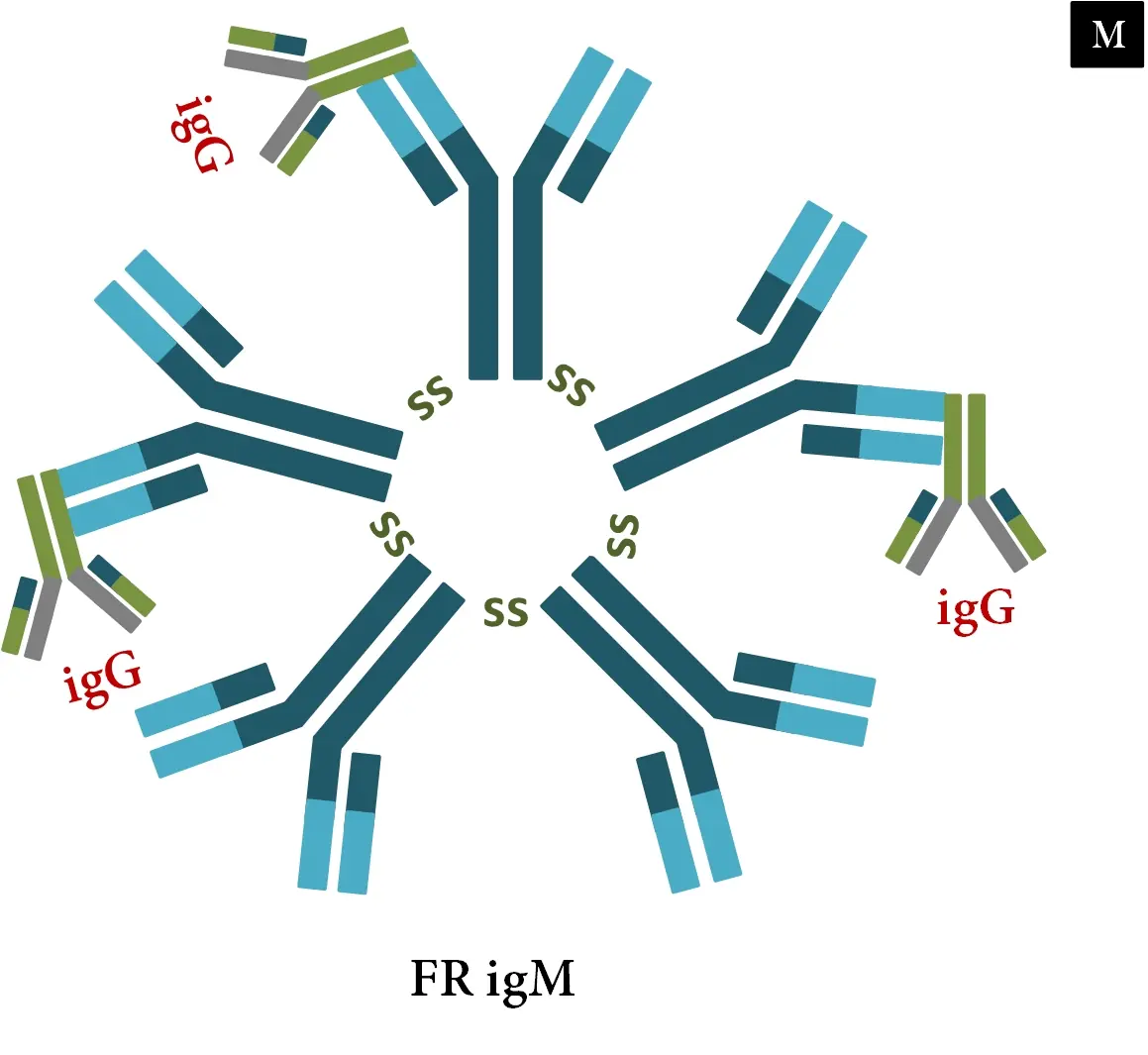
Rheumatoid factor igM
🏾 Rheumatoid factor normal range
The laboratory must report quantitative values expressed in IU/ml. A positive/negative result is of little importance.
Although "normal" rheumatoid factor values may vary from one technique to another, it is generally accepted that values >20 IU/ml are considered high.
🏾 Rheumatoid factor blood test
In general, there are no special preparations to make before the test, it is a routine blood test that can be done at any time and does not require fasting, unless your blood sample will be used for additional tests (e.g. blood sugar).
A healthcare professional will take a sample of blood from a vein in your arm, using a small needle.
🏾 Interpretation
High rheumatoid factor
High levels of rheumatoid factor in the blood are most commonly associated with autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and Sjogren's syndrome. But :
- Rheumatoid factor can be detected in some healthy people, about 5% of people without RA will have an abnormal value.
- People with autoimmune diseases sometimes have normal levels of rheumatoid factor, about 20% of people with confirmed RA will not have an abnormal value.
There are several causes of high rheumatoid factor levels: Certain types of cancer, including leukemia, mononucleosis, tuberculosis, inflammatory lung diseases, such as sarcoidosis, mixed connective tissue disease, Sjogren's syndrome, lupus, juvenile arthritis , scleroderma, hepatitis C, etc.
Note: Rheumatoid factor assay also has a prognostic value. A high level of rheumatoid factor greater than three times the laboratory positive threshold is a sign of a poor prognosis.
Low rheumatoid factor
A negative result does not exclude the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatoid factor may decrease or even become negative during the course of the disease after initiation of treatment
🏾 Assay techniques
Waaler-Rose reaction : agglutination of sheep red blood cells, or ORh– human red blood cells, sensitized with rabbit IgG.
Latex reaction : agglutination of latex particles coated with human IgG.
Immunoenzymatic methods : They are based on the principle of ELISA or dot, depending on whether the human and/or animal IgGs have been fixed to the bottom of the microtiter plate well or to a membrane. The revelation is done with an anti-IgM antiglobulin marked by an enzyme.
Nephelometric method : binding of RF to polystyrene particles sensitized by human or human and animal ã-globulins, or to aggregated ã-globulins: the intensity of the scattered light is measured by nephelemetry, it is proportional to the concentration of EN in serum
🏾 What other tests could I have with this test ?
- CRP - C-Reactive Protein : inflammation marker.
- Antinuclear Antibody Test : Measures autoantibodies attacking your cells. This is important in the diagnosis of certain autoimmune diseases.
- Sedimentation Rate (ESR) : inflammation marker.