Content :
White vaginal discharge is a common occurrence in women and can have various causes. It is usually a normal part of the menstrual cycle and helps to maintain the cleanliness and health of the vaginal area. However, white discharge can also be a sign of an underlying condition.
In this article we are going to discuss the causes, diagnosis and treatment of pathological white vaginal discharge.
◉ Definition
Vaginal discharge is common among women and refers to fluid naturally expelled from the vagina. The color of vaginal discharge may vary throughout the menstrual cycle, from person to person, or during some medical conditions.
Normal white vaginal discharge is usually milky or clear and has no strong odor. It is produced by the cervix and helps to keep the vagina lubricated and protected.
The amount and consistency of white discharge can vary throughout the menstrual cycle, with increases in the amount and stretchiness of discharge occurring around ovulation.
Abnormal white vaginal discharge may be a sign of infection or inflammation. It can be caused by factors such as yeast infections, bacterial vaginosis, sexually transmitted infections (STIs), hormonal changes, or other medical conditions.

◉ Causes of white vaginal discharge
There are possible causes of white vaginal discharge including:
- Normal physiological discharge: It is common for women to have a milky white or clear and odorless discharge throughout their menstrual cycle. This discharge helps keep the vagina clean and moisturized.
- Vaginal Yeast Infection : An overgrowth of the fungus Candida albicans can cause a thick, white, and clumpy discharge, along with itching and irritation.
- Bacterial vaginosis: This is a condition resulting from an imbalance of bacteria in the vagina. It can cause a thin, white, or gray discharge with a strong odor, similar to fish.
- Sign of early pregnancy: It occurs due to varying estrogen levels. This milky white vagianl discharge during early pregnancy is called leukorrhea.
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs): Certain STIs can cause white vaginal discharge. Other symptoms may include dysuria and pelvic discomfort.
- Cervical mucus: During certain times of the menstrual cycle, particularly around ovulation, the cervix produces more mucus that can appear creamy white and stretchy.
◉ Associated Symptoms
Depending on the cause, white vaginal discharge can be associated with various symptoms:
- Itching in the vaginal area.
- Pain and Burning Sensation.
- Redness or Swelling.
- Painful Urination (dysuria).
- Discomfort or Pain During Sexual Intercourse
◉ Diagnosis
During the diagnosis process, the healthcare professional may:
◉ 1. Take a detailed medical history
This includes asking about the nature of the discharge, associated symptoms, the timing and duration of the discharge, sexual history, contraceptive use, and previous infections or conditions.
◉ 2. Perform a physical examination
This may involve a pelvic examination to visually inspect the vagina and cervix for any abnormalities, as well as collecting samples for laboratory testing.
◉ 3. Laboratory testing
- Microscopic examination of vaginal discharge involves observing a sample of the discharge under a microscope, either directly or after staining, to detect various elements, including microorganisms like yeast cells, Trichomonas parasites, or abnormal cells like clue cells.
- PH testing: The pH of the discharge is measured to determine if it is within the normal range (3.8-4.5).
- Cultures: Specimens may be sent to a laboratory to grow and identify specific bacteria or yeast causing the infection.
- PCR tests: Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests can be used to identify the presence of specific pathogens, such as those causing sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
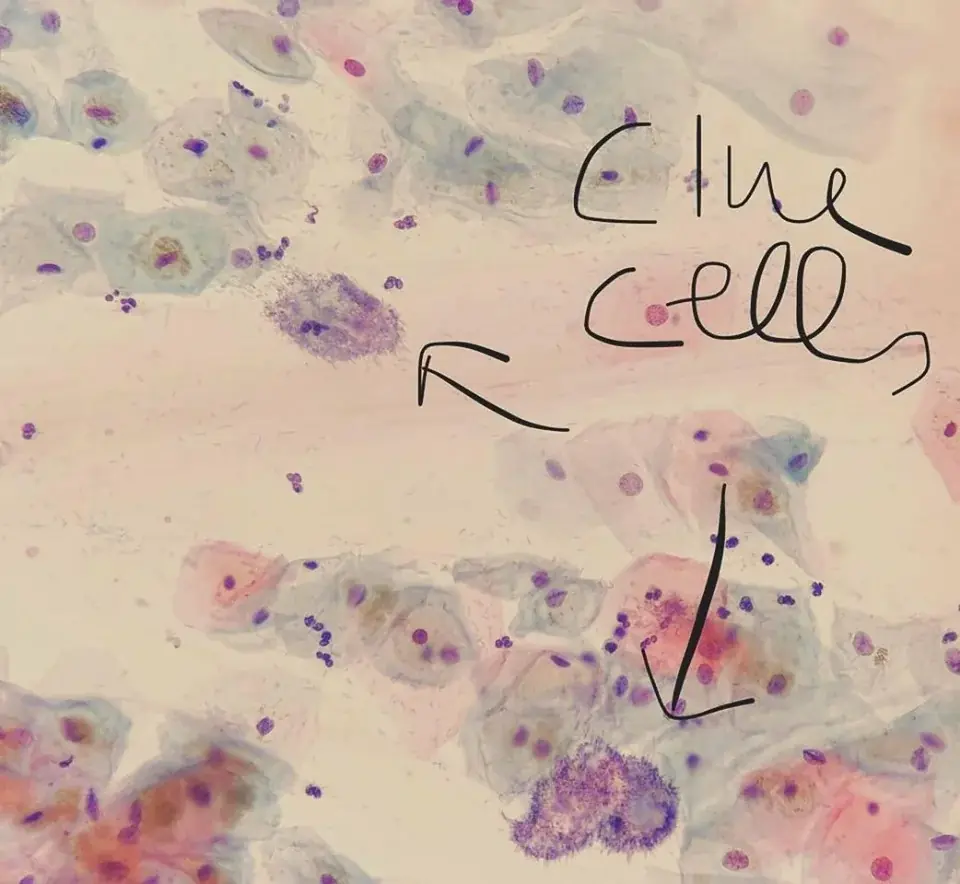
Clue cells
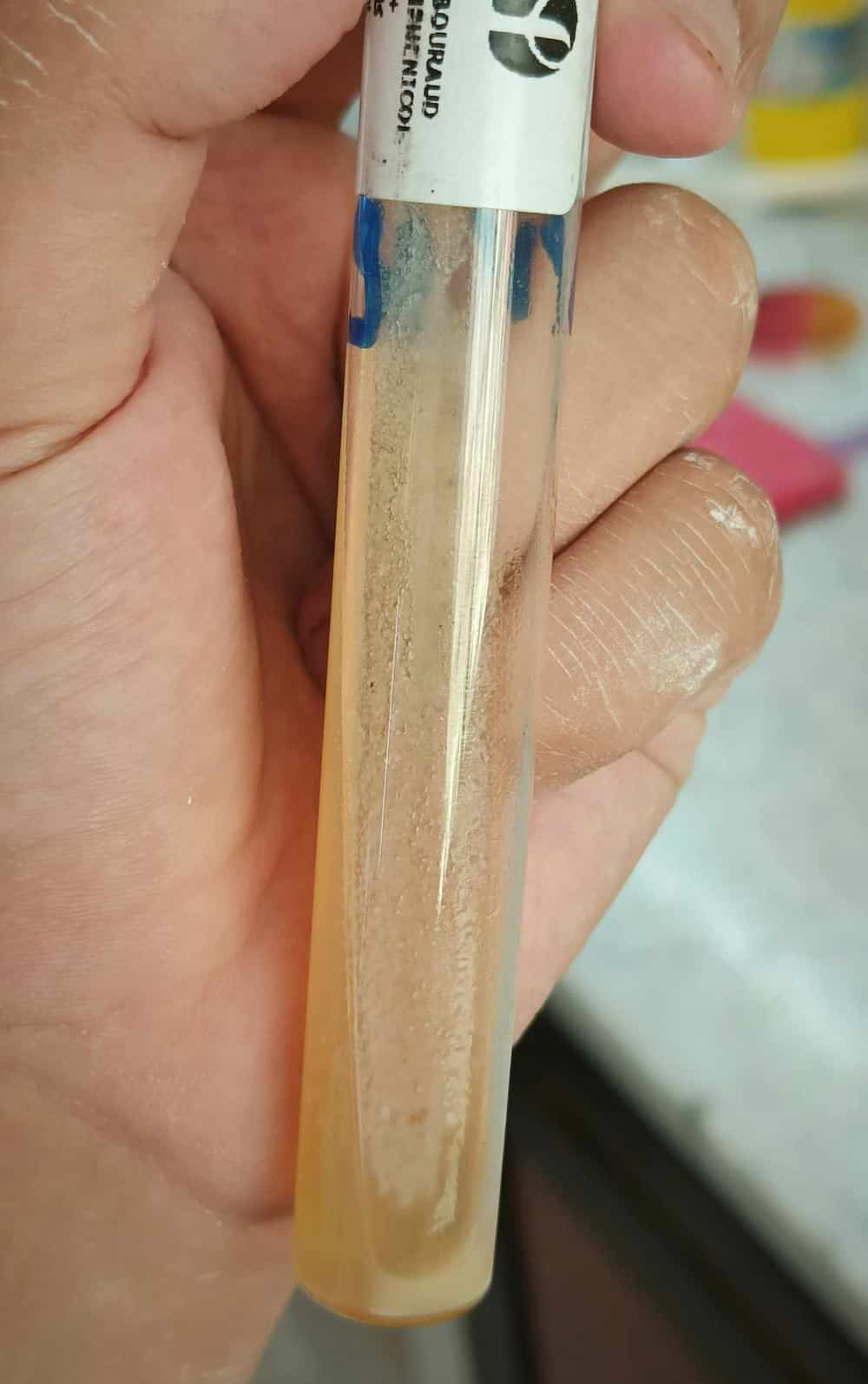

Yeast culture
◉ 4. Additional tests
Depending on the suspected cause, the healthcare professional may order tests for sexually transmitted infections, such as chlamydia or gonorrhea, or a Pap smear to screen for cervical cancer or detect abnormalities in cervical cells.
◉ Treatment
The treatment for white vaginal discharge depends on the underlying cause. Here are some common treatment options for different causes of white vaginal discharge:
- Yeast infection: Antifungal medications, such as topical creams or oral tablets, are typically prescribed to treat yeast infections. Over-the-counter antifungal treatments may also be available.
- Bacterial vaginosis: Antibiotics, such as metronidazole or clindamycin, are commonly prescribed to treat bacterial vaginosis. These can be taken orally or applied topically, depending on the severity of the infection.
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs): Treatment for STIs typically involves antibiotics or antiviral medications, depending on the specific infection. It is important to complete the full course of treatment and inform sexual partners to prevent reinfection.
- Trichomoniasis: Prescription oral medication, such as metronidazole or tinidazole, is commonly used to treat trichomoniasis. Partners must also be treated to prevent reinfection.
◉ Conclusion
White vaginal discharge is a common occurrence in women and can be normal or indicate an underlying condition. It is important to pay attention to changes in discharge and seek medical advice for a proper diagnosis and treatment if any concerning symptoms arise.