🏾 Content :
- Definition
- Pourquoi sont-ils utilisés ?
- NT-proBNP/BNP assay
- Normal value and interpretation of results
- What other tests could I have with this test?
🏾 NT-proBNP / BNP
NT-proBNP and BNP are natriuretic peptides used as biomarkers for the diagnosis of heart failure (HF), they are hormones produced , primarily by the heart and blood vessels, in response to increased stretching of myocardial fibers.
High levels of NT-proBNP or BNP can mean that your heart is not pumping as much blood as your body needs. The test is particularly useful for diagnosing and estimating the severity of heart failure.
- BNP: "Brain Natriuretic Neptide" the active hormonal form, isolated from pig brain in 1988.
- NT-proBNP: "N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide", the inactive form.
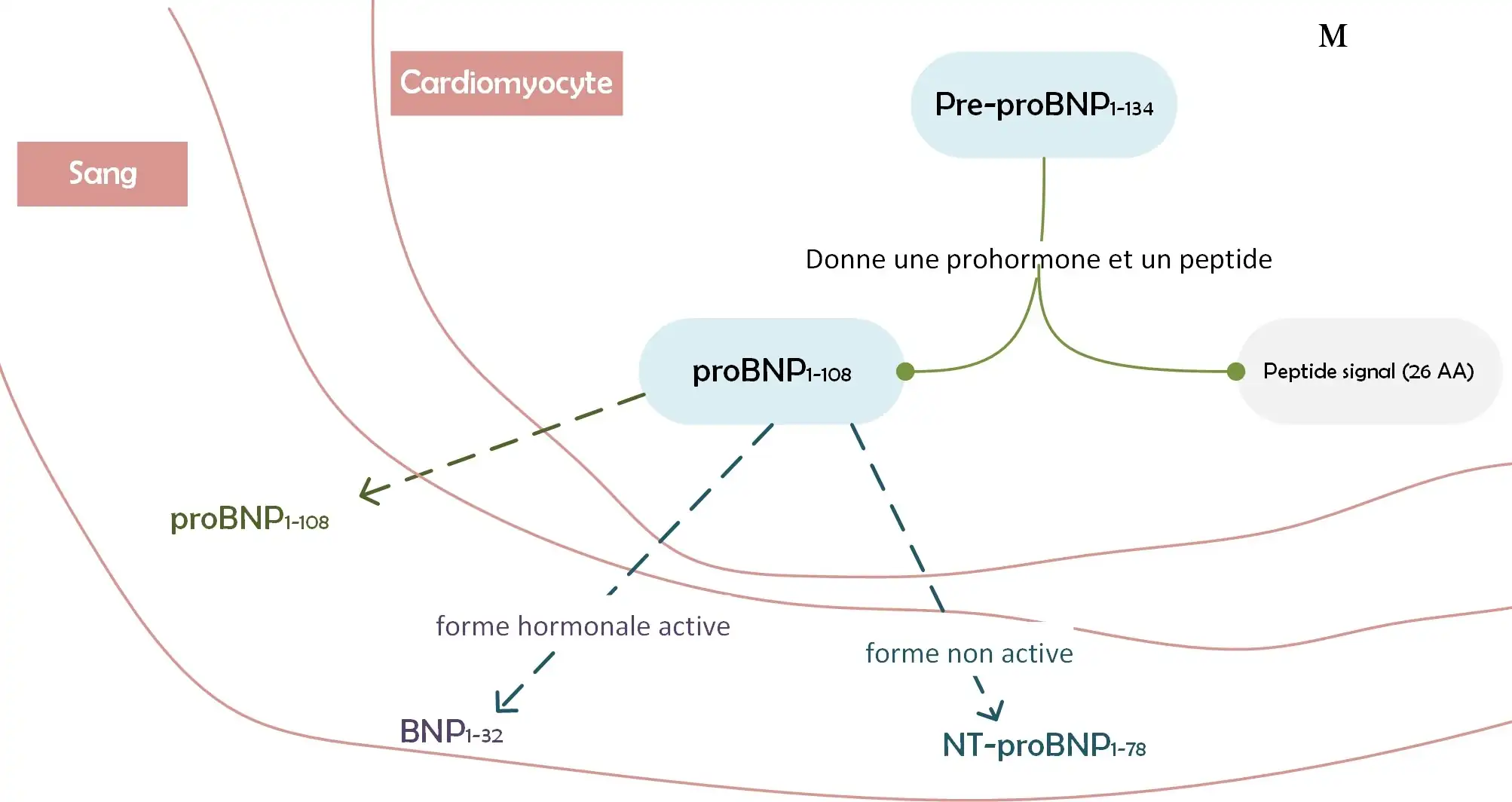
Biosynthesis of natriuretic peptides, BNP and NT-proBNP.
🏾 What are they used for?
A BNP test or NT-proBNP test is most often used to diagnose or rule out heart failure and also to help distinguish heart failure from severe lung involvement often showing the same symptoms
The BNP and the NT-proBNP are useful in early heart failure, in particular stages I and II where these markers are early informative while echocardiographic data can be faulted. .
Among the symptoms of heart failure:
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Cough or wheeze
- Tired
- Swelling of the abdomen, legs and/or ankles
- Loss of appetite or nausea
🏾 NT-proBNP/BNP assay
There are no special preparations to make before the analysis, it is a blood test that can be done at any time using a blood sample taken from a vein in your arm and does not require fasting.
- Coagulation of the sample does not lead to degradation of NT-proBNP (can be carried out either on serum or plasma) but influences that of BNP.
- NT-proBNP has good stability at room temperature for seven days and ten days at 4 ◦C, while the concentration of BNP decreases significantly from four hours
- The different NT-proBNP assay techniques are based on the same antibodies and the same calibrator, the results of the assay for this peptide are therefore comparable in the same patient from one laboratory to another, which is not the case for BNP.
🏾 Normal Value and Interpretation of Results
The NT-proBNP and/or BNP measured are expressed in picograms per millilitre (pg/mL) but may be listed by some laboratories in nanograms per liter (ng/L) or in picomoles per liter (pmol/L).
Normal value ranges may vary slightly from lab to lab. Some labs use different measurements or test different samples.
If your BNP or NT-proBNP results were normal, it likely means that your symptoms are not caused by heart failure. Your doctor may order more tests to help make a diagnosis.
1- In acute heart failure
| Condition | Age | NT-proBNP level (pg/mL) | BNP level (pg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | All | Less than 300 | Less than 100 |
| Gray area | Zone of uncertainty between the normal value and the high values where the dosage of the peptide does not make it possible to decide with a sufficient level of certainty. | ||
| Possible heart failure | Under 50 | Over 450 | Over 400 |
| Possible heart failure | Between 50 and 75 | Over 900 | Over 400 |
| Possible heart failure | Over 75 | More than 1800 | Over 400 |
When interpreted, your normal range may differ from that of other patients with different histories. Your doctor will take into account not only the reference range of the laboratory, but also your age, your body mass index, your symptoms, your medical history and the results of other test results.
2- In chronic heart failure
Compared to NT-proBNP values in patients with acute HF, lower values are expected in ambulatory patients with chronic HF. International guidelines recommend a single low threshold of 125pg/mL to rule out heart failure in patients with non-acute symptoms.
| Age | NT-proBNP level (pg/mL) | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| < 75 | < 125 | CI unlikely |
| ≥ 75 | < 450 | CI unlikely |
| < 75 | ≥ 125 | Possible heart failure |
| ≥ 75 | ≥ 450 | Possible heart failure |
🏾 What other tests could I have with this test?
Additional tests that may be performed to aid in diagnosis:
- Electrocardiogram, which examines the electrical activity of the heart
- Exercise test, which shows how well your heart handles physical activity
- Chest X-ray to see if your heart is larger than normal or if you have fluid in your lungs
- Metabolic test to check for kidney disease, which has symptoms similar to heart failure
- Complete blood count to check for anemia or other blood disorders
Reference
- P.Jourdain - NT-proBNP en pratique « De la biologie à la clinique »
- G.Dine - BNP et NT-proBNP : intérêt dans le suivi médical des sportifs de haut niveau
- E.Villar - Valeurs seuils optimales de NT-proBNP pour le diagnostic d’insuffisance cardiaque selon l’âge et la fonction rénale
- M Bay - NT-proBNP: a new diagnostic screening tool to differentiate between patients with normal and reduced left ventricular systolic function
- P.Ray - Intérêt du dosage des peptides natriurétiques en urgence
- P.Jourdain - NT-proBNP en pratique « De la biologie à la clinique »
- Medlineplus - Natriuretic Peptide Tests (BNP, NT-proBNP)
- M. GALINIER - BNP, NT-proBNP : lequel choisir en pratique ?
- biomerieux - DES VIES®NT-proBNP2
- biron - NT-proBNP