Contents:
Ⅰ. Overview
Although both are sometimes referred to as "fume hoods", biosafety cabinets and laboratory fume hoods are two entirely different categories. Both are designed to safely handle the dangers in science for which they are uniquely designed.
If we summarize the differences, biological safety cabinets (BSCs) , also known as microbiological safety workstations (MSC) , provide protection for the environment, personnel and products,while the hoods only ensure the protection of the personnel.
Hood vs BSCs protection level comparison |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Equipments | Staff | Product | Environment |
| Chemical fume hood | ✔ | ||
| Laminar flow hood | ✔ | ||
| BSCs Class I | ✔ | ✔ | |
| BSCs Class II | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| BSCs Class III | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
What is a HEPA filter?
HEPA is a type of mechanical pleated air filter. It is the acronym for "High Efficiency Particulate Air". This type of air filter can theoretically remove at least 99.97% of dust, pollen, mold, bacteria and airborne particles with a size of 0.3 microns (µm).
The filter is made of a mesh of fibers, usually layers of cellulose, synthetic fibers or glass fibers.
Ⅱ. Types and descriptions of biological safety cabinets
Microbiological safety cabinets comply with standard EN 12469 which defines three types of BSCs according to the technical means implemented and the levels of protection achieved: BSCs I, II and III.
◈ Class I biosafety cabinet
Class I BSCs ensure the protection of personnel and the environment, but do not protect the product (eg: biological material).
The air is sucked in through the front opening and passes, without being sterilized, on the work surface before being evacuated by a pipe fitted with a "HEPA" filter (the filter is either integrated or mounted on the duct. evacuation or on the building evacuation circuit)
Note : Air is never recycled inside BSCs-1
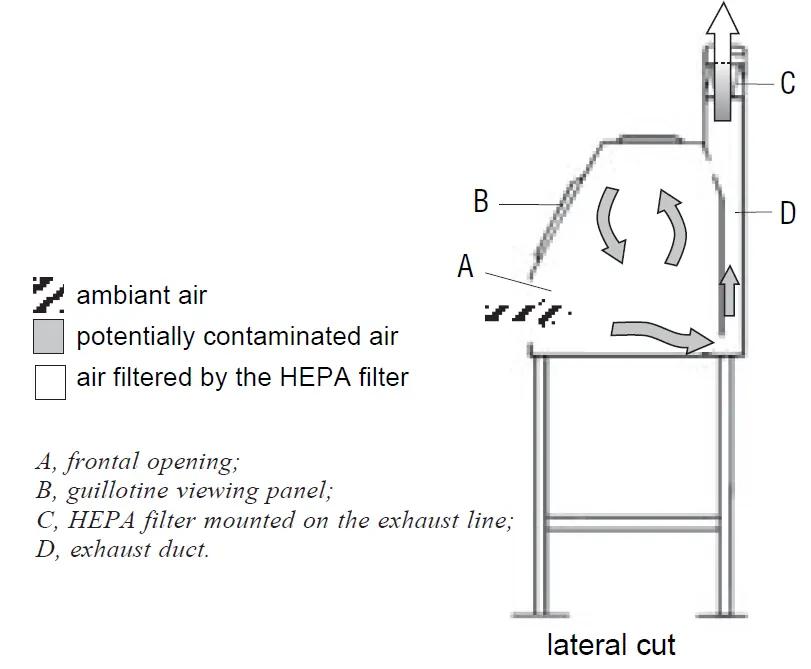
BSCs-1
◈ Class II biosafety cabinet
With these four types (A1, A2, B1 and B2), BSCs Class II have been designed not only to ensure the protection of personnel, but also to prevent the biological material present on the worktop from being contaminated by the air in the room, they only allow sterile air, that is to say air having passed through a HEPA filter, to pass onto the work surface.
Class II BSCs can be used to work with infectious agents of risk groups 2 and 3. They can also be used to work with infectious agents of risk group 4 if the operator is wearing a pressurized protective suit.
Types of Class II biosafety cabinet |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BSCs | Entry speed (m/s) | % of recirculated air | % of exhaust air | Evacuation circuit |
| Class II A1 | 0.38-0.51 | 70 | 30 | Drainage in the room or connection sleeve |
| Class II A2 | 0.51 | 70 | 30 | Drainage in the room or connection sleeve |
| Class II B1 | 0.51 | 30 | 70 | Rigid waterproof junction |
| Class II B2 | 0.51 | 0 | 100 | Rigid waterproof junction |
◈ Class III biosafety cabinet
This type of enclosure, which provides maximum protection for personnel, is used to work with infectious agents of risk group 4.
The air entering the enclosure passes through one HEPA filter and the air exiting it through two HEPA filters. To access the worktop, use very resistant rubber gloves attached to the front openings.
Class III BSCs must be equipped with an airlock capable of being sterilized
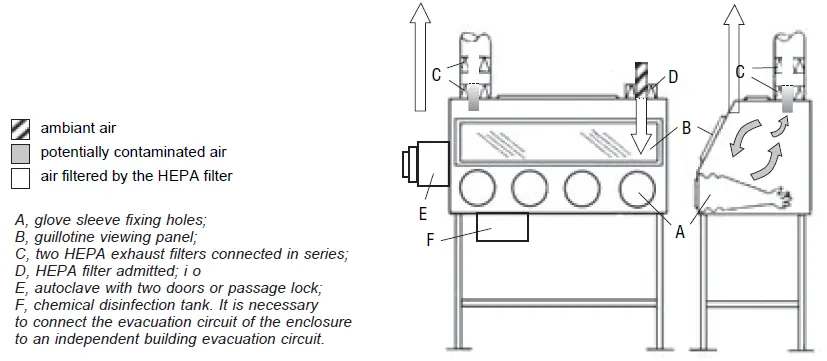
BSCs class 3