Summary :
- Ⅰ. Definition
- Ⅱ. Uses
- Ⅲ. How to use
- Ⅳ. Choosing a Syringe Filter
- Ⅴ. Types
- Ⅵ. How to order
- Ⅶ. Frequently asked questions
◉ What is a syringe filter ?
Syringe filter is single-use membrane device, attached to the end of a syringe. Used to remove particulate impurities from samples (liquid/gas) prior to some type of analysis to prevent damage to equipment (e.g. HPLC, chromatography ionic, ICP, dissolution tests etc.)
A syringe filter usually consists of a housing with a membrane that serves as a filter (classified according to composition, filter diameter and pore size). Both components must be compatible with the application and solution being filtered.
Proper sample filtration improves the quality and consistency of analytical results and reduces instrument downtime.
We provide all types of Syringe Filters in Nylon, PTFE, PES, MCE, PVDF, CA, PP and GF in 13mm, 17mm, 25mm and 30mm, all in virgin polypropylene : microbioclinique@gmail.com

Syringe filters PES 0.22µm
◉ What are syringe filters used for
They are commonly used for the following applications:
- Clarification of samples : they can remove particulate matter and debris from samples, making them clearer and easier to analyze.
- Sterile filtration : they are used for sterilizing small volumes of liquids, such as culture media, buffers, and solutions. They can remove bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms, making the samples safe for use in cell culture and other applications that require sterility.
- Sample preparation : they are used in sample preparation for analytical techniques such as HPLC (high-performance liquid chromatography) and GC (gas chromatography). They can remove impurities and particulates that can interfere with the analysis.
- Purification of biomolecules : they can be used for the purification of proteins, nucleic acids, and other biomolecules by removing contaminants and impurities from the samples.
- Environmental testing : they can be used in environmental testing to filter water, air, and soil samples. They can remove particulates, microorganisms, and other contaminants from the samples, making them suitable for analysis.
- Protein binding assays : they are used to separate free and bound protein fractions. By passing the sample through a syringe filter, free proteins can be separated from those that are bound to other molecules,
◉ How to use a syringe filter
Here are the general steps to use it :
- Select the appropriate syringe filter for your sample based on the chemical compatibility of the filter material and the properties of the sample.
- Fix the filter securely with a twisting motion. With a Luer Slip syringe, this is about a quarter turn when the filter is pushed in. If the syringe has a luer lock, attach it firmly but do not overtighten.
- Load the sample into the syringe. The sample volume should not exceed the recommended capacity of the syringe filter.
- Hold the assembled syringe and filter vertically to evenly wet the membrane (this promotes high flow rates).
- Gently depress the plunger of the syringe to push the sample through the filter. If possible discard the first 0.25-0.5ml of sample as if there is contamination present it is likely to be higher in those first microliters of sample.
- If the back pressure increases significantly, change the filter as it may have become clogged. Avoid pressing too hard as this may cause the filter housing to burst.
- Collect the filtered sample in a clean container. The filtrate can be used for further analysis or processing.
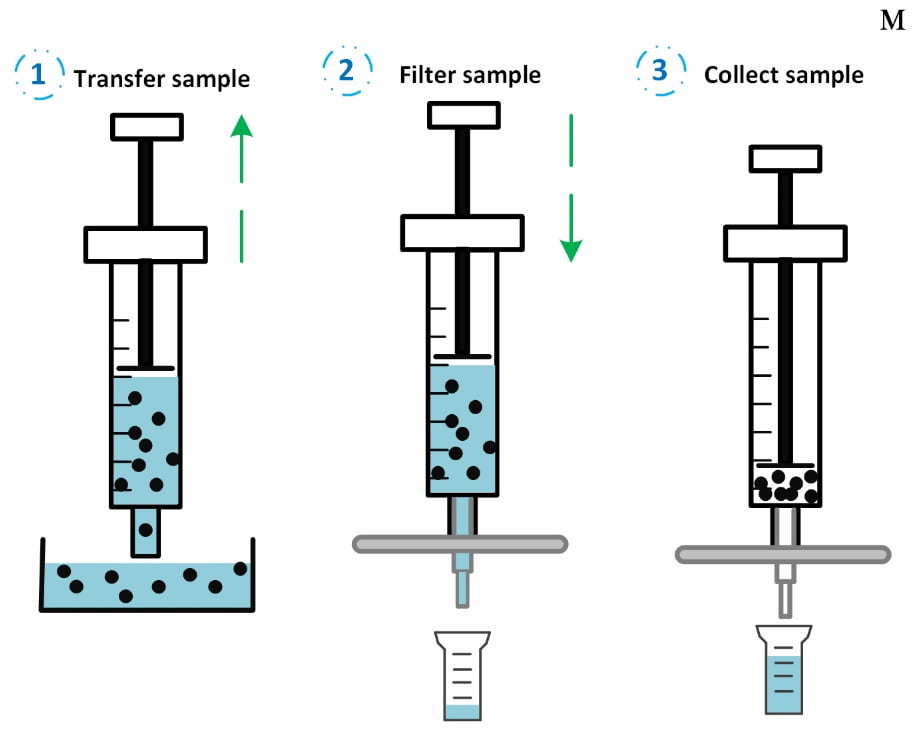
Simplified principle of the syringe filter
◉ Choosing a Syringe Filter
To choose a syringe filter, consider the following factors :
• Filter body
Disposable (polypropylene) or reusable (polycarbonate / stainless steel), Luer-lok or Luer-slip
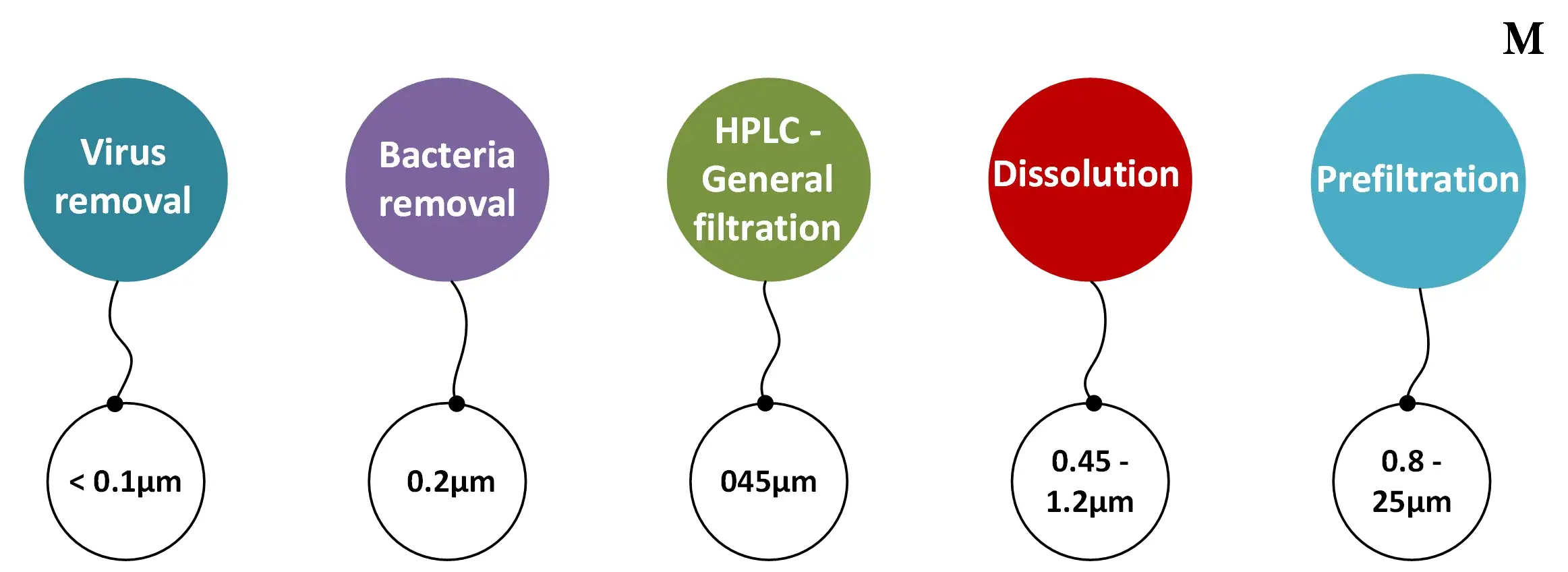
• Pore Size
The pore size is determined by the size of the particles you need to filter out of your aqueous solution. Filters are available in a variety of pore sizes. The most commonly used are 0.1µm, 0.13µm, 0.17µm, 0.22µm, 0.25µm, 0.30µm, 0.45µm, 1µm, 3µm and 5µm.
• Filter Material
There are many different filter materials used in syringe filters (Polyethersulfone (PES), Cellulose Acetate (CA), Nylon, RC, GMF, pp, etc.). The main differences are :
- Chemical compatibility : If the filter supports the chemical composition of the solution example : PH variations
- Flow rate : Speed of passage through the filter
- Burst pressure : Is the pressure at which the filter element is destroyed.
- Wettability : Hydrophilic or hydrophobic membrane.
- Binding properties : Membrane can bind analyte to varying degrees depending on membrane type and analyte type or concentration
• Filter Capacity
Refers to the maximum amount of sample volume that can be filtered through the filter without causing clogging or reducing the filter's effectiveness.
• Retention Volume
Refers to the amount of liquid that gets trapped inside the filter after filtration. Factors such as the filter's pore size, surface area, and material properties usually determine this volume.
• Sterile or Non-sterile
- Sterile syringe filters are used for filtering samples that need to be free from microbial contamination (such medical applications).
- Non-sterile syringe filters are typically used for filtering non-sterile solutions, such as for sample preparation in analytical chemistry.
◉ Types of Syringe Filters
Syringe filters come in different sizes and materials to suit different laboratory applications. Here are some common types :
- Cellulose acetate syringe filters: These filters are made from cellulose acetate and are used for the filtration of aqueous solutions, biological fluids, and proteinaceous samples. They are also suitable for use with aggressive organic solvents.
- Nylon syringe filters: These filters are made from nylon and are suitable for the filtration of aqueous and organic solutions. They are known for their excellent chemical resistance and can filter samples containing proteins, nucleic acids, and fine particles.
- PTFE syringe filters: These filters are made from PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) and are suitable for the filtration of aggressive organic solvents, acids, and alkalis. They are also used for filtering air and gas samples.
- PVDF syringe filters: These filters are made from PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride) and are suitable for the filtration of aqueous and organic solutions. They are resistant to most solvents and can filter samples containing particles and biological materials.
- PES : These filters are made from PES (polyethersulfone) and are suitable for the filtration of biological fluids, organic and aqueous solutions. They are used for filtering samples containing proteins, nucleic acids, and other biological materials.
- Glass fiber syringe filters: These filters are made from borosilicate glass fibers and are suitable for the filtration of viscous samples, aqueous solutions, and particle-laden samples. They can filter samples containing particles, and they are commonly used in environmental and food testing laboratories.
Types |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Description | |||
| Nylon (NSF), Pore Size : 0.45μm, Diameter : 13mm, 100/P | |||
| NSF, Pore Size: 0.45μm, Diameter: 25mm, 100/P | |||
| NSF, Pore Size: 0.22μm, Diameter: 25mm, 100/P | |||
| NSF, Pore Size: 0.22μm, Diameter: 13mm, 100/P | |||
| NSF customized Pore Sizes: 0.1μm, 0.80μm, 1.0μm, 3.0μm, 5.0μm. | |||
| PTFE hydrophobic, Pore Size : 0.22μm, Diameter : 13mm, 100/P | |||
| PTFE hydrophilic, Pore Size : 0.22μm, Diameter : 13mm, 100/P | |||
| PTFE hydrophobic, Pore Size : 0.22μm, Diameter : 25mm, 100/P | |||
| PTFE hydrophilic, Pore Size : 0.22μm, Diameter : 25mm, 100/P | |||
| PTFE sterile, hydrophilic, Pore Size : 0.22μm, Diameter : 30mm, 100/P | |||
| PTFE glass fiber, hydrophilic, 0.22μm, Diameter : 30mm, 100/P | |||
| PTFE hydrophobic, 0.45μm, Diameter : 13mm, 100/P | |||
| PTFE sterile, hydrophilic, 0.45μm, Diameter : 25mm, 100/P | |||
| PTFE hydrophobic, 0.45μm, Diameter : 25mm, 100/P | |||
| PTFE sterile, hydrophilic, 0.45μm, Diameter : 30mm, 100/P | |||
| PTFE glass fiber, hydrophilic, 0.45μm, Diameter : 30mm, 100/P | |||
| CA , 0.22μm, 13mm, Sterile, Prefilter: PP, 500/p | |||
| CA , 0.22μm, 25mm, Sterile, Prefilter: PP, 200/p | |||
| CA , 0.22μm, 33mm, Sterile, Prefilter: Glass fiber, 200/p | |||
| CA , 0.45μm, 13mm, Sterile, Prefilter: PP, 500/p | |||
| CA , 0.45μm, 25mm, Sterile, Prefilter: PP, 200/p | |||
| CA , 0.45μm, 30mm, Sterile, Prefilter: Glass fiber, 200/p | |||
| CA , 0.45μm, 30mm, Sterile, Prefilter: Glass fiber, 200/p | |||
| CA , 0.45μm, 33mm, Sterile, Prefilter: Glass fiber, 200/p | |||
| PES Syringe Filter , 0.1μm, 25mm, Sterile, Prefilter: PP, 200/p | |||
| PES , 0.22μm, 4mm, Sterile | |||
| PES , 0.22μm, 13mm, Sterile, Prefilter: PP, 500/p | |||
| PES , 0.22μm, 25mm, Sterile, Prefilter: PP, 200/p | |||
| PES , 0.22μm, 30mm, Sterile, Prefilter: Glass fiber | |||
| PES , 0.22μm, 33mm, Sterile, Prefilter: Glass fiber, 200/p | |||
| PES , 0.22μm, 50mm, Sterile | |||
| PES , 0.45μm, 13mm, Sterile, Prefilter: PP, 500/p | |||
| PES , 0.45μm, 25mm, Sterile, Prefilter: PP, 200/p | |||
| PES , 0.45μm, 30mm, Sterile, Prefilter: Glass fiber | |||
| PES , 0.45μm, 33mm, Sterile, Prefilter: Glass fiber, 200/p | |||
| PES , 0.45μm, 50mm, Sterile | |||
◉ How to order a syringe filter
Syringe Filters are manufactured with a polypropylene (PP) housing and are available with a wide variety of membranes and pore sizes, making it suitable for low protein binding (eg: PES) or to a wide chemical compatibility (eg: PTFE membrane).
You can choose from a variety of membrane types, pore sizes, and effective filtration areas to meet your specific application requirements : microbioclinique@gmail.com
◉ Frequently asked questions
Can Syringe Filter be Reused ?
No, It is not reusable because fine particles can reduce the performance of the filter and cause contamination.
Do syringe filters remove bacteria ?
Yes, syringe filters are frequently used for the onsite manufacture of parenteral drugs and sterile eye drops, in order to remove microbiological contaminations, 0.2/0.22um membranes are most commonly used for bacteria removal.
What is the difference between a 0.2 μm membrane and a 0.22 μm membrane ?
The performance of 0.2 and 0.22 μm filter membranes is identical, the difference is due to different pore size measuring methods
PVDF filters are hydrophilic or hydrophobic ?
PVDF filters are available in both options : hydrophilic and hydrophobic.
Which membrane should I use to filter cell culture media ?
PES or SFCA filters are used for filtering cell culture media, they have very low protein binding and rapid-flow (PES +++)
Most frequently used membrane pore sizes ?
0.45 μm (used for general filtration) and 0.2/0.22 μm (typically used to remove bacteria) are the two most frequently used membrane pore sizes for research and medical applications.
Why is a syringe filter necessary for HPLC sample preparation ?
All solvents used as mobile phase must be filtered through 0.2 μm filters before entering an HPLC system to prevent scratching of pump pistons by particles and to avoid clogging the in-line filter or the guard column.
What is difference between 0.45 and 0.22 micron filter ?
The main differences between a 0.45 micron filter and a 0.22 micron filter are particle retention and flow rate
- 0.22 micron filter has a smaller pore size compared to a 0.45 micron filter, which means it can retain smaller particles.
- 0.45 micron filter has a higher flow rate compared to a 0.22 micron filter due to its larger pore size.
