Summary :
MPV, Mean Platelet Volume, is a blood test that measures the average size of platelets in the bloodstream. Learn about the definition of MPV, the test procedure, normal and abnormal results, and other blood tests that aid in diagnosis.
◉ Definition
MPV blood test refers to the average size of platelets in a blood sample. Platelets are tiny blood components produced in the bone marrow and contribute to the formation of blood clots to prevent excessive bleeding.
A normal MPV is 8 to 12 femtoliters, the specific reference range can vary slightly between different laboratories and healthcare institutions.
The Mean Platelet Volume is calculated by measuring the volume occupied by platelets in a blood sample, providing, in conjunction with other platelet-related parameters such as Platelet Distribution Width (PDW) and Immature Platelet Fraction (IPF), insights into their health and functioning
◉ Why is the MPV Test Performed ?
The MPV blood test is typically conducted as part of a Complete blood count (CBC) to assess various components of the blood, including platelets. A CBC is a routine test ordered during annual physical exams or when evaluating specific symptoms.
- This test is a valuable tool for diagnosing bleeding disorders and diseases associated with the bone marrow.
- Additionally, it aids in assessing various blood-related conditions, providing essential insights into their severity.
- A platelet count test is often conducted in conjunction with the MPV test, which measures the total number of platelets in the blood.
◉ Preparation for Mean Platelet Volume test
- Typically, no specific preparations are required for an MPV blood test.
- However, if other blood work is done alongside, the healthcare provider may advise fasting for several hours before the test.
- It is crucial to follow any instructions provided by your healthcare professional
◉ MPV Test steps
Performing the MPV test involves the following steps:
- Blood Sample Collection : A healthcare professional will collect a blood sample from a vein in the arm using a needle. This process is known as venipuncture.
- Laboratory Analysis : The collected blood sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
- Platelet Size Measurement : In the laboratory, the mean platelet volume is calculated by determining the average size of the platelets in the blood sample.
- Result Interpretation : The laboratory will provide the MPV test result, which a healthcare provider will evaluate to assess platelet health and potential underlying conditions.
◉ Interpreting the MPV Test results
The significance of MPV blood test results is essential in assessing your overall health. Here, we outline the normal range and discuss both high and low MPV rates, along with their potential causes:
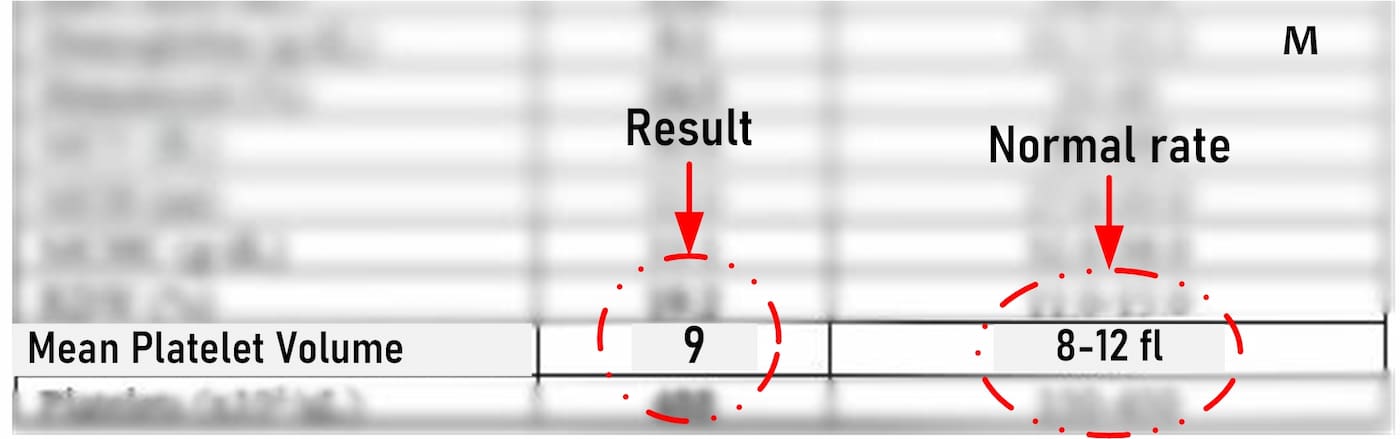
◉ Normal MPV Result
- The normal range for MPV can vary slightly depending on the laboratory and specific testing methods.
- In general, a standard MPV value falls within the range of 8 to 12 fL (femtoliters) for non-pregnant adults.
- However, it's crucial to remember that MPV results should be interpreted in conjunction with other relevant blood tests and clinical evaluations.
CBC (Complete Blood Count)
◉ High MPV : Meaning and Causes
A high mean platelet volume value suggests an increase in platelet size. It can indicate various conditions or underlying causes, including:
- Essential thrombocythemia : the bone marrow produces an excessive number of platelets. Mutations in specific genes such as JAK2 and CALR may cause this condition.
- Cancers : certain types of cancer can cause elevated MPV, such as lung cancer, ovarian cancer, endometrial cancer, colon cancer, kidney cancer, stomach cancer, pancreatic cancer, and breast cancer.
- Inflammation : Chronic inflammation can contribute to increased MPV levels.
- Bone Marrow Disorders : Conditions affecting the bone marrow, such as myeloproliferative disorders, can lead to more giant platelets and elevated MPV levels.
- Vitamin B12 or Folate Deficiency : Inadequate levels of these essential nutrients can result in larger platelets and increased MPV.
- Medications : Some medications, including certain antiplatelet drugs, can affect platelet size and increase MPV levels.
It's important to note that high MPV levels alone do not provide a definitive diagnosis. Further investigations and consultations with a healthcare professional are necessary to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
◉ Low MPV: Meaning and Causes
Conversely, a low mean platelet volume rate indicates a smaller platelet size. Several factors can contribute to low MPV, including:
- Decreased Platelet Production: Certain bone marrow disorders or conditions, such as aplastic anemia, can reduce platelet production, resulting in smaller platelets and lower MPV levels.
- Increased Platelet Destruction: Conditions like immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) can cause increased platelet destruction, leading to smaller platelets and decreased MPV levels.
- Genetic Disorders: Rare genetic disorders, such as Bernard-Soulier syndrome or May-Hegglin anomaly, can result in smaller platelets and lower MPV values.
As with high MPV, low MPV levels alone do not provide a definitive diagnosis. A comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional is crucial to determine the underlying cause and appropriate management
◉ Other Blood Tests for Diagnosis
While the mean platelet volume test provides valuable insights into platelet health, additional blood tests can complement the diagnostic process. Some relevant blood tests include:
- Platelet Count test: A platelet count measures the total number of platelets in the blood and helps evaluate platelet-related disorders.
- Platelet Distribution Width (PDW): PDW measures the variation in platelet size and provides complementary information about platelet characteristics.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): A CBC test assesses various blood components, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. It helps detect different blood-related conditions, providing a comprehensive overview of blood health.
- Immature Platelet Fraction (IPF): Reflects megakaryopoiesis (the process that results in the production of platelets).
These blood tests collectively assist healthcare providers in diagnosing various conditions, such as thrombocytopenia and thrombocytosis, and determine the appropriate treatment plans. The results of the mean platelet volume blood test should always be interpreted in conjunction with other blood test results and the patient's clinical presentation.
◉ Conclusion
The mean platelet volume test is valuable for evaluating platelet health and diagnosing potential blood disorders and bone marrow conditions. By measuring the average size of platelets, the MPV test aids healthcare providers in identifying abnormal platelet characteristics and determining appropriate treatment strategies.
A high Mean Platelet Volume may indicate primary or secondary thrombocytosis, while a low Mean Platelet Volume could be associated with thrombocytopenia or bleeding disorders.
However, MPV results should be interpreted alongside other blood tests and clinical evaluations to achieve an accurate diagnosis. Regular consultations with healthcare professionals are essential to fully understand and address potential concerns related to MPV levels and platelet health.