Hugh Leifson Medium (M.E.V.A.G.): Usage and Interpretation
The Hugh Leifson Medium (M.E.V.A.G.) is a culture medium used to study carbohydrate metabolism in bacteria. It helps determine whether bacteria utilize glucose through fermentative, oxidative, or both pathways. This medium is particularly useful for differentiating bacteria based on their ability to metabolize carbohydrates in the presence or absence of oxygen.
◉ Principles of M.E.V.A.G. Medium
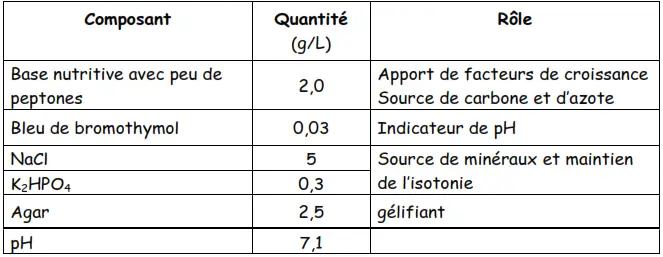
The M.E.V.A.G. medium contains:
- Glucose as the sole carbohydrate source.
- Bromothymol Blue (BTB) as a pH indicator.
- An oxygen gradient created by medium regeneration.
How It Works:
- Fermentation: In the absence of oxygen, bacteria produce acids, which acidify the medium and turn the BTB yellow.
- Oxidation: In the presence of oxygen, bacteria produce fewer acids, and the medium remains green or turns blue at the surface (alkalinization due to peptide utilization).
◉ Inoculation Technique
- Regenerate the Tube: Heat the tube for 20 minutes at 100°C to create an oxygen gradient.
- Add Glucose: Aseptically add glucose to a final concentration of 1%.
- Solidify the Medium: Cool the tube in a cold water bath.
- Inoculate: Use a central stab inoculation with a straight needle.
- Incubate: Incubate at 37°C for 24 hours with the cap loosened.
◉ Reading and Interpretation of Results
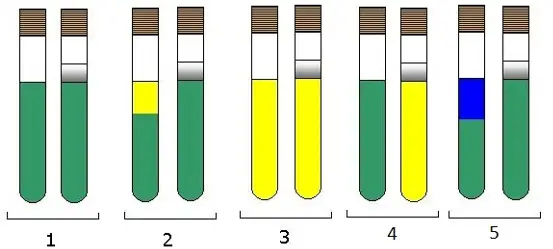
| Tube | Observation | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Tube 1 | Little or no growth, no acidification | Inert metabolism (no glucose utilization) |
| Tube 2 |
With paraffin: Little or no growth, no acidification. Without paraffin: Moderate acidification (yellow at the top, green at the bottom). |
Oxidative metabolism |
| Tube 3 | Acidification in both tubes (yellow) | Fermentative and oxidative metabolism |
| Tube 4 | Acidification only in the tube with paraffin | Fermentative metabolism only |
| Tube 5 | Top of the tube is blue | Bacteria inert to glucose (peptide utilization as an energy source) |
◉ Uses of M.E.V.A.G. Medium
- Determining the Glucose Utilization Pathway: Fermentation, oxidation, or both.
- Studying Carbohydrates Utilized by Oxidative Bacteria.
◉ Conclusion
The Hugh Leifson Medium (M.E.V.A.G.) is a vital tool for studying carbohydrate metabolism in bacteria. Its pH indicator and oxygen gradient make it easy to distinguish between fermentative and oxidative metabolic pathways. Using a Bootstrap table makes the results more accessible and easier to interpret.