Content :
CBC blood test is a group of tests that evaluate cells circulating in the blood. In this article, we will explore in detail the key components of the complete blood count and their importance to our health.
◉ What is CBC blood test?
The complete blood count (CBC), also known as hemogarm, is a blood test commonly performed in medical practice. It provides valuable information about a patient's general health status and can be used to identify abnormalities indicative of underlying pathologies.
This test analyzes the different types of blood cells, including red blood cells (RBC), white blood cells (WBC) and platelets (PLT), as well as other parameters such as hemoglobin and hematocrit.
CBC results may vary depending on a variety of factors, including the patient's age, gender, general health, medical history, and medications taken. The test should be interpreted by a healthcare professional, taking into account the patient's overall clinical context.
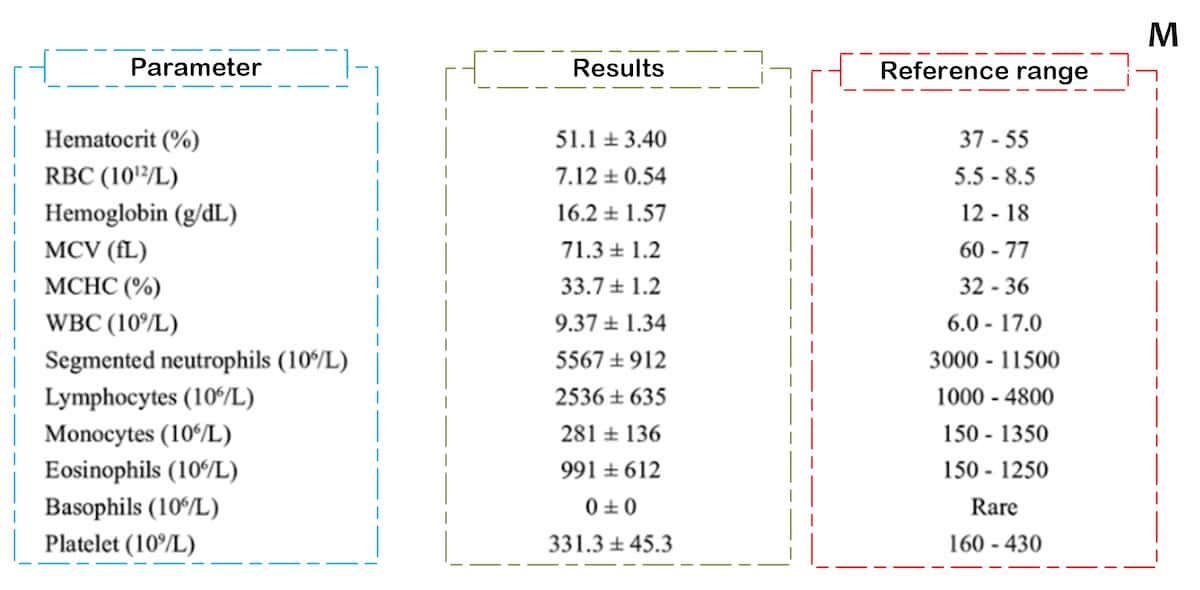
CBC (Complete Blood Count)
◉ What are the components of blood?
Blood includes many living cells that carry nutrients, hormones, vitamins, antibodies, heat, and oxygen to body tissues through the circulatory system (heart, arteries, and veins). Blood components can be classified into three main categories: blood cells, plasma and serum:
• Blood Cells
Blood cells are the cellular components of blood and include red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
- Red blood cells (erythrocytes or red blood cells): make up the majority of blood cells and contain hemoglobin, a protein that binds and transports oxygen and dioxide of carbon and gives the blood the color red.
- White blood cells (leukocytes): there are several types and they are mainly involved in the immune response to identify and eliminate pathogens (bacteria, viruses, etc.).
- Platelets (thrombocytes): are small fragments of cells involved in blood clotting to prevent excessive bleeding when blood vessels are damaged.
• Plasma and Serum
Plasma is the liquid component of blood and accounts for approximately 55% of total blood volume. It is a yellowish liquid essential for: transporting nutrients, maintaining water balance, eliminating waste and preventing infections
When blood clots, it forms a gel-like substance and the remaining liquid is called serum (similar to plasma but does not contain the clotting factors).
◉ CBC Parameters
The complete blood count measures various parameters related to the components of your blood. Here are the main parameters of the CBC:
- Red Blood Cell Count (RBC): measures the total number of red blood cells in the blood, providing information about oxygen-carrying capacity.
- Hemoglobin level.
- Hematocrit (HCT): represents the percentage of the blood that is composed of red blood cells.
- Mean corpuscular volume (MCV): measures the average size of red blood cells.
- Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration (MCHC).
- Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH): measures the average amount of hemoglobin per red blood cell.
- Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW): indicates the variation in size of red blood cells.
- White Blood Cell Count (WBC): measures the total number of white blood cells in the blood and helps assess the body's immune system.
- Polynuclear neutrophils (PN)
- Polynuclear eosinophils (PE)
- Polynuclear basophils (PB)
- Lymphocytes (LY)
- Monocytes (MO)
- Platelet Count: measures the number of platelets in the blood and is important for blood clotting.
- Mean platelet volume (MPV): MPV is a measure of the average size of platelets in a blood sample.
- Platelet Distribution Width (PDW):PDW is a measure of the variation in platelet size in a blood sample.
◉ Why prescribe a CBC test?
You may need a CBC if you have any of the following signs:
- General Health Assessment.
- Fatigue or weakness.
- Inflammation, bruising or bleeding.
- Fever, nausea and vomiting.
- Articular pain.
- Heart rate or blood pressure problems.
- Monitoring Chronic Condition.
- Allergic Reactions Assessment.
- Routine Health Screening.
◉ What does a complete blood count detect?
A complete blood count can help the doctor determine if patients have any of the following conditions, disorders, diseases, or infections:
- Anaemia, which occurs when the body does not have enough red blood cells to carry oxygen.
- Several blood diseases such as agranulocytosis, thalassemia and sickle cell disease.
- Infections or other health problems cause the white blood cell count to be too low or too high.
- Different types of cancer, such as leukemia and lymphoma.
- Vitamin and mineral deficiencies.
- Side effects of certain medications and treatments
◉ CBC blood test preparation and blood sampling
Preparing a complete blood count is usually not necessary. If your blood sample is for CBC only, you can eat and drink as usual before the test.
Overall, the complete blood count is a simple, quick, and relatively painless procedure that provides valuable information about a person's overall health and well-being.
- An CBC is a laboratory test usually performed by a healthcare professional, such as a nurse, phlebotomist, or technician in a clinical setting.
- The procedure involves drawing a small amount of blood on an appropriate anticoagulant from a vein in the arm using a needle and a sterile collection tube.
- The blood sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis, where it is processed by automated machines that count the number of different types of blood cells present in the sample.
- CBC results are usually available within hours to days, depending on lab workload and the urgency of the test.
◉ Normal values of a complete blood count
Normal levels of complete blood count parameters may vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the patient's age, gender, and medical condition. However, here are the general normal ranges for CBC settings:
|
|
3 to 10 years |
Women |
Male |
| Red blood cells (millions/mm3) |
4.0 - 5.4 |
4.0 - 5.0 |
4.5 - 5.5 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) |
12.0 - 14.5 |
12.0 - 15.5 |
13.5 - 17.5 |
| Hematocrit (%) |
36 - 45 |
34.9 - 44.5 |
38.8 - 50 |
| MCV (µ3 or fL) |
74 - 91 |
80 - 100 |
80 - 100 |
| MCHC (pg) |
24 - 27 |
28 - 32 |
28 - 32 |
| MCH (%) |
28 - 33 |
32 - 36 |
32 - 36 |
| Leukocytes (cells/µL) |
5000 - 11000 |
4000 - 10000 |
4000 - 10000 |
| Platelets (cells/µL) |
150,000 to 450,000 |
150,000 to 450,000 |
150,000 to 450,000 |
| RDW (%) |
- |
11.5% - 14.5 |
11.5% - 14.5/p> |
| Reticulocytes (%) |
0,2 - 0,8 |
0,5 - 1,5 |
0,5 - 1,5 |
Note : These are general reference ranges and each lab may have slightly different ranges. It is always best to consult a doctor to interpret CBC results.
◉Interpretation of the complete blood count
CBC results can provide important information about a patient's health status. However, abnormalities in CBC values may indicate pathologies that require further investigation. Here are some examples of these anomalies:
- The red blood cell count and hemoglobin levels can tell if a person has anemia.
- The white blood cell count can help identify infections or inflammation (requires further testing to determine the source).
- The platelet count can help diagnose bleeding disorders.
- Hematocrit: The percentage of volume occupied by red blood cells in the blood. A decrease may indicate anemia, while an increase may be related to dehydration.
- MCV (Mean Globular Volume): The MCV classifies anemia into microcytosis (low MCV), normocytosis (normal MCV) or macrocytosis (high MCV).
- MCHC (Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration): MCHC can give additional information about the hemoglobin content of red blood cells.
- MCH (Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin ): MCH can help identify different types of anemia and assess the hemoglobin content of red blood cells.
- Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW): RDW can be used to identify anemias where red blood cells are uneven in size.
- MPV (Mean Platelet Volume): It can help assess platelet size and identify certain conditions associated with abnormalities in platelet size.
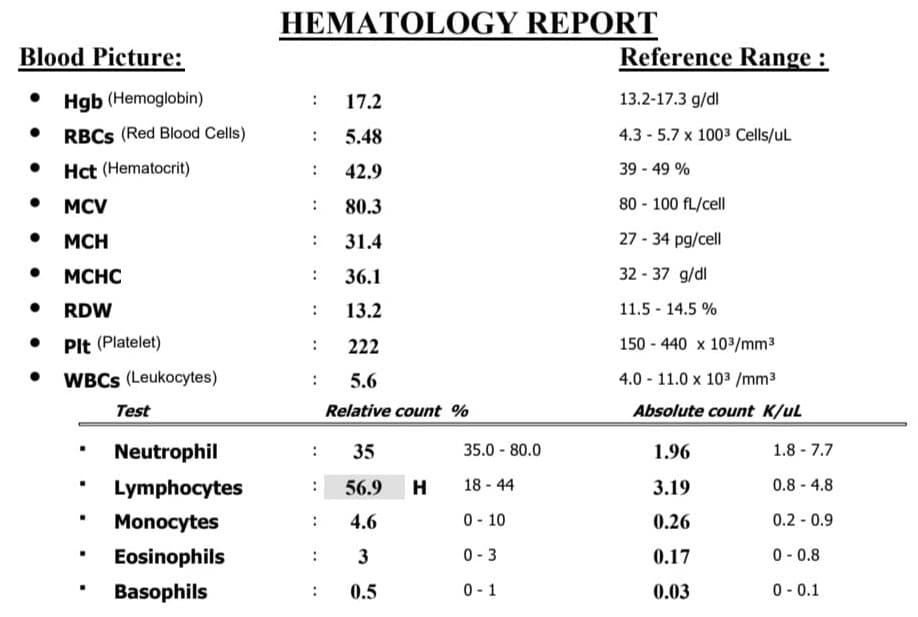
Example of CBC blood test results
◉ What are the risks of the test?
An CBC is a simple and safe test and nothing bad can happen. Rarely, some people may experience fainting or dizziness after taking the sample.
◉ Conclusion
Complete Blood Count (CBC) is a common blood test that provides essential information about the components of your blood. This test measures various parameters that offer valuable insights into your overall health and can help diagnose a wide range of medical conditions, including anemia, infections, bleeding disorders, and more.
The interpretation of CBC results plays a vital role in guiding healthcare providers when making informed choices regarding the need for additional diagnostic tests, treatment strategies, and medical interventions.