Modes of Hepatitis Transmission
Introduction
Viral hepatitis (A, B, C, D, and E) are liver infections caused by distinct viruses. Each type of hepatitis is transmitted differently. Understanding these modes of transmission is essential to prevent these infections and protect your health.
Hepatitis A: Fecal-Oral Transmission
How is hepatitis A transmitted?
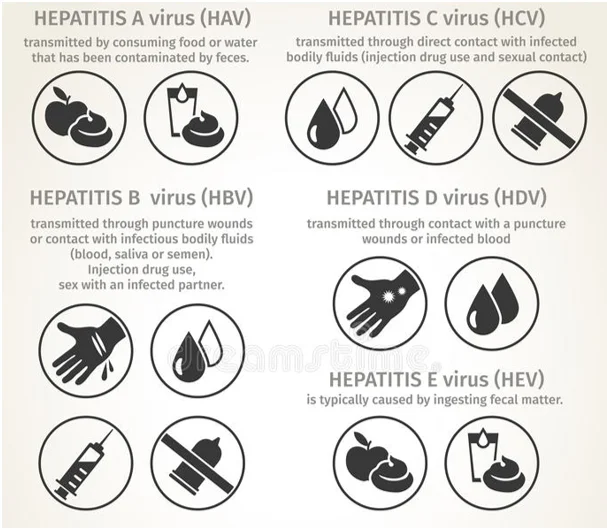
The hepatitis A virus (HAV) is primarily transmitted through:
- Ingestion of water or food contaminated with infected fecal matter.
- Direct contact with an infected person, particularly during oral-anal sexual practices.
Prevention:
- Vaccination: The hepatitis A vaccine is safe and effective.
- Hygiene: Wash your hands after using the toilet and before preparing food.
- Water and food: Consume treated water and avoid raw foods in high-risk areas.
Hepatitis B: Blood and Body Fluid Transmission
How is hepatitis B transmitted?
The hepatitis B virus (HBV) is transmitted through:
- Contact with infected blood (sharing needles, razors, or unsterilized medical equipment).
- Unprotected sexual intercourse with an infected person.
- Mother-to-child transmission during childbirth.
Prevention:
- Vaccination: The hepatitis B vaccine is the best protection.
- Precautions: Use condoms and avoid sharing personal items (razors, toothbrushes).
Note
- The hepatitis B virus is highly contagious: ten times more than the hepatitis C virus.
- WHO: The hepatitis B virus can survive outside the body for at least 7 days. During this period, it can still cause infection if it enters the body of an unvaccinated person.
Hepatitis C Transmission
How is hepatitis C transmitted?
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) is primarily transmitted through:
- Contact with infected blood (sharing needles, unsterilized medical equipment, or personal items like razors).
- Sexual transmission: Rare, but possible in cases of bleeding.
Prevention:
- No vaccine: Prevention relies on using sterile equipment and screening.
- Treatment: Antiviral medications can cure hepatitis C in more than 95% of cases.
WHO: Hepatitis C is not transmitted through breast milk, food, water, casual contact (hugging or kissing), or sharing food or drinks with an infected person.
Hepatitis D Transmission
The hepatitis D virus (HDV) only survives in the presence of the hepatitis B virus. It is transmitted through:
- Contact with infected blood or unprotected sexual intercourse.
Prevention:
- Hepatitis B vaccination: Also protects against hepatitis D.
Hepatitis E: Transmission through Contaminated Water
How is hepatitis E transmitted?
The hepatitis E virus (HEV) is primarily transmitted through:
- Water contaminated with infected fecal matter.
- Undercooked meat (pork, game).
Prevention:
- Hygiene: Drink treated water and avoid raw or undercooked meat.
- Vaccine: Available in China, but not yet widely accessible.
Summary Table of Transmission Modes
| Hepatitis | Transmission | Vaccine | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Water, food, close contact | Yes | Spontaneous recovery |
| B | Blood, sex, mother-to-child | Yes | Lifelong treatments |
| C | Blood | No | Curable (95%+) |
| D | Blood, sex (if hepatitis B +) | No* | Complex |
| E | Water, undercooked meat | In China | Spontaneous recovery |
* The hepatitis B vaccine also protects against hepatitis D.
Prevention Recommendations
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis A and B.
- Use condoms to reduce the risk of sexual transmission.
- Do not share personal items (razors, toothbrushes).
- Insist on sterile equipment for tattoos, piercings, and medical procedures.
- Wash your hands regularly, especially before eating.