Contenu:
🏾 Overview
Micropipette is a type of standard laboratory equipment, it used to measure and transfer small amounts of liquid accurately.
There are several types of micropipettes on the market which can be classified according to:
- Volume : fixed or variable volume micropipette
- The principle of operation : air displacement or positive displacement micropipette.
- The operating mechanism :mechanical or electronic micropipette
- The number of channels : single-channel or multi-channel micropipette.
Learning to use a micropipette correctly is considered an essential laboratory skill, it is a tool widely used in microbiology laboratories, medical laboratories, universities and research laboratories.
Micropipette
🏾 Micropipette parts
◉ Although micropipettes are not alike, the basic parts of all micropipettes are the same::
- A plunger is the topmost part of the micropipette, it is used for volume adjustment and to aspirate and dispense the desired amount of liquid into the tip of the micropipette. There are two stops in the plunger which are used differently to pick up liquid in forward and reverse pipetting.
- Eject Button : Tips can be easily removed from the micropipette, without touching them, by pressing the tip eject button.
- Volumes window : The adjusted volume is displayed in the volume window (volume to be aspirated / dispensed).
- Micropipette shaft : is a tube filled with air. Pushing the piston expels a volume of air contained in the rod, releasing the piston allows this air to return to the rod.
- Micropipette tips: are tips attached to a micropipette to collect liquid and then transfer it from one place to another. Tips of different sizes are used to collect different volumes of liquid.
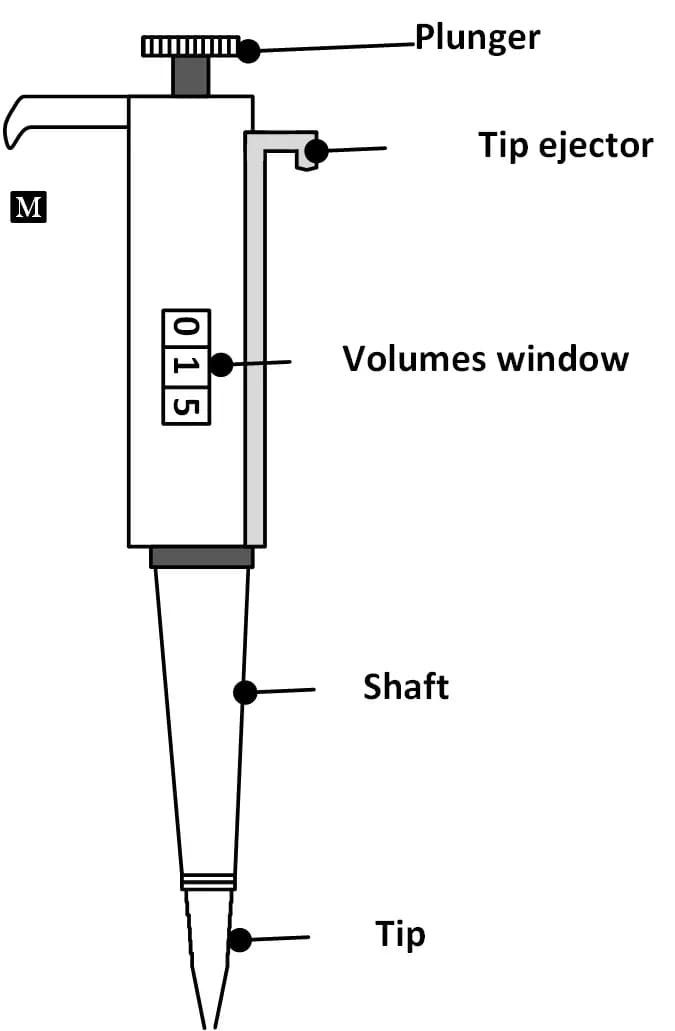
Micropipette parts
🏾 Types of micropipettes
Types of micropipettes according to volume
- Fixed volume micropipette : The volume of a fixed volume micropipette cannot be changed, it dispenses the same amount of liquid with each dispense.
- Variable volume micropipette : the volume of liquid to be aspirated or dispensed can be adjusted according to the capacity of the micropipette (a specific minimum and maximum volume range).
| Acronym | Volume |
|---|---|
| P 2 | 0.2 – 2 µ |
| P 10 | 1 – 10 µ |
| P 20 | 2 – 20 µ |
| P 100 | 20 – 100 µ |
| P 200 | 20 – 200 µ |
| P 1000 | 100 – 1000 µ |
| P 5000 | 1000 – 5000 µ |
The acronyms P10, P20, P1000, P5000 on micropipettes represent the maximum volume that can be aspirated/dispensed.

Micropipette P 200
Types of micropipettes according to the mechanism of operation
Plunger pressure and vacuum in mechanical pipettes are replaced by a button in electronic pipettes, and electronic pipettes can be programmed to follow your working protocol.
Types of micropipettes according to the mechanism of operation
Air displacement micropipette : when the plunger is depressed, it descends inside the instrument to evacuate the air. The volume of air displaced is equivalent to the volume of liquid aspirated / dispensed.
Positive displacement micropipette : the plunger comes into direct contact with the sample, in these micropipettes the tips contain both the barrel and the plunger (like a syringe).
🏾 How does a micropipette work ?
When the plunger is pressed down, the air inside the micropipette sleeve is expelled due to the force with which the liquid in the micropipette tip is also pushed out.
When the piston moves upwards, a vacuum is created in the space vacated by the piston. This causes the air in the mouthpiece to rise to fill the vacant space, and the air in the mouthpiece is then replaced by the liquid, which is drawn into the mouthpiece.
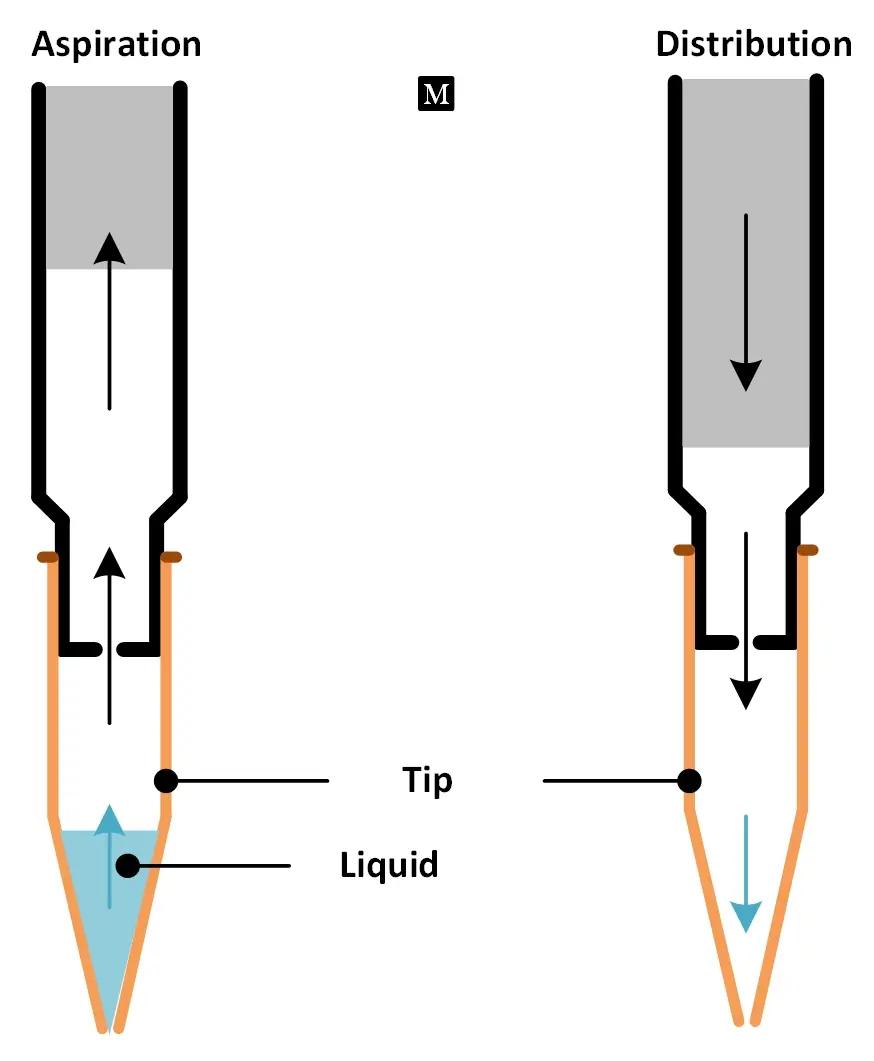
Air displacement micropipette