Content:
◉ Overview
Deoxyribonuclease (DNase) test is used to determine an organism's ability to hydrolyze DNA and use it as a source of carbon and energy for growth. Used mainly to differentiate Staphylococcus aureus from other Staphylococci.
DNases are enzymes that hydrolyze DNA and release free nucleotides and phosphate. DNases produced by bacteria are extracellular endonucleases that cleave DNA, producing a high concentration of oligonucleotides.
There are several media used to detect these enzymes, some use no indicator (requires the addition of HCl reagent) and others use various indicators (toluidine blue O or methyl green) to detect.
Ⅱ. Agar for DNase test / Principle
🏾 DNase agar without indicator
The original formulation was designed by Jeffries , who incorporated DNA into trypticase soy agar; this medium required the addition of acid (HCL) to detect polymerized DNA.
| Ingredients | gram/litre | Ingredients | gram/litre |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pancreatic Digest of Casein | 15,0 g | Papaic Digest of Soybean Meal | 5,0 g |
| Sodium Chloride | 5,0 g | Deoxyribonucleic Acid | 2,0 g |
| Agar | 15,0g | pH | 7.3 ± 0.2 |
◈ Principle : The hydrolysis of DNA was observed by a clearing of the agar after addition of HCl (the oligonucleotides dissolve in acid, but DNA salts are insoluble).
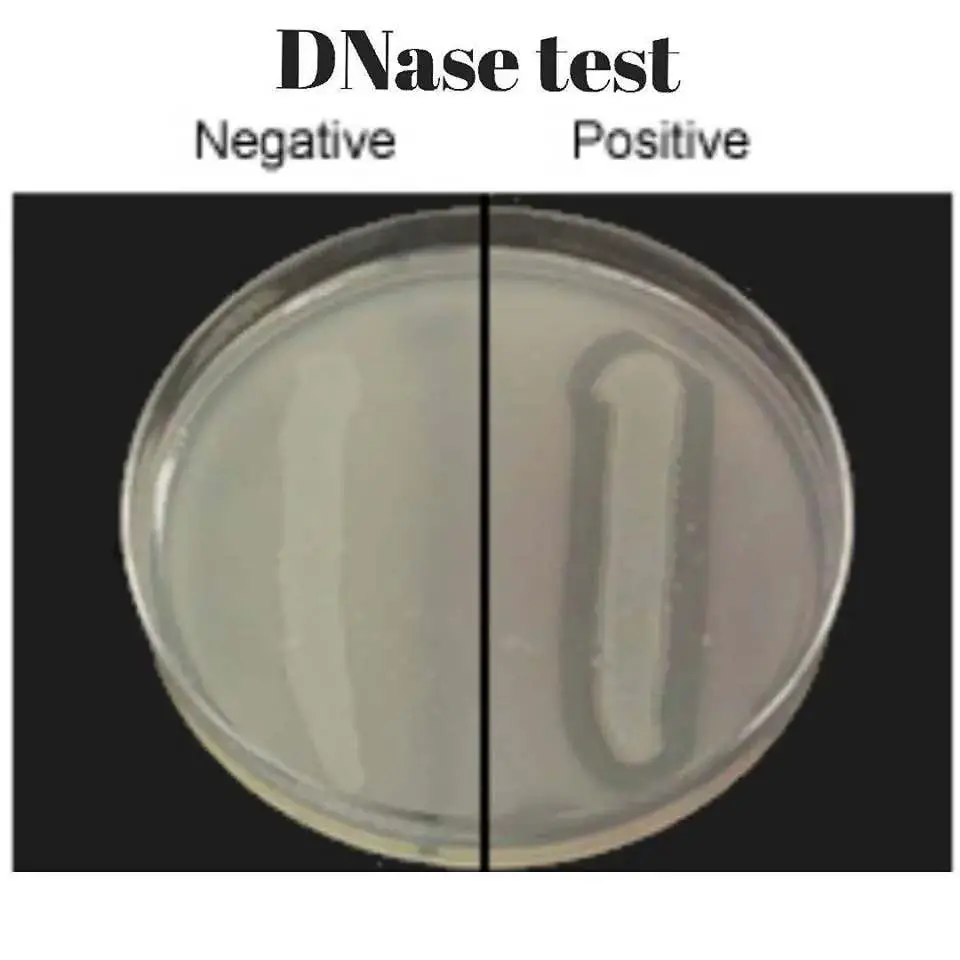
DNase test negative and positive after adding HCL
🏾 DNase agar with methyl green
Described by P. B. SMITH , the incorporation of methyl green dye into an agar medium containing deoxyribonucleic acid gives an improved medium for the detection of deoxyribonuclease-producing bacteria. The use of the dye makes it unnecessary to use acid to demonstrate deoxyribonuclease activity, thus allowing subculture or reincubation of colonies.
Methyl green ......................... 0,05g
◈ Principle : Methyl green dye is able to bind to polymerized DNA to form a stable green complex at pH 7.3. DNase action depolymerizes the DNA structure releasing methyl green, free methyl green decolorizes spontaneously at pH 7.3 resulting in colorless halos around DNase positive colonies.
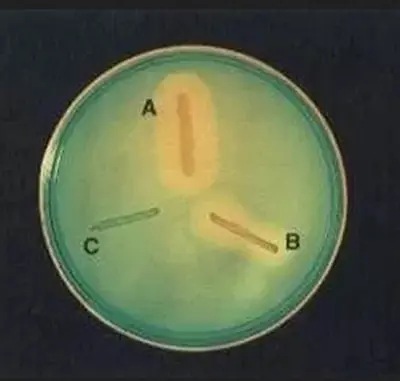
"A" and "B" DNase test positive, "C" DNase test negative
🏾 DNase agar with toluidine blue O
Described by Schreier, originally designed to easily and quickly differentiate S. marcescens from other members of the KES division: Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Serratia.
Toluidine blue O ........................ 0,1 g
◈ Principle : When toluidine blue O (TBO) is added, a complex forms with the DNA, which changes structure when the DNA is hydrolyzed, resulting in a bright pink color.
Ⅲ. DNase Test Procedure / Results
- You will make a single line down the center of the box (if you are using 2 species of staphylococci, you can split the box in half and pass each organism down one side).
- Incubate at 30º C or 37º C.
- AFTER INCUBATION: If the DNase medium does not contain a color indicator: Flood the dish with 1N hydrochloric acid and Let the dish stand for a few minutes to allow the reagent to adsorb. Decant the excess hydrochloric acid, then examine the box within 5 minutes against a dark background.
🏿 DNase test positive :
- 1. Serratia marcescens (Serratia fonticola is the only Serratia sp. that is DNase negative.)
- 2. Staphylococcus aureus
- 3. Campylobacter jejuni
- 4. Moraxella catarrhalis
- 5. Corynebacterium diphtheriae