Esculin is a glycoside composed of glucose and esculetin. Some bacteria hydrolyze aesculin by breaking the glucosidic bond releasing glucose and aesculetin.
Through its phenol function, esculetin reacts with the Fe3+ of the iron citrate contained in the medium and forms a brown precipitate. This precipitate darkens the medium surrounding the growth.
Bile is the selective agent added to the medium to separate the Streptococcus bovis group and enterococci from other streptococci.
Among streptococci, only enterococci and members of the Streptococcus bovis group (S. equinus, S. gallolyticus, S. infantarius, and S. alactolyticus) tolerate bile and hydrolyze aesculin.
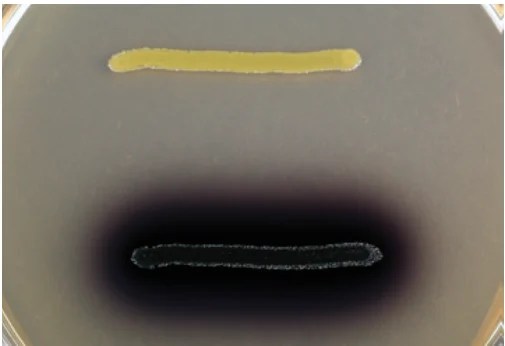
bile-esculine test