Contents:
🏾 Definition
Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin) is the percentage of hemoglobin that has bound sugar (glucose) in the blood. When the glucose level is high in the blood, it tends to bind to different proteins, including hemoglobin, according to a non-enzymatic process: glycation, hence the name "glycated hemoglobin".
Measuring Hemoglobin A1c is the gold standard for monitoring the progression of diabetes (type 1 and 2 diabetes). It allows, by a blood test, to evaluate the glycemic balance over a longer period (2 to 3 months).
For most type 2 diabetic patients, the HbA1c target to be achieved is ≤ 7%, and depending on whether or not this target is achieved, the doctor can reassess the patient's management (diet, physical activity and drug treatments).
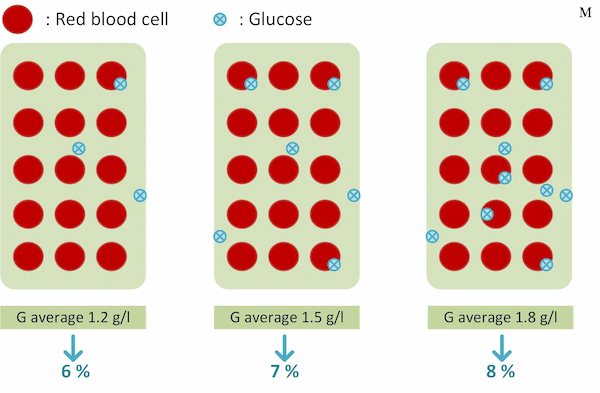
Link between average blood sugar and glycated hemoglobin
🏾 The normal level of Hemoglobin A1c ?
The measured Hemoglobin A1c is expressed as a percentage (%), but also in IFCC units (mmol/mol = mmol HbA1c/mol Hb).
- A normal level of glycated hemoglobin : For people without diabetes, the normal range for HbA1c levels is between 4% and 5.6%.
- Prediabetes : HbA1c levels between 5.7% and 6.4% mean you have prediabetes and are at a higher risk of developing diabetes.
- High: Levels of 6.5% or higher means you have diabetes. A person who has had diabetes that has not been treated for a long time may have a rate higher than 8%.
Note : Younger people have more years ahead of them with diabetes, so their goal may be lower to reduce the risk of complications, unless they often suffer from low blood sugar.
🏾 A1C test
The A1C test test is performed in a medical laboratory using a blood sample from a finger or your arm
Routinely, the most reliable assay method is high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) (the reference method is mass spectrometry, an expensive method, reserved for only a few laboratories)
You don't have to do anything special to prepare for your A1C test(fasting is not necessary). However, ask your doctor if other tests will be done at the same time and if you should prepare for them.
This parameter is independent of daily variations in blood sugar, it is not affected by fasting, physical exercise or recent ingestion of sugars. It increases very slightly with age. Its interindividual variations are low, which makes it a good marker.
🏾 Other causes of Hemoglobin A1c variation
A high A1c test does not always indicate diabetes, as there are many causes other than diabetes that can influence HBa1c levels.
The validity of a glycated hemoglobin result is conditioned by a normal lifespan of red blood cells, 120 days, and normal hemoglobin synthesis, 97 to 99% HbA. Any change in erythropoiesis and/or the lifespan of red blood cells will affect the reliability of the HBa1c level:
| Falsely low HbA1c level | • The presence of reticulocytes (relatively immature red blood cells): in the event of haemolysis, acute anemia or chronic liver disease, but also treatment with iron, erythropoietin, vitamin B12 and certain antiviral drugs, or a recent transfusion
• Hb structural changes : the presence of Hb S (sickle cell disease) or Hb C will underestimate the HbA1c value. • Vitamin C or vitamin E: abnormal Hb glycation. |
| Falsely elevated HbA1c level | • Extending the lifespan of red blood cells: advanced age, alcoholism, splenectomy, iron deficiency, folate or vit. B12.
• Hb structural changes : An abnormally high proportion of Hb F (thalassemia) generally increases the HbA1c level. • Chronic renal failure : responsible for an overestimation of HbA1c by accumulation of carbamylated Hb that can interfere with the assay method. |
Tell your doctor if any of these factors apply to you and ask if you need further tests to find out.
🏾 Relationship between mean blood glucose and glycated hemoglobin
The percentage of glycated hemoglobin is directly proportional to the average blood sugar.
A blood sugar of 7% corresponds to an average blood sugar of 1.5g/l. 1% more HbA1c represents an average increase in blood sugar of 0.30g/l.
| Average blood sugar g/l | HbA1c % |
| 1,2 or 6,65 mmol/l | 6 % |
| 1,5 or 8,32 mmol/l | 7 % |
| 1,8 or 9,98 mmol/l | 8 % |
| For each increase of 0.3 (1.66 mmol/l) | Increase of 1% |
🏾 How often do you need the A1c test?
Your doctor will likely ask you to take the A1c test as soon as you are diagnosed with diabetes.
You will probably be tested once a year if you have prediabetes, which means you have a high chance of developing diabetes.
You can get tested twice a year if you have type 2 diabetes, don't use insulin, and your blood sugar is generally within your target range.
You might get it three or four times a year if you have type 1 diabetes.
🏾 How to lower your HbA1c levels
Many factors can change your HbA1c levels, and you and your doctor can take steps to bring them back to your target level:
- Your doctor may need to review your medicine and increase the dose or try a new one.
- Being more active, moving more is good for everyone, but it can specifically help lower your HbA1c levels.
- Get tips for a healthy and balanced diet.
- Quit smoking, smoking makes it more difficult for blood to circulate in your body.
Reference
- CDC - All About Your A1C
- SANOFI- QU'EST-CE QUE L'HEMOGLOBINE GLYQUEE (HBA1C) ?
- société francaise diabétologie - HbA1c : attention aux pièges
- Ann Biol Clin 2000 - Dosage de l’hémoglobine A1c et hémoglobinopathies : problèmes posés et conduite à tenir.
- biominis - HEMOGLOBINE GLYQUEE
- Fédération Française des Diabétiques - L’HBA1C OU HÉMOGLOBINE GLYQUÉE
- Diabetes UK - what is hba1c?