Content :
Acetic Acid : Definition, Properties, Production and Uses
Due to its versatility, availability, and relatively low cost, acetic acid has become a popular and widely used chemical compound in many aspects of our daily lives. This article provides more information about acetic acid, including its physical and chemical properties, various production methods, and wide applications in various industries.
◉ What is Acetic Acid ?
Acetic acid, also known as ethanoic acid, is a weak organic acid with the chemical formula CH3COOH. It is a colorless liquid that has a pungent odor and is commonly found in vinegar, which is usually a dilute solution of acetic acid.
It can be produced both naturally (fermentation) and synthetically. It has a role as a protein solvent, food acidity regulator, antimicrobial food preservative and in photographic chemistry.
More concentrated solutions can be found in the laboratory. Glacial Acetic Acid is a highly concentrated and pure form of acetic acid containing only traces of water (99.4% acid).
It is important to note that acetic acid can cause irritation and burns. Therefore, it should be handled with care and used at appropriate concentrations and in appropriate environments.
| CAS number | 64-19-7 |
| Product code | LC10100 |
| Formula | C2H4O2 |
| Structure | CH3COOH |
| Synonyms | Glacial acetic acid / vinegar alcohol / C2 carboxylic acid / ethanoic acid / ethyl acid / methane carboxylic acid / pyroligneous acid / vinegar acid |
Acetic acid - CH3COOH : chemical structure representation
◉ Physical properties
Acetic acid is a clear, colorless, combustible liquid with an acrid vinegar odor. The odor threshold would be between 0.21 and 1.0 parts per million (ppm). This substance is commercially available in concentrations ranging from 6% to over 99% acid, by weight.
The term "glacial" in "glacial acetic acid" refers to its ability to freeze at a relatively low temperature, usually around 16.6 degrees Celsius, forming a strong crystalline structure. The freezing temperature decreases as the water content increases.
It is miscible with water and many organic solvents, especially ethanol, diethyl ether and glycerol, insoluble in carbon disulphide.
◉ The acidity of acetic acid
The hydrogen (H) atom of the carboxyl group (–COOH) of carboxylic acids such as acetic acid can be released as the H+ ion (proton). It is the ability to release this proton that gives it its acidity. Acetic acid is a weak, mono-protonic acid in aqueous solution, with a pKa of approximately 4.8 at 25°C.
◉ Production of acetic acid
The Production of acetic acid can be carried out by two main methods: the chemical method and the fermentation method:
- Chemical Method (Synthetic): The chemical method being the predominant method in current industrial practice. Acetic acid can be produced synthetically by various methods. One of the common methods is the methanol carbonylation process, in which methanol reacts with carbon monoxide in the presence of a catalyst.
- Fermentation method: The fermentation method is mainly suitable for the generation of food grade acetic acid. This method is based on the use of microorganisms, generally acetic bacteria of the genus Acetobacter or Gluconacetobacter.
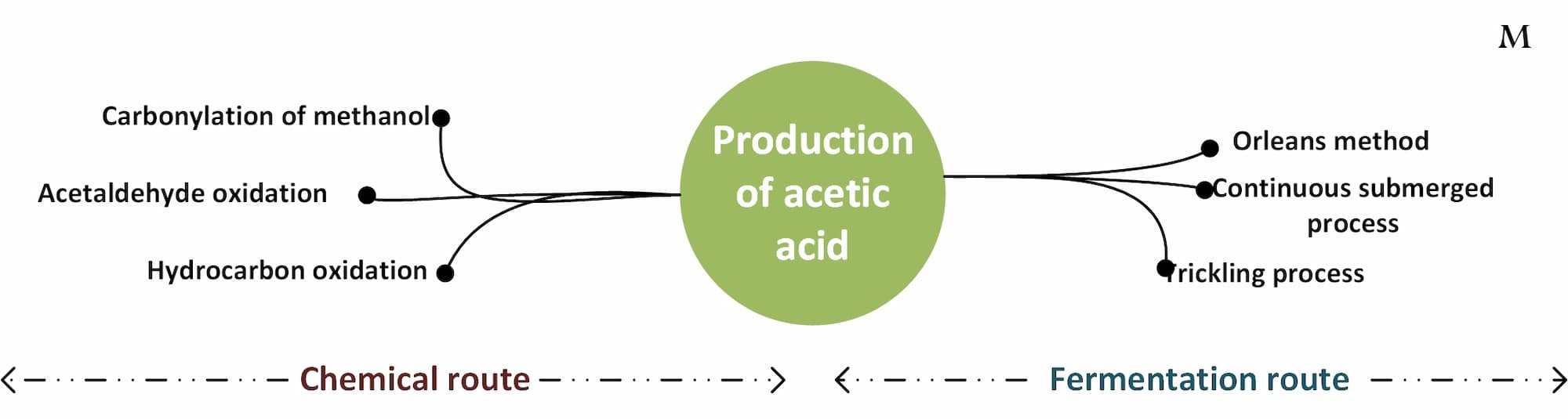
Production of acetic acid
It is important to note that the production of acetic acid, whatever method is used, must be carried out in appropriate industrial facilities and in accordance with environmental and safety regulations.
◉ Use of Acetic Acid
Acetic acid has many uses in different fields. Here are some of the common uses of acetic acid:
- Food industry: Acetic acid is used in food production as a preservative (inhibits the growth of bacteria), flavor and regulator of pH. It is an essential component of vinegar and is used in the preparation of various food products such as sauces, marinades and condiments. It is considered "food grade" if it meets the specifications of the Food Chemicals Codex .
- Chemical industry: Acetic acid is used as a raw material in the production of other chemicals. It is used in the manufacture of plastics, solvents, esters, dyes and other industrial chemicals.
- Textile: Acetic acid is used in the textile industry for the dyeing and finishing process of fabrics. It helps to fix the dyes on the fibers and improve the resistance of fabrics to fading.
- Cleaning: Due to its antibacterial and degreasing properties, acetic acid is used in household cleaning products. It is effective in removing lime deposits, stains and residue from surfaces.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Acetic acid is used in the production of drugs, including in the formulation of some topical pharmaceuticals.
- Laboratories: In laboratories, acetic acid is used to adjust the pH of solutions, prepare buffers and perform specific chemical reactions.
- Medical use: Acetic acid has several medical uses: antiseptic, treatment of warts, examination of the cervix (Visual Inspection with Acetic Acid (VIA)), treatment of ear infections, etc
◉ Is acetic acid harmful to humans ?
When used correctly and as directed, acetic acid found in common household products, such as diluted cooking vinegar, is generally considered safe and should not have adverse health effects.
However, it is important to note that in high concentrations acetic acid is a corrosive chemical and can be harmful to humans if used, handled or ingested inappropriately. Here are some considerations about its toxicity:
- Skin Contact: Contact with concentrated acetic acid may cause burns and skin irritation. Prolonged or repeated exposure may cause serious skin damage.
- Inhalation: Inhalation of acetic acid vapors may cause respiratory tract irritation, difficulty breathing, coughing and burning sensation in throat . At high concentrations or with prolonged exposure, this can lead to lung damage.
- Ingestion: Ingestion of this concentrated acid can cause severe burns in the mouth, throat, esophagus and stomach. This can lead to abdominal pain, vomiting, difficulty swallowing and potentially serious complications.
- Eyes: Direct contact of acid with eyes may cause burns, severe irritation, corneal damage and decreased vision. In case of contact, immediate and abundant rinsing of the eyes is essential.
It is essential to handle acetic acid with care and to follow proper safety precautions, including the use of personal protective equipment. In case of exposure or contact, it is important to seek immediate medical attention and follow the recommended first aid measures.