Content
◉ Having a High Hematocrit Level
Hematocrit (Hct) is a blood test that measures the percentage of red blood cells. It is an accurate method for assessing the degree of anemia or polycythemia.
Having high hematocrit levels (>50% for men, >44% for women) means having a higher than normal number of red blood cells in the blood, often referred to as polycythemia, which increases blood viscosity and the risk of thrombosis.
It is usually included in a series of blood tests called Complete Blood Count (CBC), providing a comprehensive assessment of blood composition
Increased hematocrit can be associated with various causes. The interpretation of the results should be done in conjunction with other analyzes and taking into account the clinical manifestations, thus allowing a more in-depth evaluation.
◉ When do we start talking about a high hematocrit value?
Hematocrit can be measured manually by a process called micro-hematocrit using a capillary tube or automatically using automated analyzers. Both methods provide accurate assessments. For more details, please see the article on "How to measure hematocrit ".
We speak of a high hematocrit, expressed as a percentage, if it exceeds the following thresholds considered normal:
- Men: 41% to 50%
- Women: 36% to 44%
- Infants: 32% to 42%
- Newborns: 45% to 61%
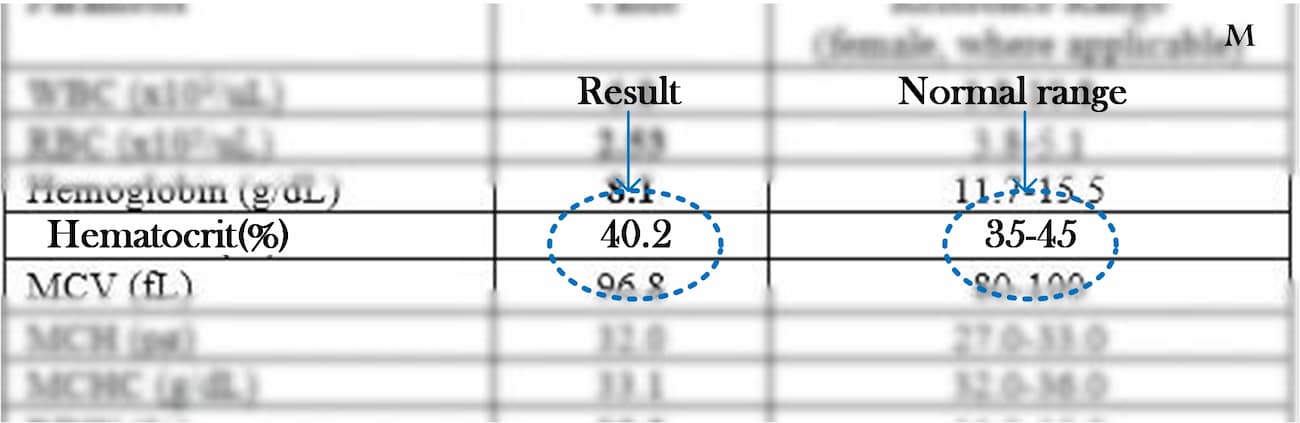
The reference value for hematocrit may vary from laboratory to laboratory due to differences in equipment, techniques and demographics. Therefore, it is crucial to consider the specific reference range provided by the laboratory performing the analysis.
◉ Why is my hematocrit level high?
There are many causes that increase the hematocrit level, some of which are non-pathological. This increase is often secondary to one of the following mechanisms:
- Primary bone marrow abnormality.
- Secondary hyperproduction in response to excessive secretion of other substances, such as the hormone EPO (erythropoietin).
- Secondary to a hypoxia situation.
◉ High Hematocrit: Causes
- Dehydration: A reduction in blood volume due to a decrease in the body's water content, leading to a higher concentration of red blood cells in the blood.
- Polycythemia vera (Vaquez's disease): An excess of red blood cells in the blood, sometimes linked to excessive production of erythropoietin.
- Kidney disease: Kidney dysfunction can cause excessive production of erythropoietin, thereby stimulating the production of red blood cells.
- Congenital heart disease.
- Respiratory failure.
- Thickening or scarring of the lungs: Such as pulmonary fibrosis.
- Hemoconcentration: An increase in the concentration of cellular constituents in the blood.
- Pre-eclampsia.
- Cancers: Certain types of cancer, such as leukemia, lymphoma and multiple myeloma, can increase the production of red blood cells.
- Exposure to carbon monoxide: Prolonged inhalation of carbon monoxide can affect oxygen transport, stimulating the production of red blood cells.
- Stroke: A stroke can cause a compensatory response, increasing the production of red blood cells.
- High altitude: Less available oxygen at high altitudes stimulates red blood cell production.
- Smoking.
◉ Symptômes et Signes d'un Hématocrite Elevé
- Headaches and dizziness.
- Easy fatigue and general weakness
- Tachypnea.
- Bruises
- Decreased activity and inability to exercise as usual
- Heart palpitations
- Epistaxis.
- Nosebleeds.
- Confusion and blurred vision.
- Discomfort in the stomach.
- Dry mouth, lips and eyes.
◉ Related tests
Faced with a high hematocrit, the doctor may order other tests to fully understand the cause of this elevation.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): CBC is a blood test that provides information about various types of blood cells.
- Reticulocyte count: This test evaluates the performance of the bone marrow.
- Blood smear: This is a sample of blood examined under a microscope.
- : This test measures the amount of erythropoietin hormone.
◉ Treatment of high hematocrit levels
To treat high hematocrit levels, it is necessary to treat the underlying cause. High hematocrit levels can be reduced by natural methods and medications.
- Therapeutic phlebotomy to remove excess red blood cells.
- Smoking cessation: Cigarette components such as nicotine and tobacco reduce blood flow by impairing the oxygen-carrying capacity of red blood cells, prompting the bone marrow to compensate by producing more blood cells red.
- Maintain adequate hydration: by drinking a sufficient amount of water (8 to 12 glasses) and avoiding caffeine and alcohol.
- Eat foods rich in antioxidants: Antioxidants protect the body against free radicals, which can cause cancer and other blood-related diseases.
- Moderate regular exercise.
- Drugs that can decrease hematocrit level:
- Aspirin is an antiplatelet drug that lowers hematocrit levels.
- Desmopressin.
- Metformin.
- Stay at low altitude.
◉ Conclusion
A high hematocrit is a non-specific medical condition that can occur due to a variety of causes. The management plan will be determined based on the underlying cause and associated symptoms.