Content :
Amoxicillin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that belongs to the penicillin group of drugs. It is one of the most commonly prescribed medications in the world, and its effectiveness and safety have made it a cornerstone of modern medicine. This essay will explore the drug category, various uses, mechanism of action, chemical properties, recommended doses, and potential side effects of Amoxicillin.
◉ Drug Category
Amoxicillin falls under the category of beta-lactam antibiotics, specifically within the penicillin subclass. The beta-lactam antibiotics, including penicillin, cephalosporins, and carbapenems, work by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis, making them effective against a wide range of bacterial infections.
◉ Chemical Properties
Amoxicillin is chemically known as (2S, 5R, 6R)-6-[(R)-(-)-2-Amino-2-(p-hydroxyphenyl) acetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid (Figure 1). It is a white to off-white, crystalline powder with a molecular weight of approximately 365.4 g/mol. Amoxicillin is sparingly soluble in water and stable under normal storage conditions.
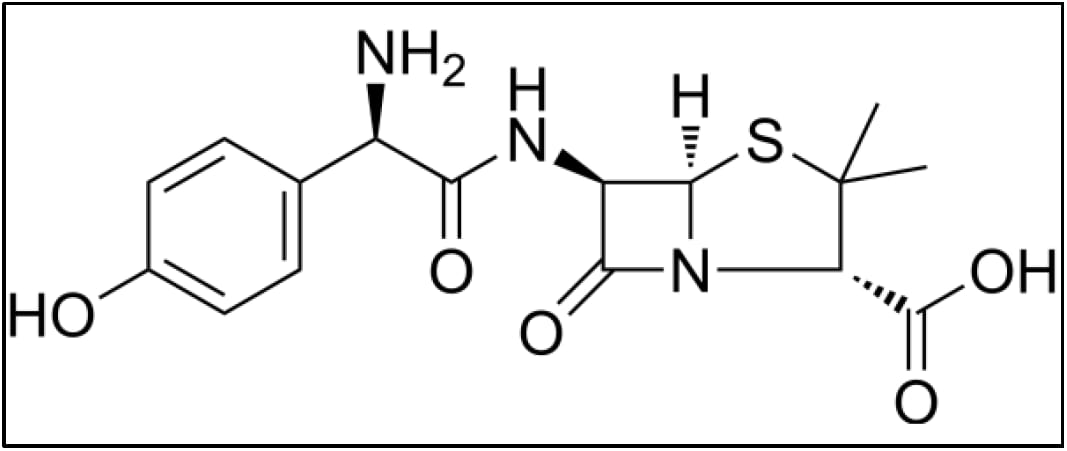
Figure 1: Chemical Structure of Amoxicillin Antibiotic.
◉ Uses
Amoxicillin is utilized to treat a diverse array of bacterial infections. Some of the common conditions for which it is prescribed include:
- Respiratory Tract Infections: Amoxicillin is used to treat bacterial sinusitis, bronchitis, and pneumonia.
- Ear Infections: Otitis media, an infection of the middle ear, can be effectively treated with Amoxicillin.
- Urinary Tract Infections: It is often prescribed for uncomplicated urinary tract infections caused by susceptible bacteria.
- Skin and Soft Tissue Infections: Amoxicillin can be used to treat various skin infections, including cellulitis.
- Dental Infections: For dental abscesses and infections, Amoxicillin is frequently the first-line antibiotic.
- Helicobacter pylori Eradication: It is employed in combination with other drugs for the treatment of H. pylori-related peptic ulcers.
◉ Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of Amoxicillin lies in its ability to interfere with bacterial cell wall synthesis. Bacterial cell walls are crucial for their survival and protection. Amoxicillin works by inhibiting the activity of an enzyme called transpeptidase, which plays a vital role in cross-linking the peptidoglycan chains in the bacterial cell wall. This interference weakens the cell wall, causing it to rupture and the bacterium to die. The drug primarily targets Gram-positive bacteria but also has activity against certain Gram-negative bacteria.
◉ Doses
The dosing of Amoxicillin varies depending on the type and severity of the infection, the age and weight of the patient, and the specific product prescribed.
- Patient from 1 month to 15 year(s) and Weight < 40 kg: 20 to 90 mg/kg in 1 to 2 doses per day.
- Patient from 1 month to 15 year(s) and Weight >= 40 kg : 250 to 500 mg every 8 hours (1000 mg every 8 hours in severe cases).
- Patient from 15 years old : 250 to 500 mg every 8 hours (1000 mg every 8 hours in severe cases).
◉ Side and Adverse Effects:
Amoxicillin is generally well-tolerated, and most people do not experience significant side effects. However, some common side effects may include:
- Gastrointestinal Disturbances: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort are among the most frequent side effects. Taking the medication with food can help reduce these symptoms.
- Allergic Reactions: Amoxicillin can cause allergic reactions in some individuals, ranging from mild skin rashes to severe anaphylactic reactions. Patients with a history of penicillin allergy should exercise caution and inform their healthcare provider.
- Candidiasis: Antibiotics, including Amoxicillin, can disrupt the normal balance of microorganisms in the body, leading to an overgrowth of Candida, resulting in oral or vaginal yeast infections.
- Rash: Some individuals may develop a non-allergic rash, which is generally not serious and resolves upon discontinuation of the medication.
- Pseudomembranous Colitis: In rare cases, Amoxicillin can lead to the development of a severe condition called pseudomembranous colitis, caused by the overgrowth of the bacterium Clostridium difficile.
It is essential for patients to notify their healthcare provider if they experience any unusual or severe side effects while taking Amoxicillin.
◉ Conclusion
Amoxicillin has undoubtedly earned its place as a crucial antibiotic in the treatment of bacterial infections. Its broad-spectrum activity, relatively low cost, and overall safety profile have made it a go-to option for many healthcare professionals. By inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis, Amoxicillin effectively combats a wide range of infections, from respiratory tract infections to skin and soft tissue infections. However, caution should be exercised, as allergic reactions and other side effects may occur in some individuals. Overall, when used responsibly and under the guidance of healthcare professionals, Amoxicillin continues to play a vital role in improving global health outcomes.