Content :
🏾 Introduction
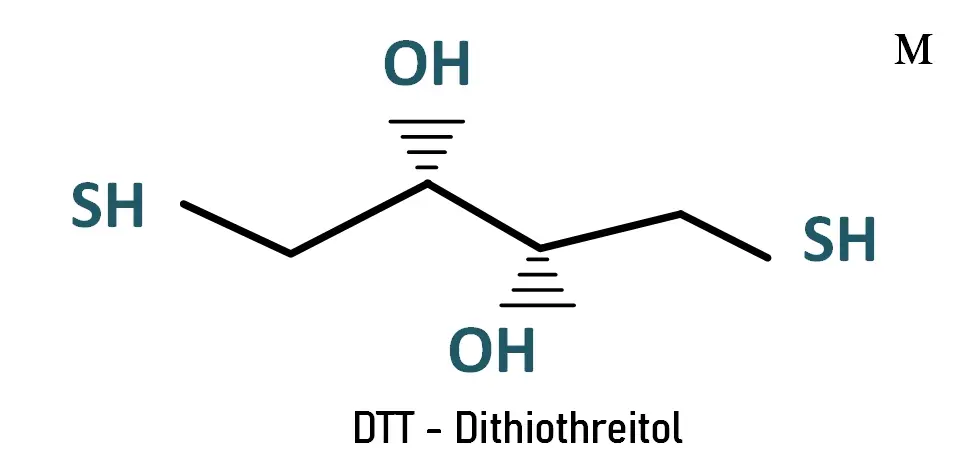
Dithiothreitol (DTT), also known as Cleland's Reagent, is a small redox molecule. widely used in biochemical work to reduce disulfide bridges and denature proteins prior to analysis by electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE).
DTT is frequently used to reduce disulfide bonds in peptides and proteins and, more generally, to prevent the formation of intramolecular and intermolecular disulfide bonds between cysteine residues in proteins
Its oxidized form is a disulfide bonded 6-membered ring. Its name derives from the four-carbon sugar, threose.
DTT - Dithiothreitol |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS number | 3483-12-3 | ||||||||
| Molecular mass | 154.25 g/Mol | ||||||||
| Formula | C4H10O2S2 | ||||||||
| Chemical name | (2S,3S)-1,4-bis(sulfanyl)butane-2,3-diol | ||||||||
| Purity | > 99% | ||||||||
| Solubility | In: water, ethanol, acetone and ethyl acetate. | ||||||||
Dithiothreitol - DTT
🏾 Properties
The optimum pH range for DTT is between 7.1 and 8.0, but the reagent can be used effectively at pH 6.5 to 9.0. DTT is quite stable (longer shelf life in powder form than 2-mercaptoethanol), but stock solutions should be used immediately and any remaining solution should be discarded.
Dithiothreitol is a strong reducing agent with a redox potential of -0.33 V at pH 7. Reduction of a disulfide bond is followed by two sequential thiol-disulfide exchange reactions