Contents:
Hemagglutination: Understanding Reactions and Their Uses in the Laboratory
◉ Introduction
Hemagglutination is a biological phenomenon where red blood cells (or erythrocytes) clump together to form visible aggregates. This process relies on the interaction between antigens present on the surface of red blood cells and specific antibodies or viral proteins called hemagglutinins. Hemagglutination is widely used in medicine, biology, and virology for applications such as blood typing, diagnosing infectious diseases, and studying viruses.
Hemagglutination
◉ The Three Types of Hemagglutination Reactions
1. Direct Hemagglutination: Blood Typing
In this type of reaction, specific antibodies are used to interact with surface antigens on red blood cells. For example, anti-A and anti-B antibodies are used to determine blood groups (A, B, AB, O). When antibodies bind to their corresponding antigens, red blood cells clump together, forming visible aggregates. This principle is the basis of blood typing tests in medical transfusion.
2. Passive Hemagglutination: Detection of Soluble Antigens
In passive hemagglutination, red blood cells serve as inert carriers to which soluble antigens are artificially attached. These modified red blood cells are then agglutinated by specific antibodies targeting these antigens. A common application of this technique is the TPHA (Treponema Pallidum Hemagglutination Assay), used to diagnose syphilis. This test detects antibodies against Treponema pallidum, the bacterium responsible for the disease.
3. Viral Hemagglutination: Study of Viruses
Certain viruses, such as influenza or measles, possess surface proteins called hemagglutinins. These proteins can bind to receptors on the surface of red blood cells. When a virion (viral particle) binds to two neighboring red blood cells, it causes their agglutination. This phenomenon is used in virology to study viral properties, assess viral concentration, or develop vaccines.
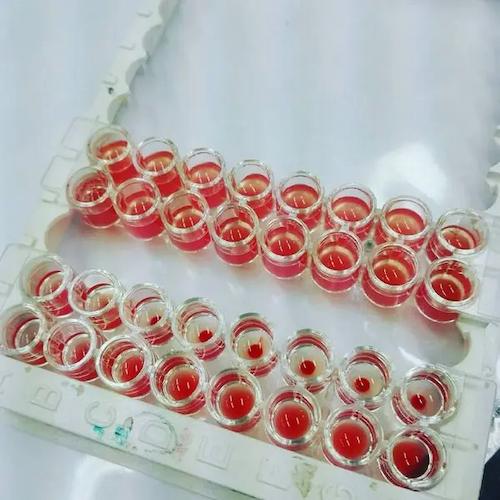
◉ Interpretation of Results
- Positive Reaction: The formation of a veil or network on the surface of the reaction medium indicates red blood cell agglutination, signifying a specific interaction between antigens and antibodies or between hemagglutinins and receptors.
- Negative Reaction: The appearance of a button or deposit at the bottom of the well indicates the absence of agglutination, meaning the reaction did not occur.
◉ Applications of Hemagglutination
Hemagglutination is a versatile technique with various applications:
- Blood transfusion: Blood typing and donor-recipient compatibility.
- Medical diagnosis: Detection of specific antibodies or antigens in infectious diseases (e.g., syphilis, viral hepatitis).
- Virology: Study of viral properties, viral titration, and vaccine development.
- Basic research: Study of antigen-antibody interactions and viral infection mechanisms.
◉ Conclusion
Hemagglutination is a simple, rapid, and reliable technique that plays a vital role in many areas of medicine and biology. Whether for blood typing, diagnosing infections, or studying viruses, this method remains an indispensable tool. Its ease of use and versatility make it a preferred technique for laboratories worldwide.