Content :
◉ what is HCT blood test?
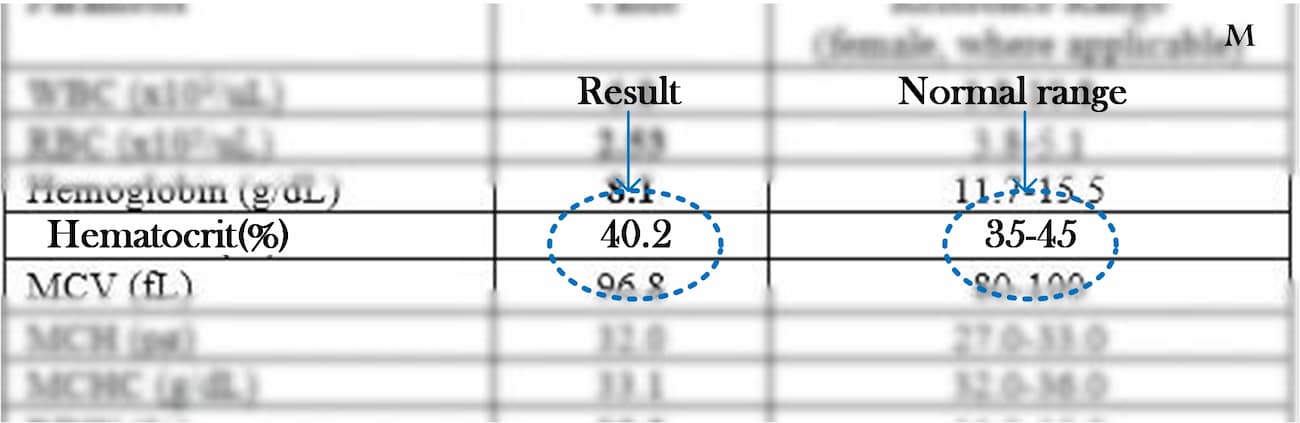
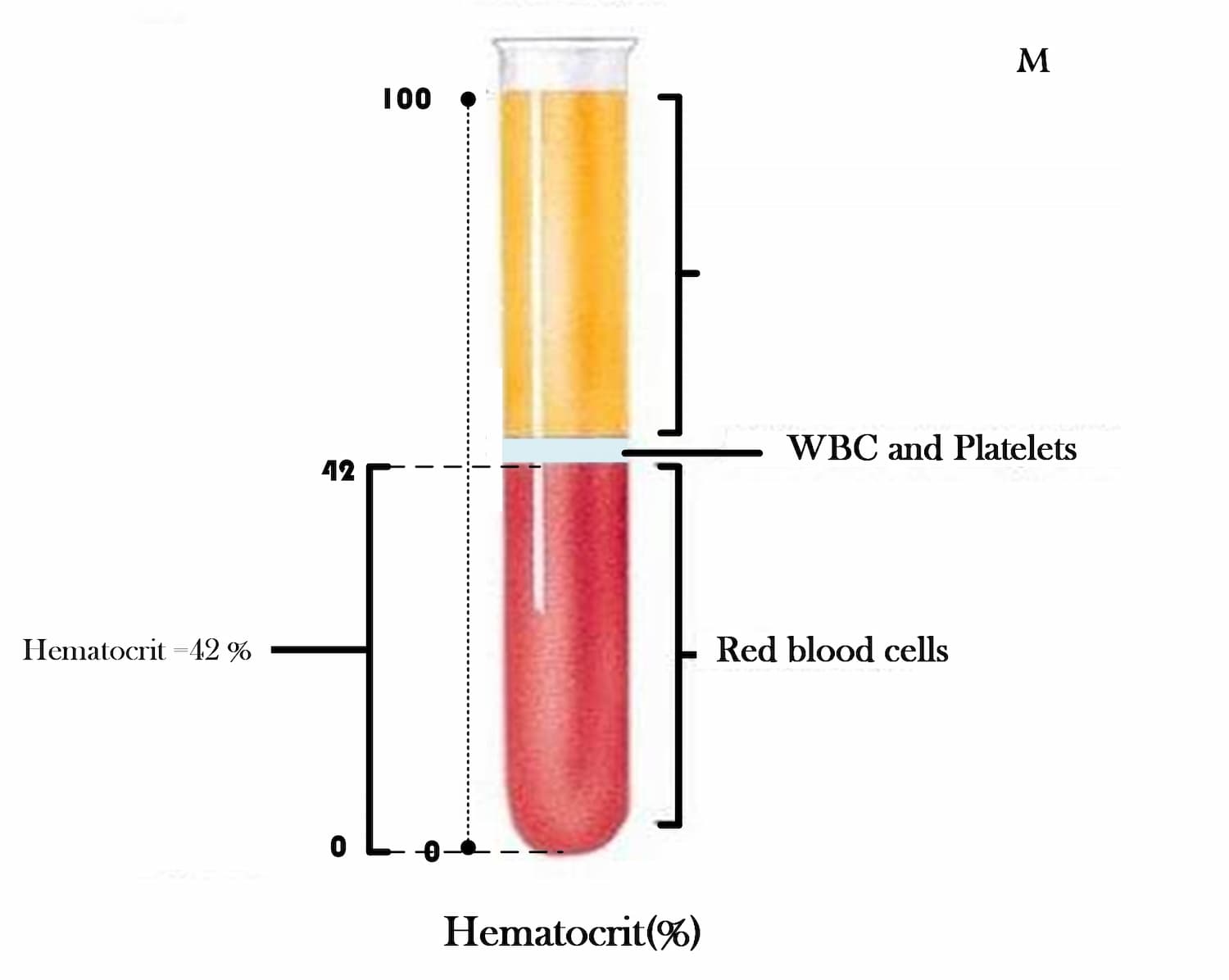
Hematocrit (Ht or HCT) refers to the proportion of red blood cells in the total volume of blood, typically expressed as a percentage.
Hematocrit measurement provides valuable information about the overall blood composition and can help diagnose and monitor various medical conditions.
- A low hematocrit can indicate anemia, which is a condition where you have too few red blood cells.
- A high hematocrit can indicate dehydration, polycythemia, which is a disorder that causes your body to produce too many red blood cells.
To put it simply, when you have a hematocrit of 45%, it means that in 100 ml of blood drawn, there are 45 ml of red blood cells.
◉ Other names
There are other names for the hematocrit, such as:
- PCV: Packed cell volume.
- VPRC: Volume of packed red cells.
- EVF: Erythrocyte volume fraction
◉ Why I need HCT test?
The HCT test is usually done as part of a complete blood count (CBC), which also measures other types of blood cells and hemoglobin levels. Your health care provider may recommend this test at following cases:
- Fatigue, poor health, or unexplained weight loss.
- Headaches.
- Assessing Dehydration and Poor nutrition.
- Problems concentrating.
- Monitoring of anemia and its cause.
- Monitoring during treatment for cancer.
- Leukemia or other problems in the bone marrow.
- Chronic medical problems, such as kidney disease or certain types of arthritis.
- During pregnancy.
- Heavy menstrual periods.
- Blood in your stools, or vomit.
- Monitoring Erythropoietic Therapy, such as treatment with erythropoietin or iron supplementation.
- Before and after major surgery.
◉ Preparation and blood sampling
- To prepare for an hematocrit blood test, you don't need any special preparations or fasting. You just need to give a small sample of blood from a finger prick or a vein in your arm.
- Venous blood sample collected in EDTA (1.5 mg EDTA for 1ml of blood) will be sent to a laboratory for evaluation using a centrifuge (machine that spins the blood at a high speed to separate the red blood cells from the plasma).
- Note: Test should be performed within 6 hours of collection.
◉ Normal range of HCT
As it is a ratio, it doesn't have any unit. Multiplying the ratio by 100 gives the accurate value, which is the accepted reporting style for hematocrit. Here are normal hematocrit levels by sex and age:
- Adult males: 41% to 50%
- Adult females: 36% to 44%.
- Infants: 32% to 42%
- Newborns: 45% to 61%
◉ High levels of HCT blood test
◉ 1. Causes of High HCT Levels
- Polycythemia: This is a rare bone marrow disorder characterized by the overproduction of red blood cells. It is usually caused by a mutation in the JAK2 gene.
- Too little water in the body (dehydration)
- Lung or heart disease: These diseases can reduce the amount of oxygen in your blood, which may stimulate your body to produce more red blood cells.
- Anabolic androgenic steroids use: These drugs can increase the production of red blood cells and hemoglobin, which can raise your hematocrit level.
- Erythropoietin-secreting tumors: Some tumors, such as renal cell carcinoma, may produce excess erythropoietin, a hormone that stimulates RBC production.
◉ 2. Symptoms of High HCT Levels
The symptoms associated with elevated hematocrit levels can vary depending on the underlying cause.
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Itchy or flushed skin
- Enlarged spleen (splenomegaly)
- Blurred vision
Note: If you have symptoms that may be linked to a HCT level, it's advisable to reach out to your healthcare provider.
◉ Low levels of HCT blood test
Low hematocrit levels, can be a sign of anemia and can be caused by various factors and medical conditions.
◉ 1. Causes of Low HCT Levels
- Iron Deficiency Anemia.
- Vitamin Deficiency Anemia(Vitamin B12 and folic acid).
- Chronic bleeding.
- Cancer: These cancers spread to bone marrow, such as leukemia and lymphoma.
- Bone marrow disorder: This includes aplastic anemia, which damages stem cells in bone marrow.
- Chronic Diseases: such as chronic kidney disease, inflammatory bowel disease, or cancer, can interfere with the production or lifespan of red blood cells.
- Hemolytic Anemia: This type of anemia occurs when red blood cells are destroyed prematurely, either due to inherited conditions, autoimmune disorders, or certain medications.
◉ 2. Symptoms of Low HCT Levels
The symptoms experienced by individuals with low HCT levels can vary depending on the underlying cause and the severity of anemia. Common symptoms include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Pale skin or mucous membranes
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Dizziness
- Cold hands and feet
- Headaches
- Brittle nails
◉ Related analytical tests
Some other related tests to HCT test are:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): This test provides a comprehensive analysis of different components of blood, including red blood cells count, white blood cells count, and platelets count.
- Reticulocyte count: This blood test determines how well your bone marrow (the spongy tissue inside bones) makes red blood cells.
- Iron studies: A group of blood tests, these are interpreted together to check for iron deficiency or iron overload (hemochromatosis).
- Vitamin B12 and folate levels: these tests to see if you have enough of the nutrients needed to create blood cells.
- Erythropoietin (EPO) Test: EPO is a hormone produced by the kidneys that stimulates the production of red blood cells.
- Blood smear: This small blood sample is examined under a microscope for signs of problems.
◉ Conclusion
The HCT blood test is a fundamental component of diagnostic evaluations in medicine, providing valuable insights into a patient's blood composition and overall health. It assists healthcare professionals in diagnosing and monitoring various conditions, optimizing treatment plans, and assessing patient eligibility for certain interventions.
By incorporating the hematocrit test into routine clinical practice, healthcare providers can enhance patient care, improve outcomes, and contribute to the overall well-being of individual