Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
Summary :
◉ what is hand foot and mouth disease
Hand Foot and Mouth Disease is a mild and highly contagious viral infection common in children under 5 years of age, but anyone can get it. to catch.
Most often, the disease is caused primarily by a Coxsackie virus that tends to spread quickly among children in day care centers and schools, summer camps, or within
the family.
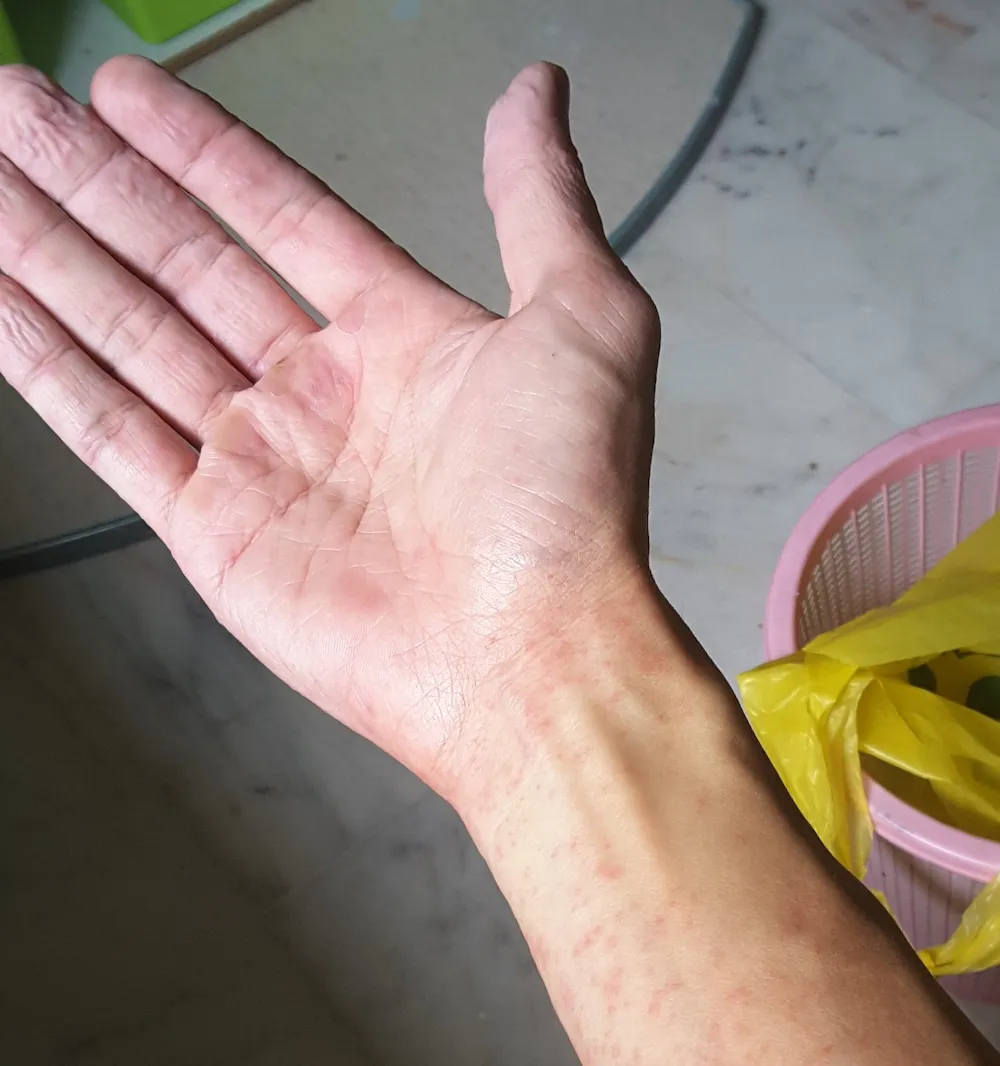
Hand Foot and Mouth Disease gets its name from the blister-like rash that forms on the hands, feet, and mouth. The diagnosis is clinical and its evolution spontaneously favorable in 8 to 10 days.
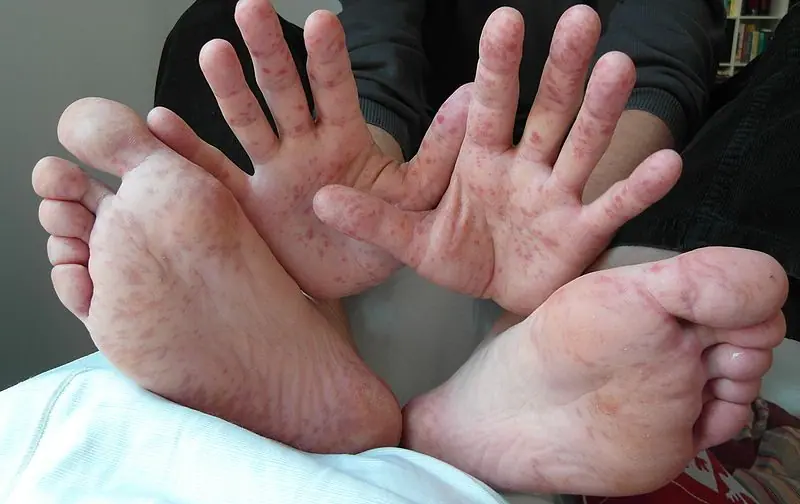
Hand Foot and Mouth Disease described in 1957 in Canada.
◉ Causes
Hand, foot and mouth disease is caused by viruses belonging to the enterovirus family.
Many strains can be responsible. Coxsackievirus A16 (CV-A16) and Enterovirus 71 (EV-71) are the two most common causes, respectively.
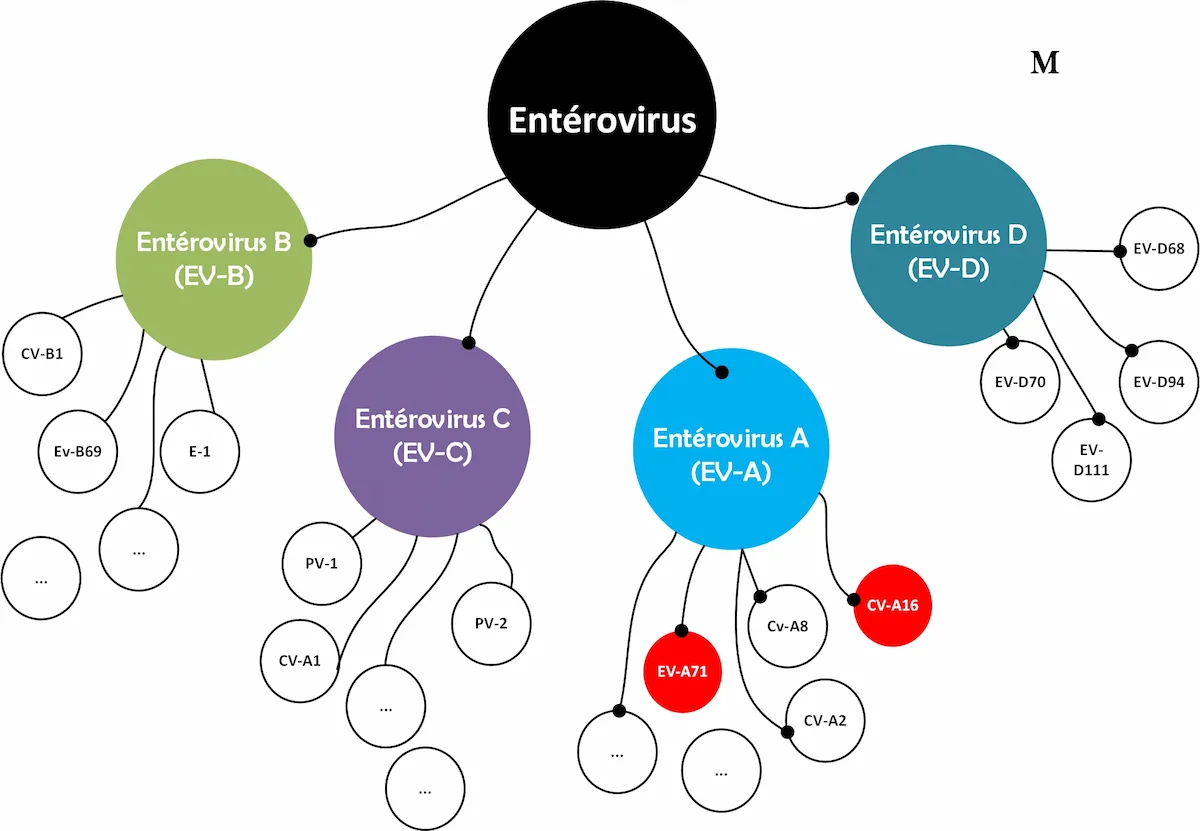
Causes of Hand Foot and Mouth Disease
◉ Hand foot and mouth disease symptoms
After incubation for 3 to 7 days, Hand, Foot and Mouth disease may begin with mild fever, sore throat, runny nose, decreased appetite and general malaise.
After a few days, these flu-like symptoms disappear and these new symptoms develop:
- Rash: on the palms of the hands, soles of the feet, knees, elbows, genitals or buttocks.
- Painful mouth sores: These sores usually start as small red spots, often on the tongue and inside the mouth
- Lack of appetite due to painful swallowing.
- Signs of dehydration
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck.
◉ Hand foot and mouth infection may also present with atypical features such as:
- Extensive vesiculobullous lesions.
- Purpuric lesions.
- A coxsackium eczema.
- A Gianotti-Crosti-like rash.
◉ Transmission
The virus spreads easily from person to person when a person comes into contact with the bodily fluids of an infected person, especially during the first week of their illness.
This can happen :
- If you touch an infected person's secretions, such as saliva, drool, or nasal mucus.
- If you touch liquid from blisters or scabs.
- If you breathe in air droplets from the infected person.
- If you kiss or hug someone infected with the virus.
- Contact with soiled stool.
- If you touch objects and surfaces infected with the virus.
- Rarely, if you swallow recreational water, such as swimming pool water.
The child can remain contagious long after the symptoms have disappeared, especially through the stools (the virus can be detected in the stools for about 6 weeks after infection).
◉ How long is hand, foot and mouth disease contagious ?
The hand-foot-mouth infection is contagious often 2 days before the appearance of the rash. The blisters usually dry up in about 10 days. You are less likely to pass it on to others once the blisters have dried.
However, the virus can live in the stool for weeks after the rash has cleared.
◉ Diagnosis
The diagnosis of hand-foot-mouth disease in its classic form is clinical.
The doctor can usually determine if a person has the condition by examining the patient and the appearance of the rash along with a basic history, age, and other symptoms.
In rare circumstances, a confirmatory diagnosis may be performed where samples of the patient's throat or feces are sent to a laboratory to test for the virus.
According to A. Mirand et al., virological diagnosis is carried out in three circumstances:
- Faced with any severe neurological or cardiorespiratory impairment.
- In front of an atypical shape.
- Epidemiologically in the event of a resurgence of neurological damage (EV-A71 virus) in the population.
◉ Treatment
There is no specific medical treatment for Hand, Foot and Mouth disease. Most people heal on their own without any complications in 7-10 days.
To ease symptoms:
- Offer fluids to prevent dehydration.
- Rinse your mouth with warm salt water.
- Offer soft foods that are easy to swallow, such as compote and mashed potatoes.
- If age permits, suck on ice cubes or popsicles.
- Avoid hot and spicy foods.
- Avoid acidic drinks, such as fruit juice.
- Paracetamol to relieve sore mouth, throat and fever.
◉ Prevention
There are no preventive measures specific to Hand-foot-mouth disease. However, the risk of infection can be reduced by adopting good hygiene practices:
- Always wash your hands: after changing diapers, after using the bathroom.
- Disinfect all common areas of your home regularly.
- Disinfect toys, pacifiers and other items that may be contaminated with the virus.
- Keep children home when they have a fever or open blisters on the skin and in the mouth.
- Avoid hugging and kissing an infected child.
- Avoid touching your eyes, nose and mouth
🏿 Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How long is the virus contagious?
A: Skin blisters from Hand-Feet infection are contagious until they become crusty and there is no more fluid in blisters. The virus can also be shed in the faeces for several weeks after the blisters have disappeared.
Q: Is there a vaccine?
A: There is no vaccine to prevent Hand-foot-mouth disease.
Q: What is the incubation time?
A: The incubation period for Foot Hand and Mouth is 3 to 7 days.
Q: What are the risks of hand, foot and mouth disease during pregnancy?
A: Although there is usually no direct risk to pregnancy or the baby, it is best to avoid close contact with anyone who has hand-foot-mouth disease.
Q: Who can get Foot Hand and Mouth infection?
A: Hand-feet mainly affects children, but adults can get it too.


